USB on-the-go full-speed/high-speed (OTG_FS/OTG_HS) RM0390
1234/1328 RM0390 Rev 4
transfers, the OTG_HS host continues fetching the next packet (up to the value
specified in the MC field) before switching to the next channel.
3. The OTG_HS host attempts to send an OUT token at the beginning of the next (odd)
frame/micro-frame.
4. After successfully transmitting the packet, the OTG_HS host generates a CHH
interrupt.
5. In response to the CHH interrupt, reinitialize the channel for the next transfer.
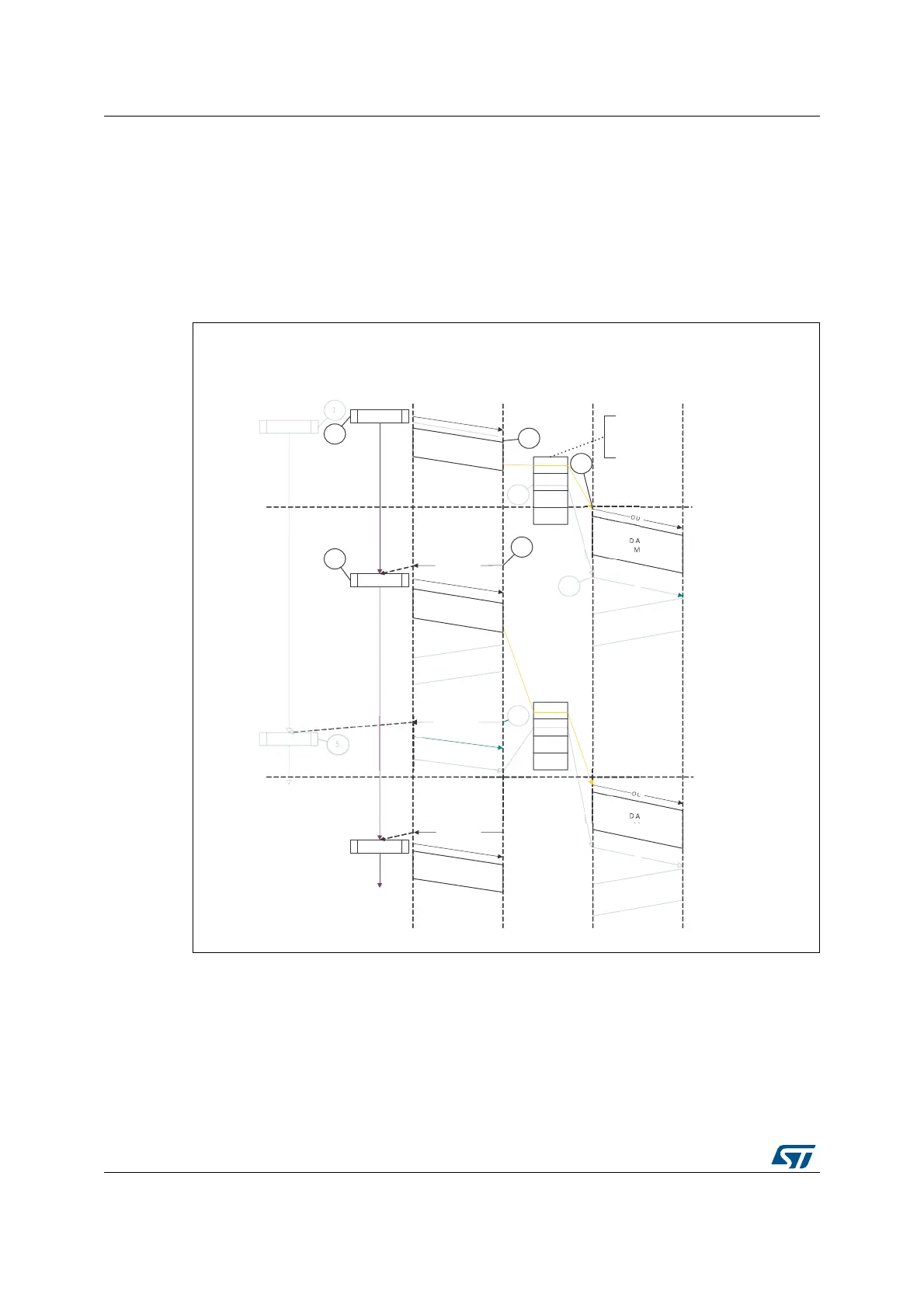
Figure 422. Normal isochronous OUT transaction - DMA mode
• Isochronous IN transactions in DMA mode
The sequence of operations ((channel x) is as follows:
1. Initialize and enable channel x as explained in Section : Channel initialization.
2. The OTG_HS host writes an IN request to the request queue as soon as the channel x
gets the grant from the arbiter (round-robin with fairness). In high-bandwidth transfers,
the OTG_HS host performs consecutive write operations up to MC times.
06Y9
K
h
d
d
Ϭ
D
W
^
ϭ
DW^
ϭ
DW^
ŝŶŝƚͺƌĞŐ;ĐŚͺϭͿ
ŝŶŝƚͺƌĞŐ
ĐŚͺϮ
ĐŚͺϮ
ĐŚͺϭ
/
E
K
h
d
d
Ϭ
D
W
^
Ś
,
ů
ƚ
Ě
ŝ
Ŷ
ƚ
Ğ
ƌ
ƌ
Ƶ
Ɖ
ƚ
WĞƌŝŽĚŝĐZĞƋƵĞƐƚ
YƵĞƵĞ
ƐƐƵŵĞƚŚĂƚƚŚŝƐ
ƋƵĞƵĞĐĂŶŚŽůĚ
ϰĞŶƚƌŝĞƐ
ϭ
d
Ϭ
/
E
ϭ
DW^
Ś,ůƚĚŝŶƚĞƌƌƵƉƚ
ŝŶŝƚͺƌĞŐ;ĐŚͺϮ
ŝŶŝƚͺƌĞŐ;ĐŚͺϭͿ
Ś
,
ůƚ
Ě
ŝ
Ŷ
ƚ
Ğ
ƌ
ƌ
Ƶ
Ɖ
ƚ
ϭ
DW^
d
Ϭ
ĐŚͺϮ
ϰ
ϯ
KĚĚ
;ŵŝĐƌŽͿ
ĨƌĂŵĞ
ǀĞŶ
;ŵŝĐƌŽͿ
ĨƌĂŵĞ
+RVW
$SSOLFDWLRQ 'HYLFH$+% 86%

 Loading...
Loading...