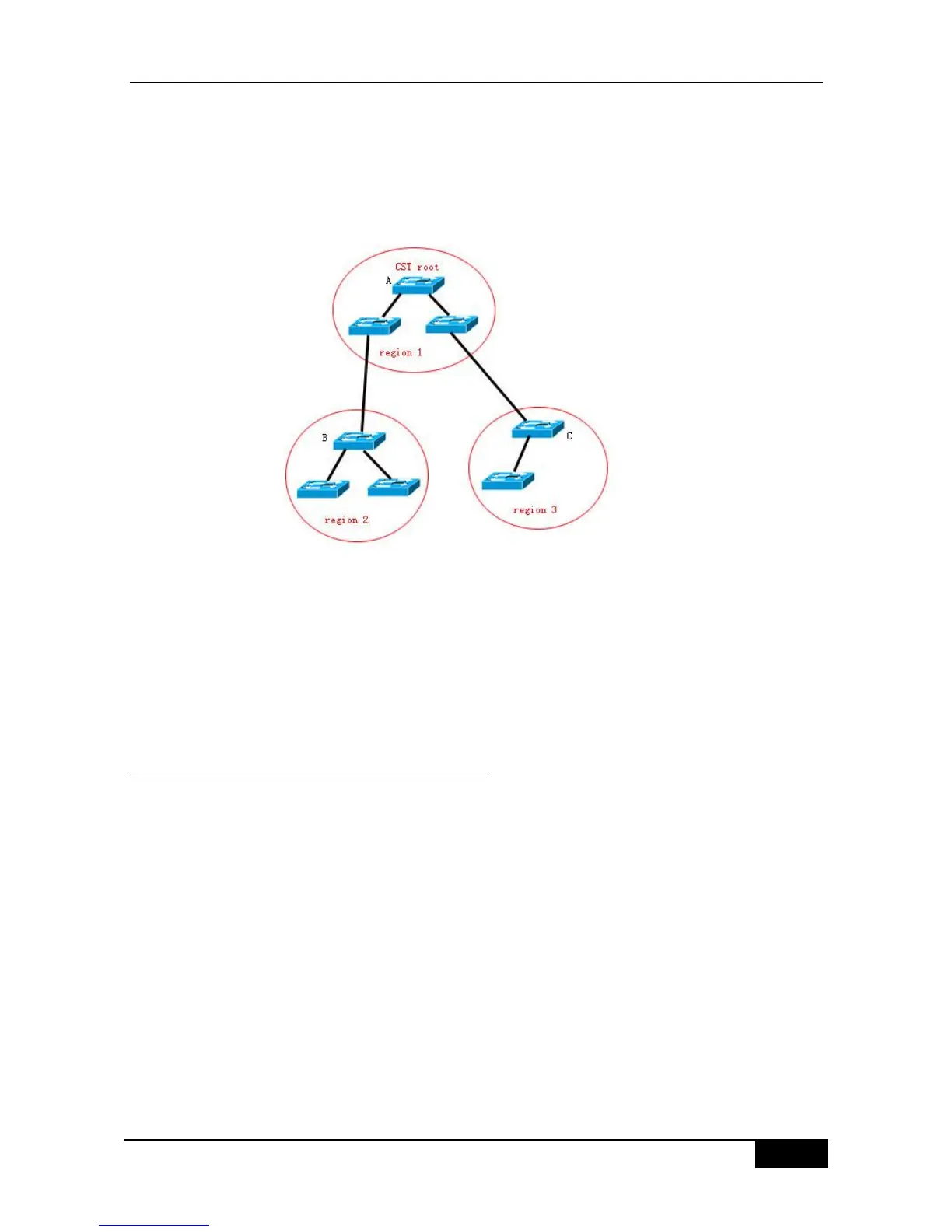
In Region 2, since Root Path Cost from device B to CST Root is the lowest one, device B is
selected as the CIST Regional Root in this region. Similarly, device C is chosen as the CIST
Regional Root in Region 3.
Figure 17-20
CIST Regional Root is not necessarily the device with the smallest Bridge ID in that region. It
is the device in the region that has the lowest Root Path Cost to the CST Root.
At the same time, the Root Port of the CIST regional root takes a new Port Role for the MSTI,
namely the ―Master port”, as the ―outlet‖ of all instances, which is FORWARDING to all
Instances. In order to make the topology more stable, we recommend each ―outlet‖ for the
Region to the CST root is only on one device of this Region as much as possible!
17.1.2.5 Hop Count
The IST and MSTI will not take the Message Age and Max Age to calculate whether the
BPDU information is timeout, but the mechanism similar to the TTL of the IP message is
used, namely the Hop Count.
You can set it by using the global configuration command spanning-tree max-hops. In the
Region, starting from Region Root Bridge, Hop Count decreases by 1 every time when a
device is passed until it is 0, which means the BPDU information is timeout. Devices discard
BPDUs with the Hops value 0.
In order to be compatible with the STP and the RSTP, the MSTP still remains the message
age and Max age mechanism.
 Loading...
Loading...











