Analog-to-digital converter (ADC) RM0453
580/1461 RM0453 Rev 1
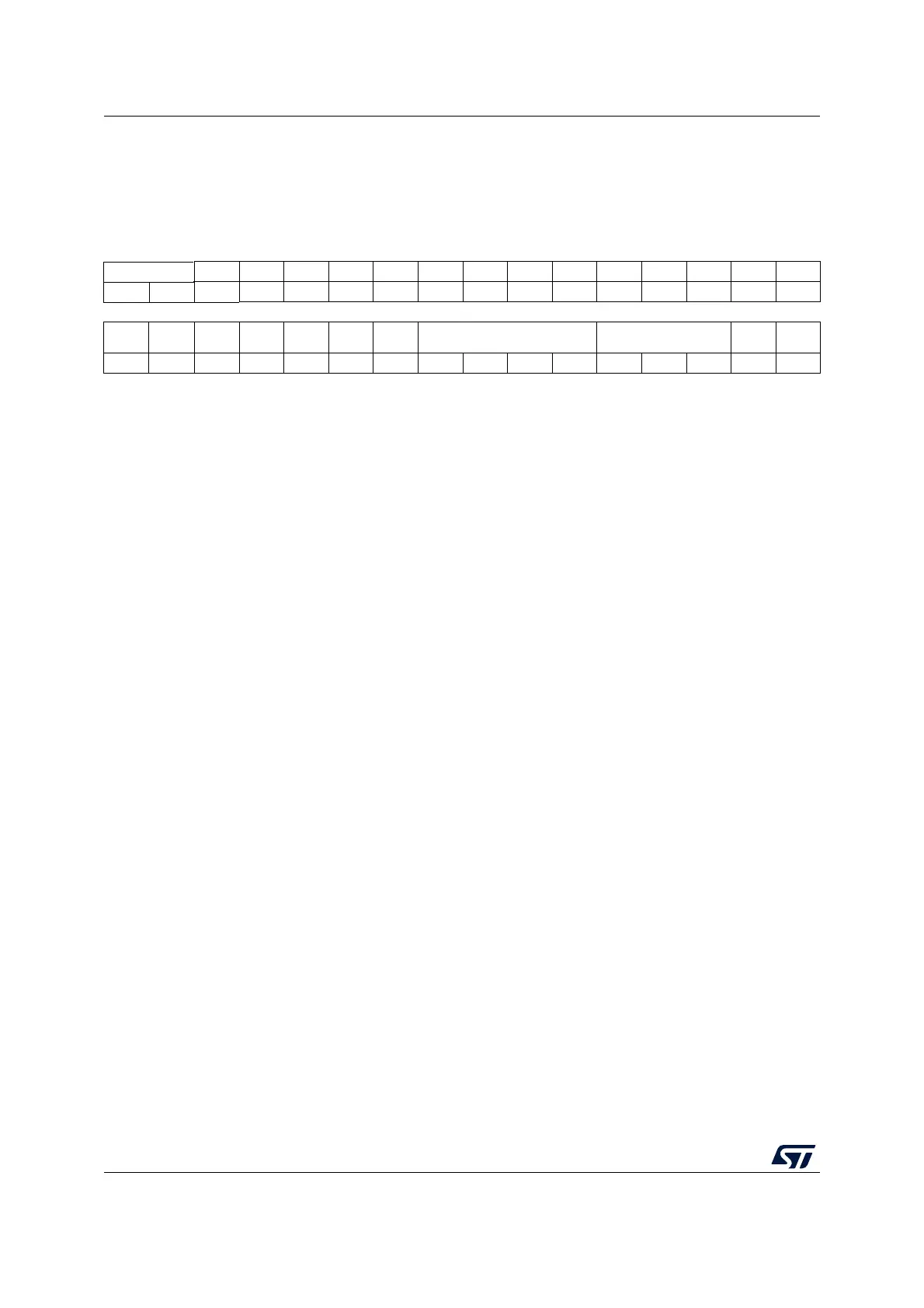
18.12.5 ADC configuration register 2 (ADC_CFGR2)
Address offset: 0x10
Reset value: 0x0000 0000
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
CKMODE[1:0] LFTRIG Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res.
rw rw rw
1514131211109876543210
Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. Res. TOVS OVSS[3:0] OVSR[2:0] Res. OVSE
rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw
Bits 31:30 CKMODE[1:0]: ADC clock mode
These bits are set and cleared by software to define how the analog ADC is clocked:
00: ADCCLK (Asynchronous clock mode), generated at product level (refer to RCC section)
01: PCLK/2 (Synchronous clock mode)
10: PCLK/4 (Synchronous clock mode)
11: PCLK (Synchronous clock mode). This configuration must be enabled only if PCLK has a 50%
duty clock cycle (APB prescaler configured inside the RCC must be bypassed and the system clock
must by 50% duty cycle)
In all synchronous clock modes, there is no jitter in the delay from a timer trigger to the start of a
conversion.
Note: The software is allowed to write these bits only when the ADC is disabled (ADCAL = 0,
ADSTART = 0, ADSTP = 0, ADDIS = 0 and ADEN = 0).
Bit 29 LFTRIG: Low frequency trigger mode enable
This bit is set and cleared by software.
0: Low Frequency Trigger Mode disabled
1: Low Frequency Trigger Mode enabled
Note: The software is allowed to write this bit only when ADSTART bit is cleared to 0 (this ensures
that no conversion is ongoing).
Bits 28:10 Reserved, must be kept at reset value.
Bit 9 TOVS: Triggered Oversampling
This bit is set and cleared by software.
0: All oversampled conversions for a channel are done consecutively after a trigger
1: Each oversampled conversion for a channel needs a trigger
Note: The software is allowed to write this bit only when ADSTART = 0 (which ensures that no
conversion is ongoing).

 Loading...
Loading...