15-34
Cisco ONS 15454 DWDM Reference Manual, R8.5
78-18343-02
Chapter 15 Management Network Connectivity
15.3.7 DCN Case Study 4: Two Linear Cascaded Topologies With Two DCN Connections
The OSPF virtual link requires its neighbor to be indicated with its router ID, not the physical or tunnel
interface connected to the network. Using a loopback interface on the NOC router makes the router ID
selection independent from real interface IP address.
15.3.6.2 DCN Case Study 3 Limitations
DCN Case Study 3 shows that OSPF can provide better DCN resilience and more efficient routing
choices, which results in better performance. OSPF also provides better network scalability. Some
limitations of using OSPF include:
• OSPF introduces additional complexity, for example, provisioning the OSPF virtual links and
advertisement on the ONS 15454s and routers requires thought and planning.
• OSPF must be enabled on the DCN connection between the NOC and the site routers. This can also
be done through GRE tunnels, as shown in this case study.
• Planning and thought must be given to the separation of the OSPF areas. Creation of virtual links to
overcome the limitations described in the “15.3.2 OSPF” section on page 15-23 and to avoid
isolated areas and segmentation in the backbone area requires planning as well.
15.3.7 DCN Case Study 4: Two Linear Cascaded Topologies With Two DCN
Connections
DCN Case Study 4, shown in Figure 15-21, extends the simple linear topology shown in DCN Case
Study 3. However in this example, two linear DCN connections go to the same site router and all the
ONS 15454s are in the same subnet. A GRE tunnel logically connects the remote Router 1 and Router 2
over the OSC/DCC/GCC network, which is similar to the DCN Case Study 1 configuration
(Figure 15-18). The GRE tunnel provides the remote routers with an alternate path to reach the NOC
network in case a DCN failure occurs. However, the alternate paths might overload the router routing
tables and carry a higher cost because all alternate paths are host-based due to the fact the ONS 15454s
reside in the same subnet.
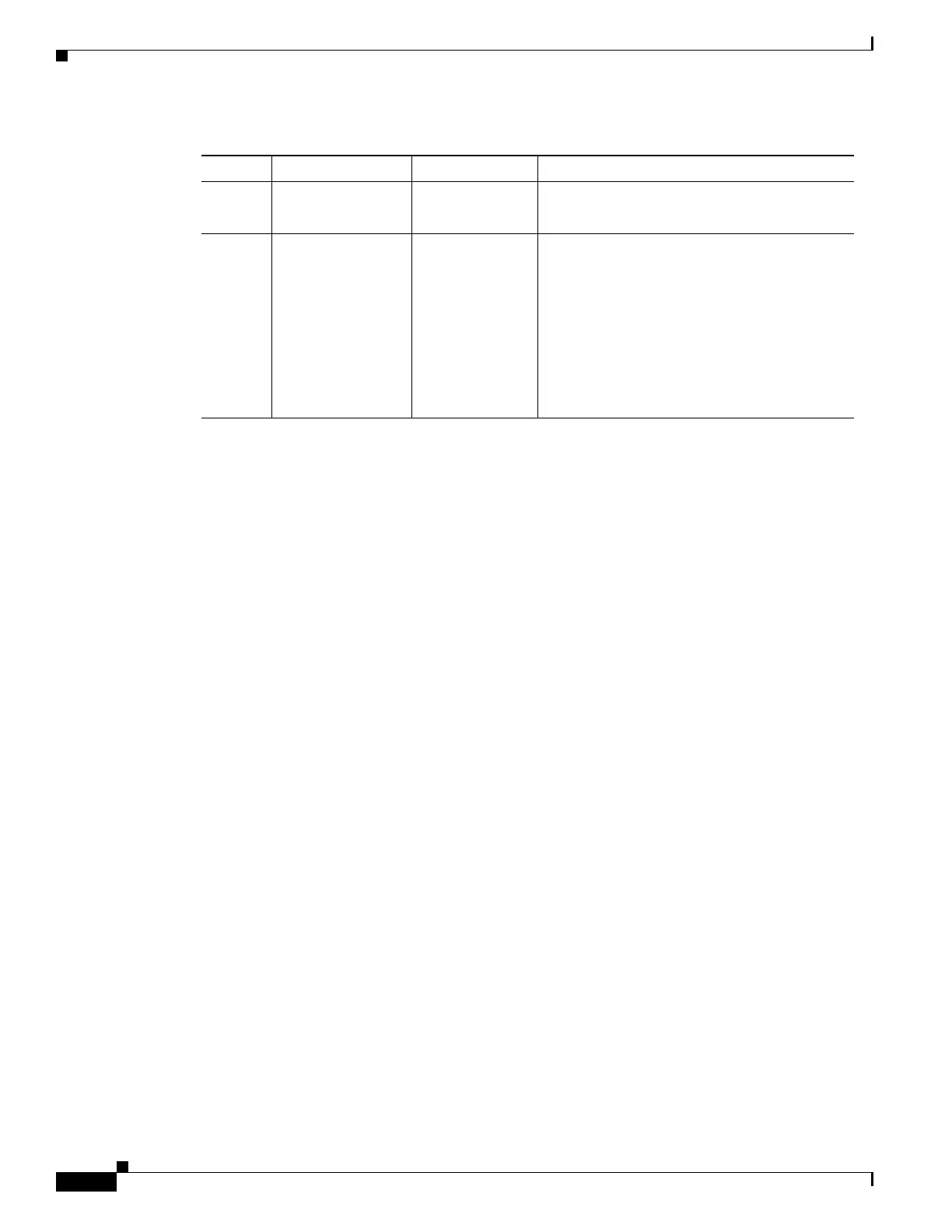
Node 3 192.168.100.78/24 0.0.0.0 DCC/OSC/GCC area: 0.0.0.1
OSPF disabled on LAN
Node 4 192.168.100.77/24 192.168.100.1 DCC/OSC/GCC area: 0.0.0.1
LAN area: 0.0.0.200
OSPF Area Range Table:
• 192.168.100.80/32 - Area 0.0.0.1
• 192.168.100.79/32 - Area 0.0.0.1
• 192.168.100.78/32 - Area 0.0.0.1
Virtual Link Table: 1.1.1.1
Table 15-7 DCN Case Study 3 Node IP Addresses (continued)
Node IP Address/Mask Default Gateway OSPF Configuration

 Loading...
Loading...