22 DNS Configuration
22.1 DNS Overview
Each IP address may present a host name, which consists of one or more strings, and it is
separated by the decimal between the strings. For the host name, it is not necessary to
remember the IP address of each IP device, but remember the meaningful host name. This
is the function the DNS protocol should implement.
There are two methods to map to the IP address from the host name: 1) Static Mapping,
each device is equipped with the mapping from the host to the IP address, various devices
maintain their mapping table individually and only provide for the use of the device itself; 2)
Dynamic Mapping, establish a set of the domain name system (DNS), only dedicated DNS
server is equipped with the mapping from the host to the IP address, it is necessary for the
network to use the device for the host name communication. Firstly, it is necessary to query
the IP address corresponding to the host from the DNS server.
The process that the IP address which corresponds to the host name by the host name is
referred to as the domain name resolution (or host name resolution). The DGS-3610 series
support the host name resolution locally or by the DNS. During the resolution of domain
name, the static method may be used firstly. If it fails, use the dynamic method instead.
Some frequently used domain names can be put into the resolution list of static domain
names. In this way, the efficiency of domain name resolution can increase considerably.
22.2 Configuring Domain Name
Resolution
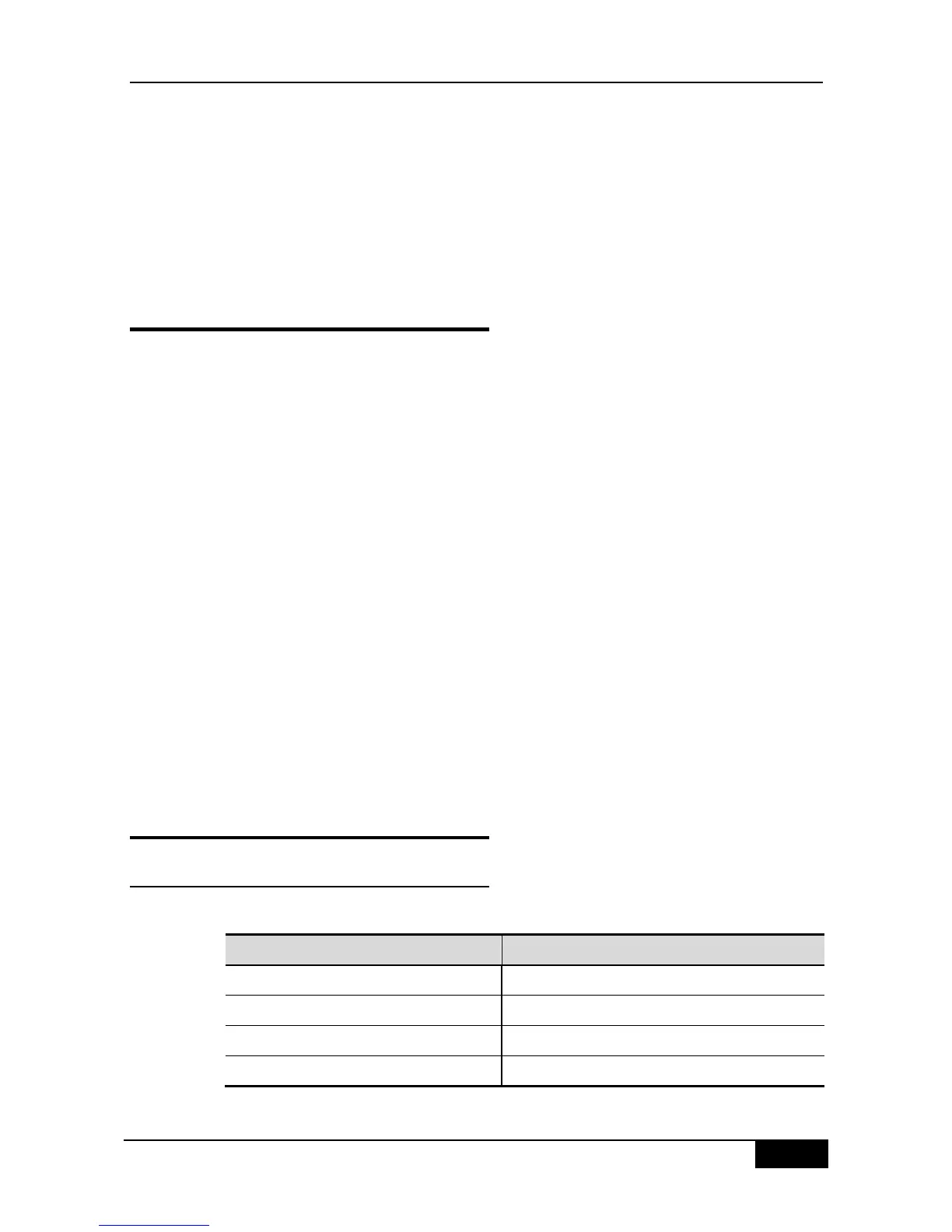
22.2.1 Default Configuration of DNS
The default configurations of DNS are as follows:

 Loading...
Loading...











