Controller area network (beCAN) RM0016
376/449 Doc ID 14587 Rev 8
Filter match index
Once a message has been received in the FIFO it is available to the application. Typically
application data are copied into RAM locations. To copy the data to the right location the
application has to identify the data by means of the identifier. To avoid this and to ease the
access to the RAM locations, the CAN controller provides a Filter Match Index.
This index is stored in the mailbox together with the message according to the filter priority
rules. Thus each received message has its associated Filter Match Index.
The Filter Match Index can be used in two ways:
– Compare the Filter Match Index with a list of expected values.
– Use the Filter Match Index as an index on an array to access the data destination
location.
For non-masked filters, the software no longer has to compare the identifier.
If the filter is masked the software reduces the comparison to the masked bits only.
Note: The index value of the filter number does not take into account the activation state of the
filter banks.
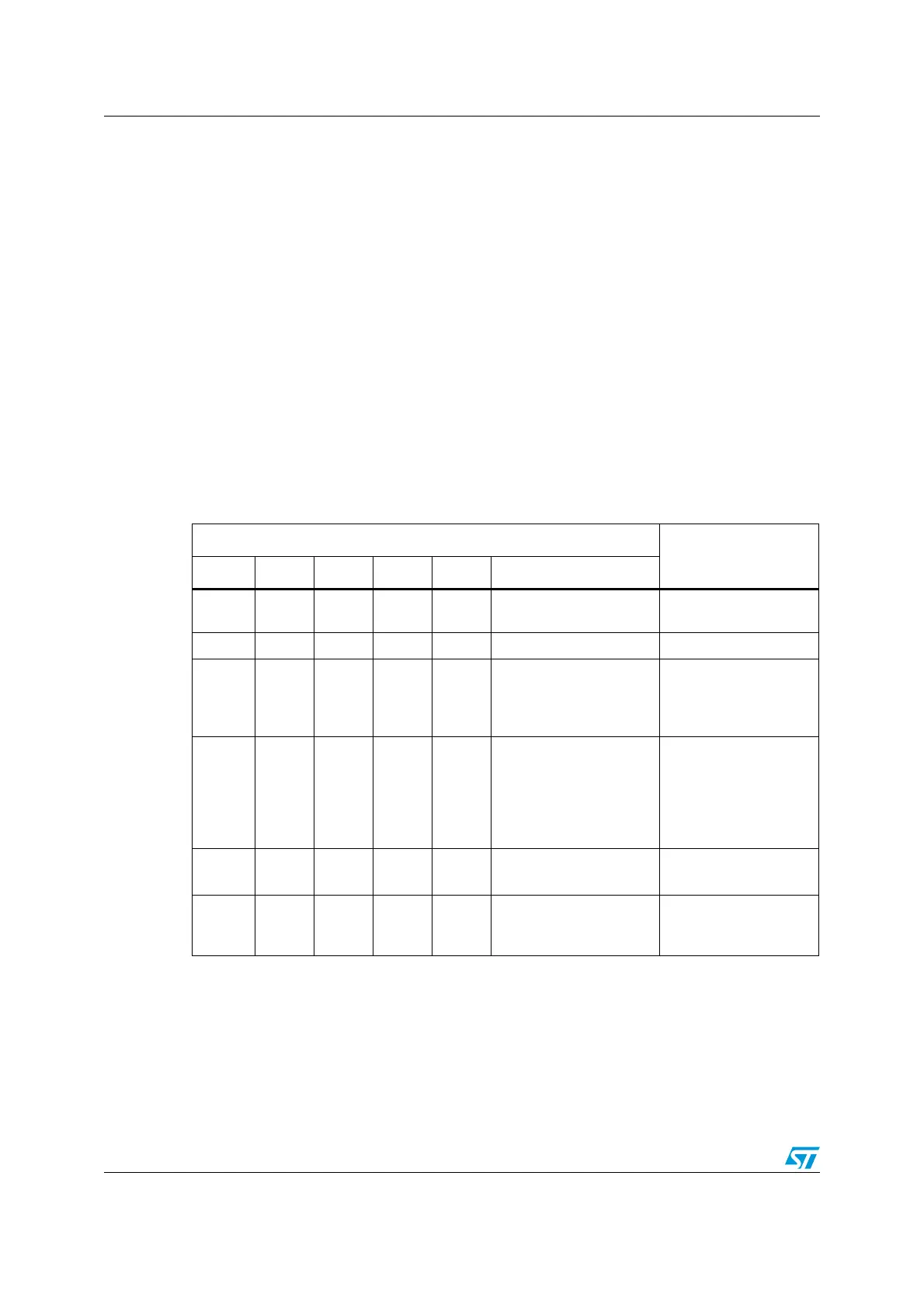
Table 64. Example of filter numbering
Filter bank
Filter number
Number FCS FMH FML FACT Configuration
0 0b11 1 1 1 Identifier list (32-bit)
0
1
1 0b11 0 0 1 Identifier mask (32-bit) 2
2 0b10 1 1 1 Identifier list (16-bit)
3
4
5
6
3 0b00 0 1 0
Deactivated
Identifier List/Identifier
mask (8-bit)
7
8
9
10
11
12
4 0b10 0 0 0
Deactivated
Identifier Mask (16-bit)
13
14
5 0b01 0 0 1 Identifier Mask (16/8-bit)
15
16
17
 Loading...
Loading...