13-10
Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual, R8.5
78-18343-02
Chapter 13 Security Reference
13.4.2 Shared Secrets
For a configuration that uses a RADIUS client, a RADIUS proxy, and a RADIUS server, the shared
secret that is used between the RADIUS client and the RADIUS proxy can be different than the shared
secret used between the RADIUS proxy and the RADIUS server.
Shared secrets are used to verify that RADIUS messages, with the exception of the Access-Request
message, are sent by a RADIUS-enabled device that is configured with the same shared secret. Shared
secrets also verify that the RADIUS message has not been modified in transit (message integrity). The
shared secret is also used to encrypt some RADIUS attributes, such as User-Password and
Tunnel-Password.
When creating and using a shared secret:
• Use the same case-sensitive shared secret on both RADIUS devices.
• Use a different shared secret for each RADIUS server-RADIUS client pair.
• To ensure a random shared secret, generate a random sequence at least 22 characters long.
• You can use any standard alphanumeric and special characters.
• You can use a shared secret of up to 128 characters in length. To protect your server and your
RADIUS clients from brute force attacks, use long shared secrets (more than 22 characters).
• Make the shared secret a random sequence of letters, numbers, and punctuation and change it often
to protect your server and your RADIUS clients from dictionary attacks. Shared secrets should
contain characters from each of the three groups listed in Table 13-5.
The stronger your shared secret, the more secure the attributes (for example, those used for passwords
and encryption keys) that are encrypted with it. An example of a strong shared secret is
8d#>9fq4bV)H7%a3-zE13sW$hIa32M#m<PqAa72(.
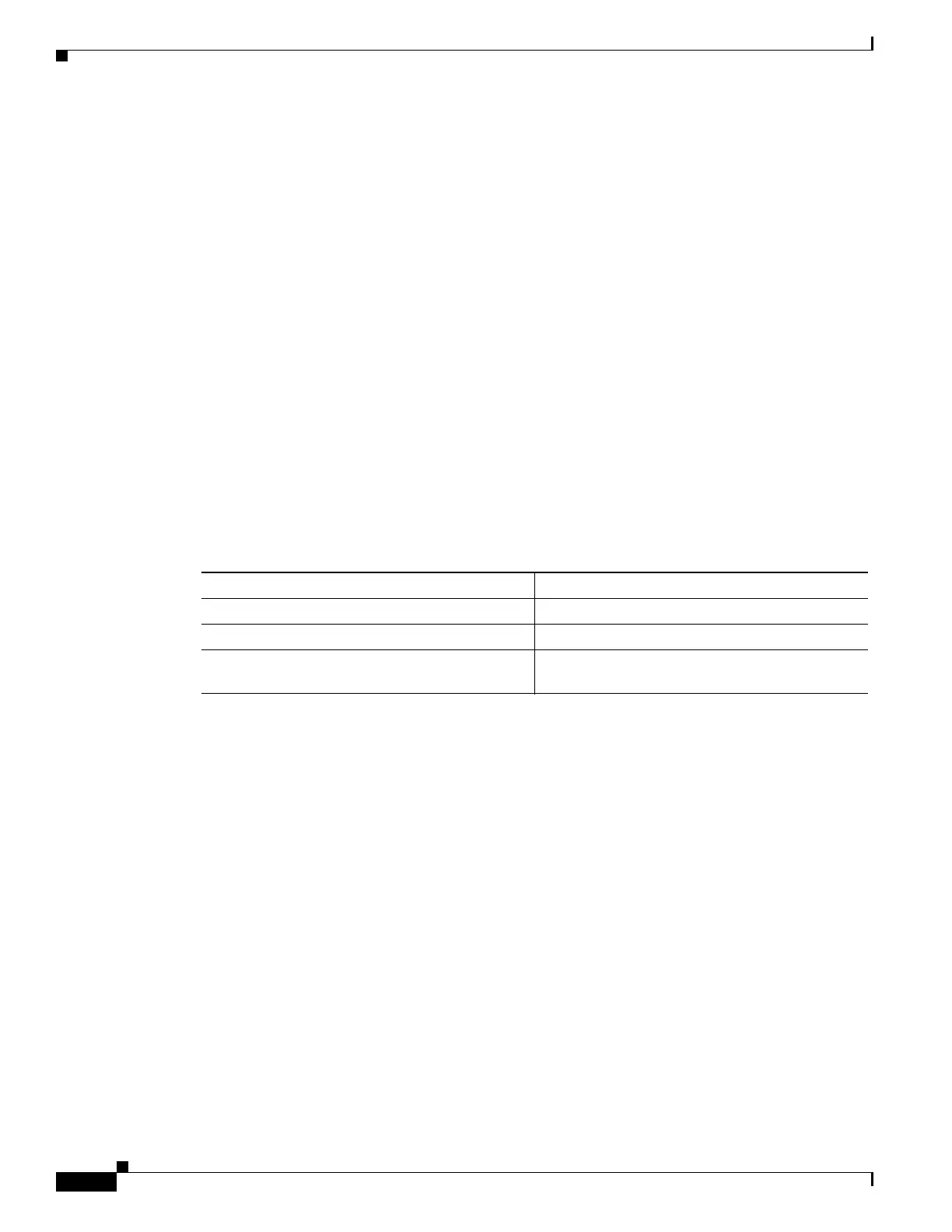
Table 13-5 Shared Secret Character Groups
Group Examples
Letters (uppercase and lowercase) A, B, C, D and a, b, c, d
Numerals 0, 1, 2, 3
Symbols (all characters not defined as letters or
numerals)
Exclamation point (!), asterisk (*), colon (:)

 Loading...
Loading...