CMS32L051 User Manual |Chapter 14 Serial interface IICA
www.mcu.com.cn 509 / 703
14.5.8 Interrupt request (INTIICAn) generation timing and wait control
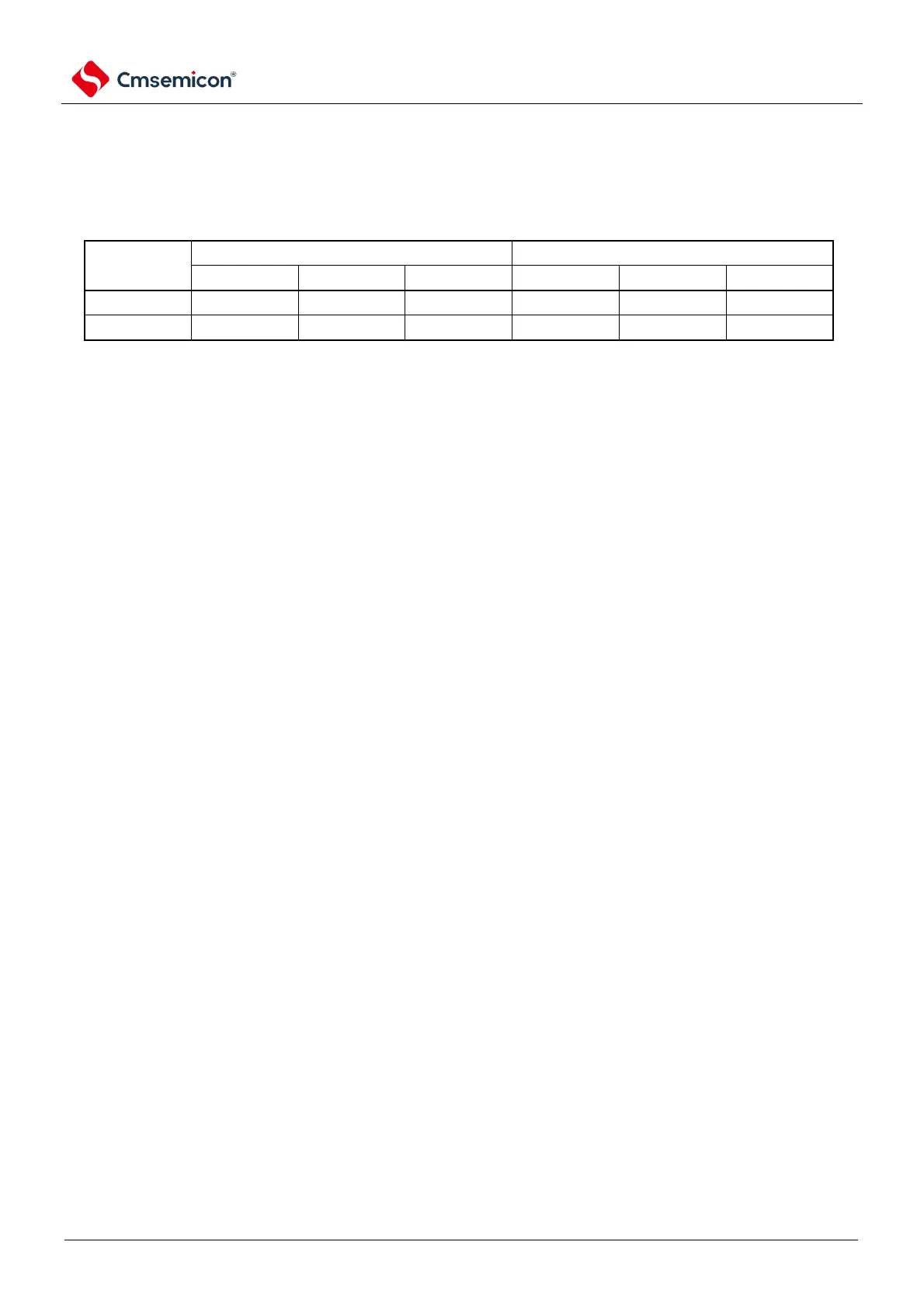
Control register n0 (IICCTLn0) by setting bit3 (WTIMn) by setting IICA in Table 14-2 The timing shown
generates INTIICAn and performs wait control.
Table 14-2 Timing and wait control of INTIICAn
Note 1. The slave generates INTIICAn on the falling edge of the 9th clock only if the received address and the set
address of the slave address register n (SVAn) are the same signal and enter a waiting state.
At this point, regardless of the setting of bit2 (ACKEn) of the IICCTLn0 register, a response is generated. The
slave device that receives the extension code generates INTIICAn on the falling edge of the 8th clock. If the
address is different after the restart, INTIICAn is generated on the falling edge of the 9th clock, but does not enter
the waiting state.
2. If the contents of the received address and the dependent address register n (SVAn) are different and the
extension code is not received, INTIICAn is not generated and does not enter the wait state.
The numbers in the Remarks table represent the number of clocks for the serial clock. Both interrupt request and wait
control are synchronized to the falling edge of the serial clock.
(1) Transmitting and receiving addresses
Slave operation: Independent of the WTIMn bit, the timing of interruptions and waits is determined
according to the conditions in Notes 1 and 2 above.
Master Operation: Independent of the WTIMn bit, the timing of interrupts and waits is generated on
the falling edge of the 9th clock.
(2) Data reception
Master operation/Slave operation: Determines the timing of interrupts and waits by WTIMn bit.
(3) Data transmission
Master operation/Slave operation: Determines the timing of interrupts and waits by WTIMn bit.
Note n=0
 Loading...
Loading...