Window watchdog (WWDG) RM0390
648/1328 RM0390 Rev 4
In some applications, the EWI interrupt can be used to manage a software system check
and/or system recovery/graceful degradation, without generating a WWDG reset. In this
case, the corresponding interrupt service routine (ISR) should reload the WWDG counter to
avoid the WWDG reset, then trigger the required actions.
The EWI interrupt is cleared by writing '0' to the EWIF bit in the WWDG_SR register.
Note: When the EWI interrupt cannot be served, e.g. due to a system lock in a higher priority task,
the WWDG reset will eventually be generated.
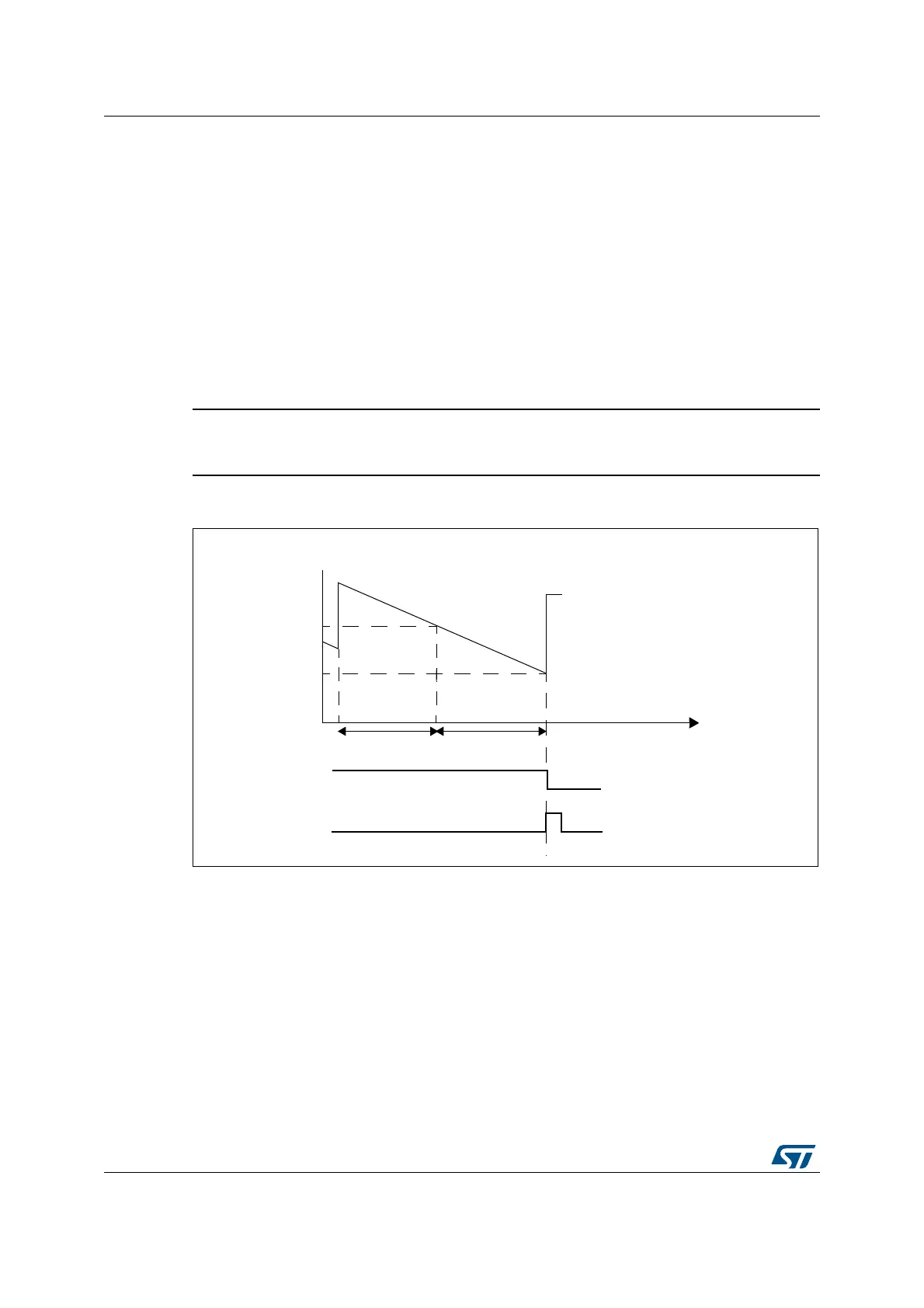
21.4 How to program the watchdog timeout
The formula in Figure 239 must be used to calculate the WWDG timeout.
Warning: When writing to the WWDG_CR register, always write 1 in the
T6 bit to avoid generating an immediate reset.
Figure 239. Window watchdog timing diagram
The formula to calculate the timeout value is given by:
where:
t
WWDG
: WWDG timeout
t
PCLK1
: APB1 clock period measured in ms
4096: value corresponding to internal divider.
AIC
7;=
4;=#.4DOWNCOUNTER
2EFRESHNOTALLOWED
X&
2EFRESHALLOWED
4IME
4BIT
2%3%4
t
WWDG
t
PCLK1
4096× 2
WDGTB[1:0]
× T5:0] 1+()×= ms()

 Loading...
Loading...