Power management RM0016
102/449 Doc ID 14587 Rev 8
10.1.1 Clock management for low consumption
Slowing down the system clock
In Run mode, choosing the oscillator to be used as the system clock source is very
important to ensure the best compromise between performance and consumption. The
selection is done by programming the clock controller registers. Refer to the Clock control
(CLK) section.
As a further measure, f
CPU
can be reduced by writing to the CPUDIV[2:0] bits in the Clock
divider register (CLK_CKDIVR). This reduces the speed of the CPU and consequently the
power consumption of the MCU. The other peripherals (clocked by f
MASTER)
are not affected
by this setting.
To return to full speed at any time in Run mode, clear the CPUDIV[2:0] bits.
Peripheral clock gating
For additional power saving you can use peripheral clock gating (PCG). This can be done at
any time by selectively enabling or disabling the f
MASTER
clock connection to individual
peripherals. Refer to the Clock control (CLK) section.
These settings are effective in both Run and Wait modes.
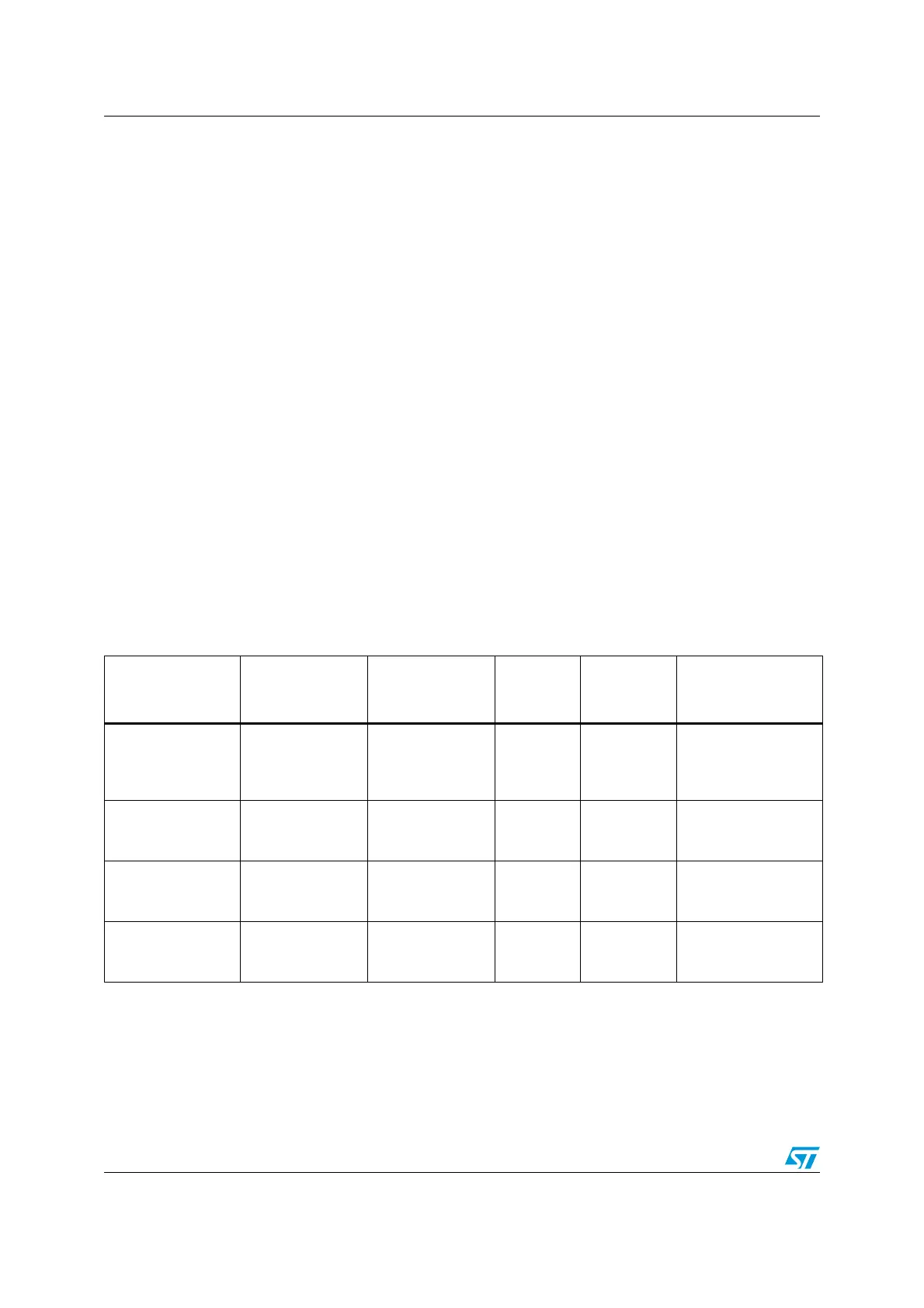
10.2 Low power modes
The main characteristics of the four low power modes are summarized in Table 2 0.
Table 20. Low power mode management
Mode
(consumption
level)
Main voltage
regulator
Oscillators CPU Peripherals
Wakeup trigger
event
Wait
( - )
On On Off On
(1)
All internal interrupts
(including AWU) or
external interrupts,
reset
Active-halt
( - - )
On
Off
except LSI (or
HSE)
Off Only AWU
(2)
AWU or external
(3)
interrupts, reset
Active-halt with
MVR auto power off
( - - - )
Off
(low power
regulator on)
Off
except LSI only
Off Only AWU
(2)
AWU or external
(3)
interrupts, reset
Halt
( - - - - )
Off
(low power
regulator on)
Off Off Off
(2)
External
(3)
interrupts,
reset
1. If the peripheral clock is not disabled by peripheral clock gating function.
2. If activated, BEEP or IWDG stay switched on. In this case, the LSI clock is forced to run.
3. Including communication peripheral interrupts.

 Loading...
Loading...