Controller area network (beCAN) RM0016
368/449 Doc ID 14587 Rev 8
Note: As the Tx line is still active in this mode, be aware that it can disturb the communication on
the CAN bus.
23.5.3 Loop back combined with silent mode
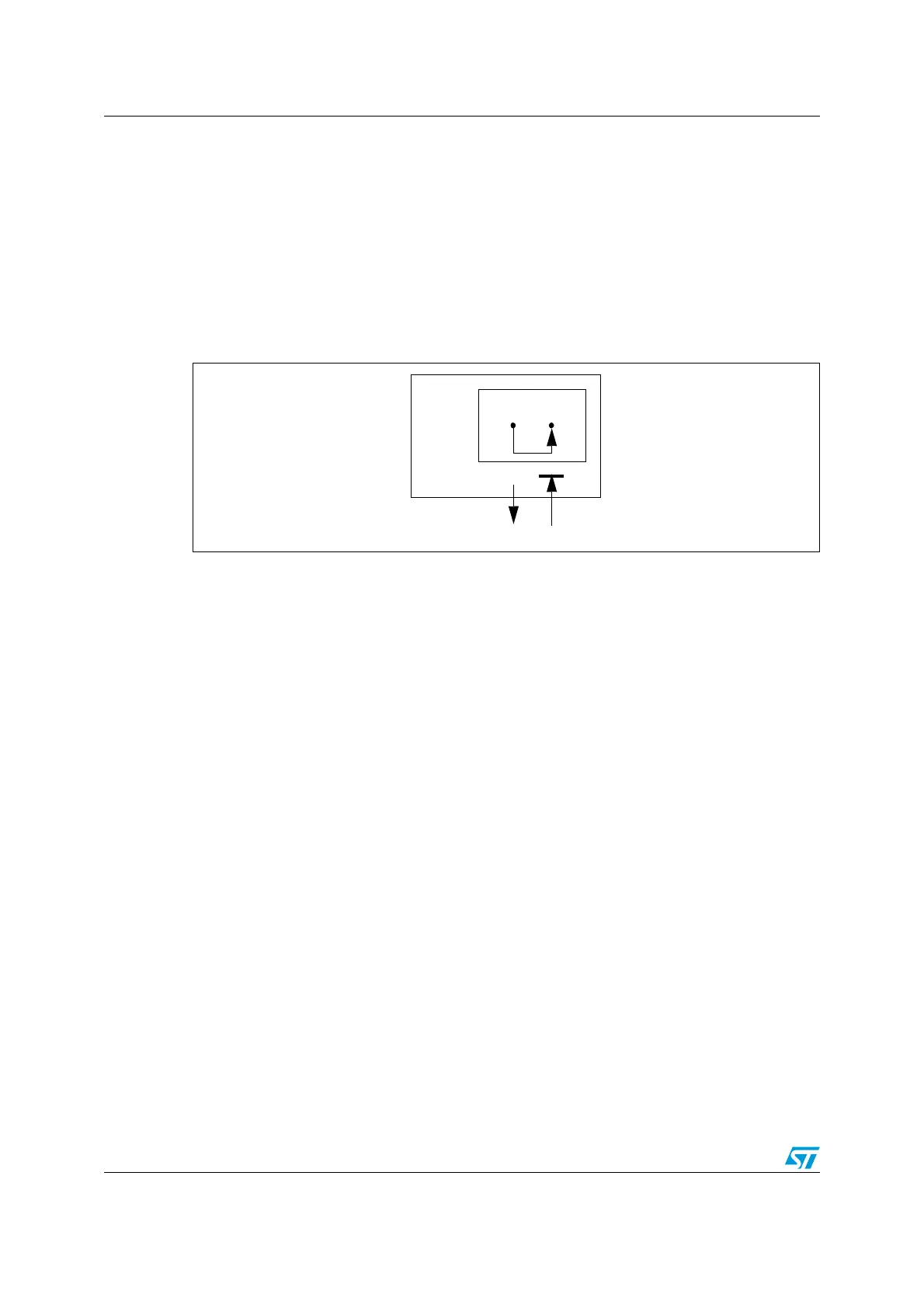
It is also possible to combine Loop Back mode and Silent mode by setting the LBKM and
SILM bits in the CAN_DGR register. This mode can be used for a “Hot Selftest”, meaning
the beCAN can be tested like in Loop Back mode but without affecting a running CAN
system connected to the CANTX and CANRX pins. In this mode, the CANRX pin is
disconnected from the beCAN and the CANTX pin is held recessive.
Figure 144. beCAN in combined mode
23.6 Functional description
23.6.1 Transmission handling
In order to transmit a message, the application must select one empty transmit mailbox, set
up the identifier, the data length code (DLC) and the data before requesting the transmission
by setting the corresponding TXRQ bit in the CAN_MCSR register. Once the mailbox has
exited empty state, the software no longer has write access to the mailbox registers.
Immediately after the TXRQ bit has been set, the mailbox enters pending state and waits to
become the highest priority mailbox, see Transmit Priority. As soon as the mailbox has the
highest priority it will be scheduled for transmission. The transmission of the message of
the scheduled mailbox will start (enter transmit state) when the CAN bus becomes idle.
Once the mailbox has been successfully transmitted, it will become empty again. The
hardware indicates a successful transmission by setting the RQCP and TXOK bits in the
CAN_MCSR and CAN_TSR registers.
If the transmission fails, the cause is indicated by the ALST bit in the CAN_MCSR register in
case of an Arbitration Lost, and/or the TERR bit, in case of transmission error detection.
Transmit priority
By identifier:
When more than one transmit mailbox is pending, the transmission order is given by the
identifier of the message stored in the mailbox. The message with the lowest identifier value
has the highest priority according to the arbitration of the CAN protocol. If the identifier
values are equal, the lower mailbox number will be scheduled first.

 Loading...
Loading...