Controller area network (beCAN) RM0016
380/449 Doc ID 14587 Rev 8
23.6.5 Error management
The error management as described in the CAN protocol is handled entirely by hardware
using a Transmit Error Counter (CAN_TECR register) and a Receive Error Counter
(CAN_RECR register), which get incremented or decremented according to the error
condition. For detailed information about TEC and REC management, please refer to the
CAN standard.
Both of them may be read by software to determine the stability of the network.
Furthermore, the CAN hardware provides detailed information on the current error status in
CAN_ESR register. By means of CAN_EIER register and ERRIE bit in CAN_IER register,
the software can configure the interrupt generation on error detection in a very flexible way.
Bus-Off recovery
The Bus-Off state is reached when TEC is greater then 255, this state is indicated by BOFF
bit in CAN_ESR register. In Bus-Off state, the beCAN is no longer able to transmit and
receive messages.
Depending on the ABOM bit in the CAN_MCR register beCAN will recover from Bus-Off
(become error active again) either automatically or on software request. But in both cases
the beCAN has to wait at least for the recovery sequence specified in the CAN standard
(128 x 11 consecutive recessive bits monitored on CANRX).
If ABOM is set, the beCAN will start the recovering sequence automatically after it has
entered Bus-Off state.
If ABOM is cleared, the software must initiate the recovering sequence by requesting
beCAN to enter initialization mode. Then beCAN starts monitoring the recovery sequence
when the beCAN is requested to leave the initialization mode.
Note: In initialization mode, beCAN does not monitor the CANRX signal, therefore it cannot
complete the recovery sequence. To recover, beCAN must be in normal mode.
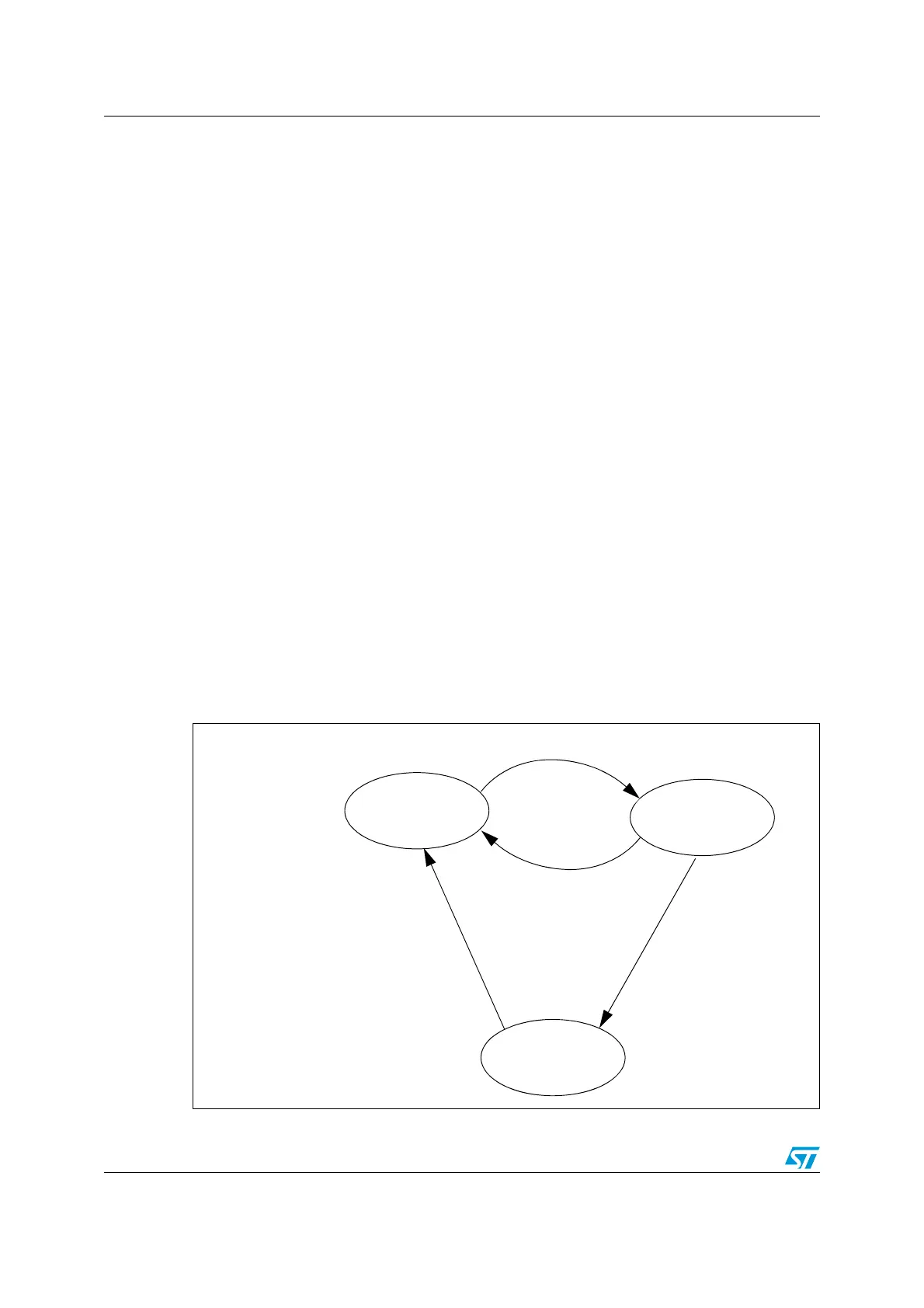
Figure 152. CAN error state diagram
ERROR PASSIVE
When TEC or REC > 127
When TEC and REC < 128
ERROR ACTIVE
BUS OFF
When TEC > 255When 128 * 11 recessive bits occur
 Loading...
Loading...