Chapter 44 Access Control List Configuration DGS-3610 Series Configuration Guide
of a packet and the source port field of UDP. In this way, these two ACEs use different
filtering domain templates.
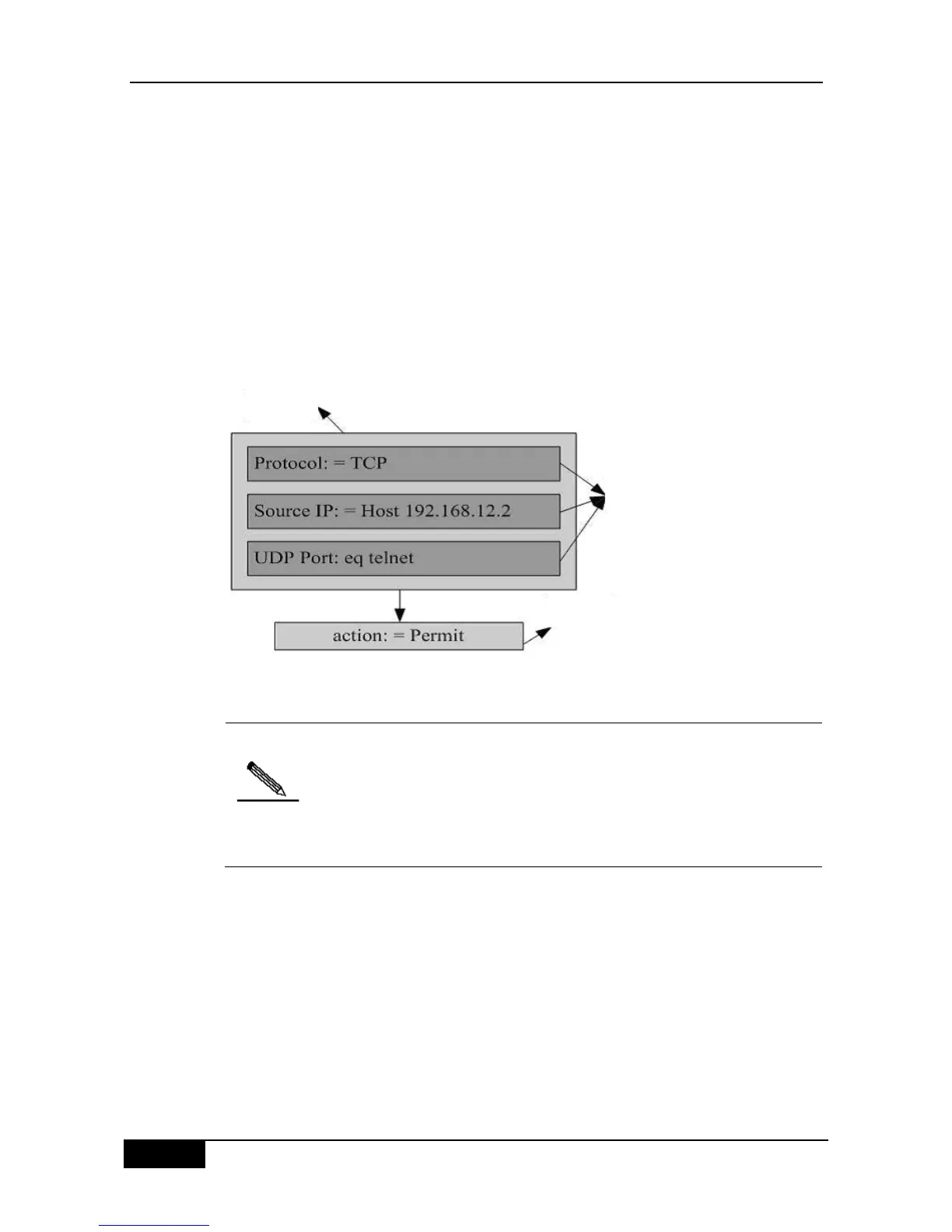
Rules refer to the values of the ACE filtering domain template. For example, one ACE is:
permit tcp host 192.168.12.2 any eq telnet
In this ACE, the filtering domain template is a collection of the following fields: Source IP
Address Fields, IP Protocol Fields and Destination TCP Port Fields. Corresponding values
(rules) are respectively as follows: Source IP Address=host 192.168.12.2; IP Protocol=tcp;
TCP Destination Port=Telnet.
Figure 44-2 Analysis of the ACE: permit tcp host 192.168.12.2 any eq telnet
A filtering domain template can be the collection of L3 fields (Layer 3
Field) and L4 fields (Layer 4 Field) or the collection of multiple L2 fields
(Layer 2 Field). However, the filtering domain templates of a standard and
extended ACL cannot be the collection of L2 and L3, L2 and 4, L2 and L3,
or L4 fields. To use the combination of L2, L3 and L4 fields, you can apply
the Expert ACLs.
Precaustions for ACL associating with SVI in the DGS-3610 series out direction:
1. Priority higher than that of ACL in the in direction;
2. No default deny any any;
3. Supporting application of IP standard, IP extended, MAC extended and expert ACLs;
4. There are some restrictions during the matching of destination IP addresses and
destination MAC addresses in ACL. If the destination MAC address is matched in MAC
extended and expert ACLs, table entries are set but do not take effect when the ACL is
applied in the SVI out direction. If the destination IP address is matched in IP standard, IP
extended and expert ACLs, the configured ACL does not take effect when the destination IP
 Loading...
Loading...











