Configure Switching Information
209
M4300 Series and M4300-96X Fully Managed Switches User Manual
6. To refresh the page with the latest information on the switch, click the Update button.
The following table describes the nonconfigurable iSCSI Sessions Detailed information.
Spanning Tree Protocol
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides a tree topology for any arrangement of bridges.
STP also provides one path between end stations on a network, eliminating loops. Spanning
tree versions supported include Common STP, Multiple STP, and Rapid STP.
Classic STP provides a single path between end stations, avoiding and eliminating loops. For
information on configuring Common STP, see Configure CST Port Settings
on page 217.
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) supports multiple instances of Spanning Tree to
efficiently channel VLAN traffic over different interfaces. Each instance of the Spanning Tree
behaves in the manner specified in IEEE 802.1w, Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP), with slight
modifications in the working but not the end effect (chief among the effects, is the rapid
transitioning of the port to Forwarding). The difference between the RSTP and the traditional
STP (IEEE 802.1D) is the ability to configure and recognize full-duplex connectivity and ports
which are connected to end stations, resulting in rapid transitioning of the port to Forwarding
state and the suppression of Topology Change Notification. These features are represented
by the parameters pointtopoint and edgeport. MSTP is compatible to both RSTP and STP. It
behaves appropriately to STP and RSTP bridges. A MSTP bridge can be configured to
behave entirely as a RSTP bridge or a STP bridge.
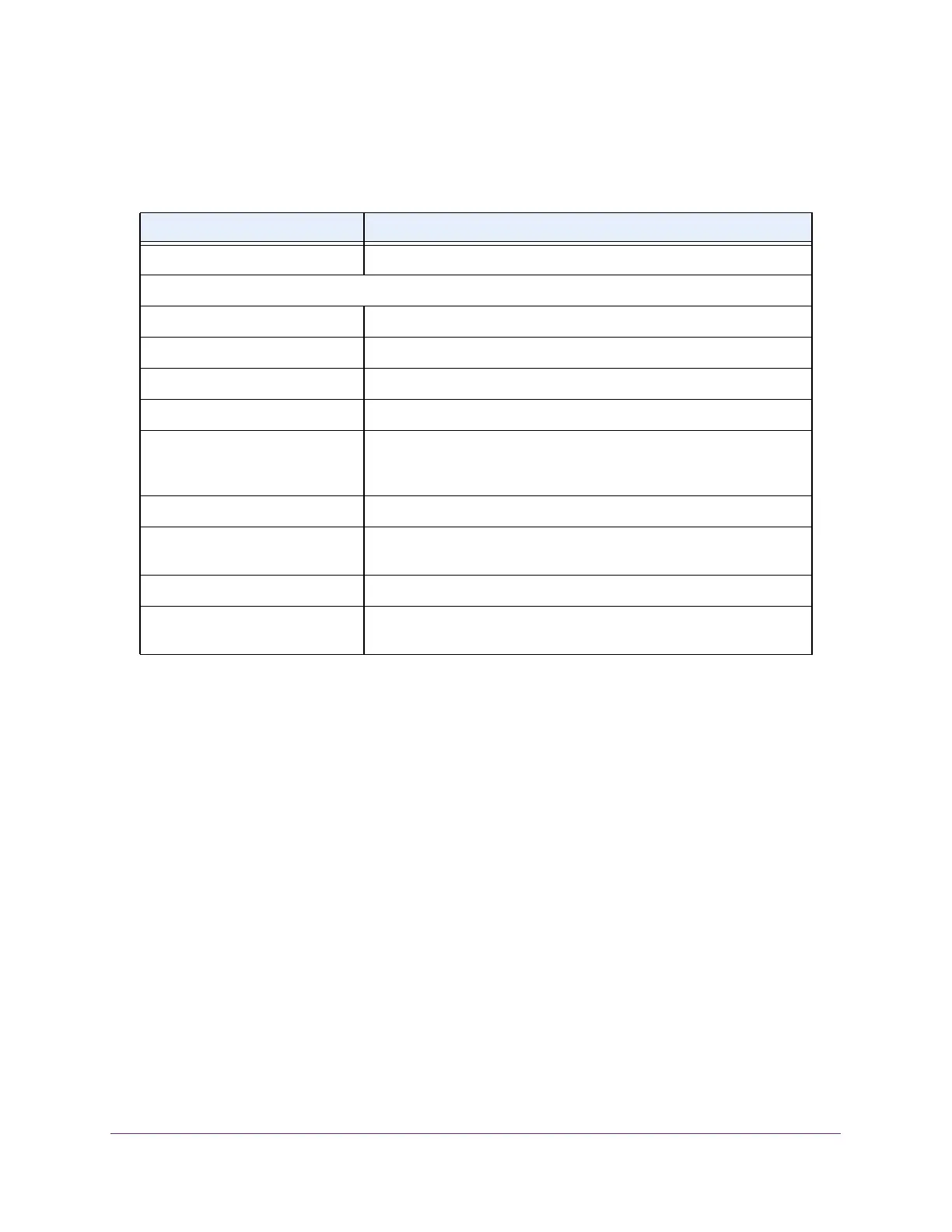
Table 72. iSCSI Sessions Detailed
Field Description
Session Index The list of session indices.
The rest of the fields on this page correspond to the currently selected Session Index.
Target Name The target’s name.
Initiator Name The initiator’s name.
Up Time The time elapsed since the creation of the current session.
Time for Aging Out (in Seconds) The time left for the current session to expire in seconds.
Initiator Session ID (ISID) The unique identifier an initiator assigns to its session endpoint which,
when combined with the iSCSI initiator name, provides a unique name
for the iSCSI initiator port.
Initiator IP Address The initiator’s IP address.
Initiator TCP Port The initiator’s TCP port number of one of the connections between the
target and initiator
.
T
arget IP Address The IP address of the target.
Target TCP Port The target’s TCP port number of one of the connections between the
target and initiator
.

 Loading...
Loading...











