RM0016 Window watchdog (WWDG)
Doc ID 14587 Rev 8 129/449
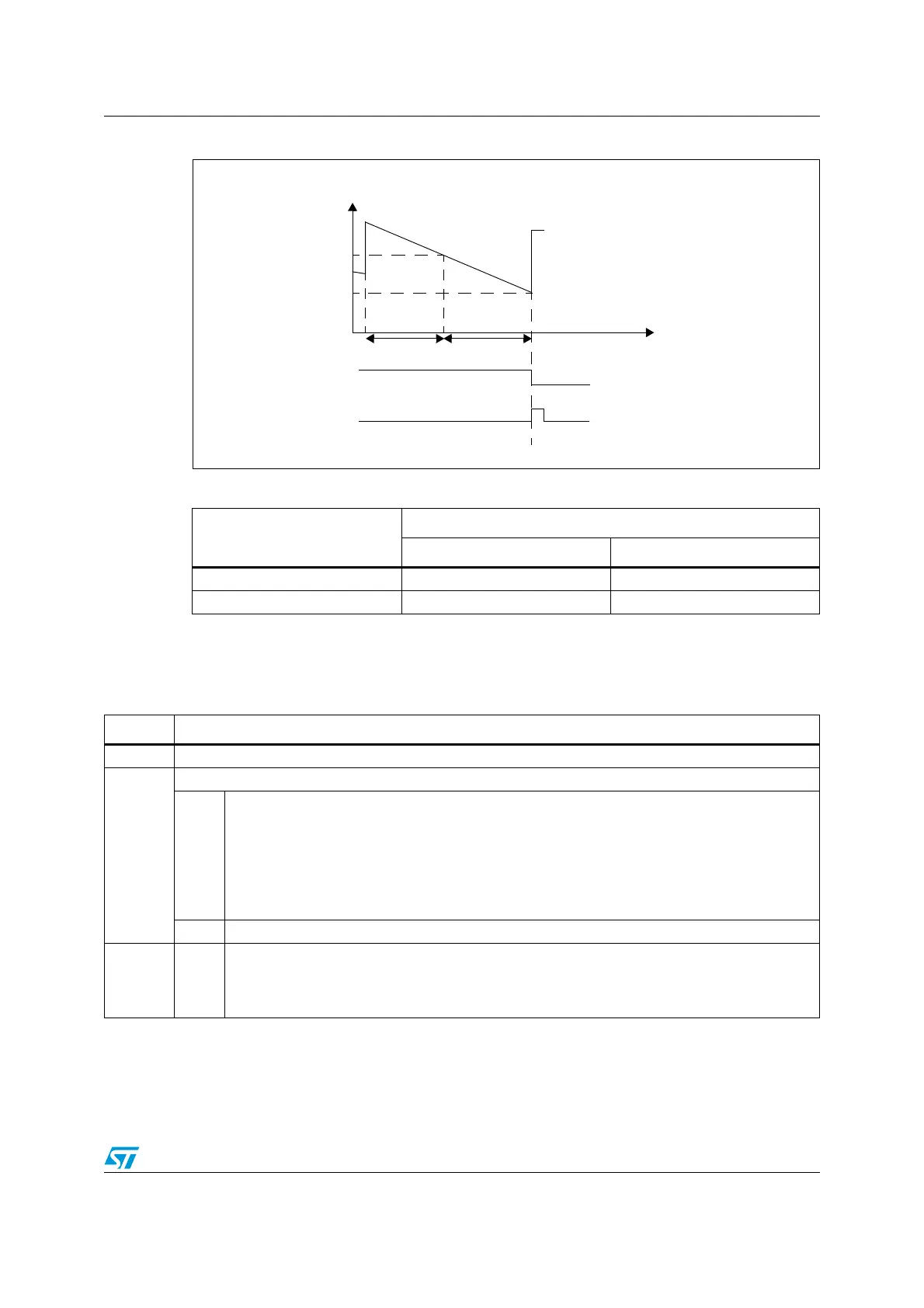
Figure 30. Window watchdog timing diagram
15.5 WWDG low power modes
Table 30. Window watchdog timing example
T[6:0]
f
CPU
(MHz)
216
40h 6.144 0.768
7Fh 393.216 49.152
T6 bit
Reset
WDGWR
T[5:0] CNT downcounter
time
Refresh WindowRefresh not allowed (step = 12288/f
clk_wwdg_ck
)
0x7F
Table 31. Effect of low power modes on WWDG
Mode Description
Wait No effect on watchdog: The downcounter continues to decrement.
Halt
WWDG_HALT in option byte
0
No watchdog reset is generated. The MCU enters Halt mode. The watchdog counter is
decremented once and then stops counting and is no longer able to generate a watchdog reset
until the MCU receives an external interrupt or a reset.
If an interrupt is received (refer to interrupt table mapping to see interrupts which can occur in
Halt mode), the watchdog restarts counting after the stabilization delay. If a reset is generated,
the watchdog is disabled (reset state) unless hardware watchdog is selected by option byte. For
application recommendations see Section 15.8 below.
1 A reset is generated instead of entering Halt mode.
Active-
halt
x
No reset is generated. The MCU enters Active-halt mode. The watchdog counter is not
decremented. It stops counting. When the MCU receives an oscillator interrupt or external
interrupt, the watchdog restarts counting immediately. When the MCU receives a reset the
watchdog restarts counting after the stabilization delay.

 Loading...
Loading...