In general, the contents of SPRs are undefined after a reset. Reset initializes the minimum number of
SPR fields required for allow successful instruction fetching. "Contents of Special Purpose Registers
after Reset" on page 8-4 describes these
initial values. System software fully configures the
processor.
"Machine
State Register Contents after Reset" on page 8-3 describes the MSR contents.
The
MCI field of the Exception Syndrome Register (ESR) is cleared so that it can be determined if
there has been a machine check during initialization, before machine check exceptions are
enabled.
Two SPRs contain status on the type of reset that has occurred. The Debug Status Register (DSSR)
contains the most recent reset type. The Timer Status Register (TSR) contains the most recent
watchdog reset.
8.6 Processor Register Contents After Reset
After a reset, the contents of the SPRs control the initial processor state. The initial register contents
vary with the type of reset that occurred.
Chapter 25, "Register
Summary," contains descriptions of the registers referred to
in
Table
8-1
through Table 8-3.
8.6.1
Machine State Register Contents after Reset
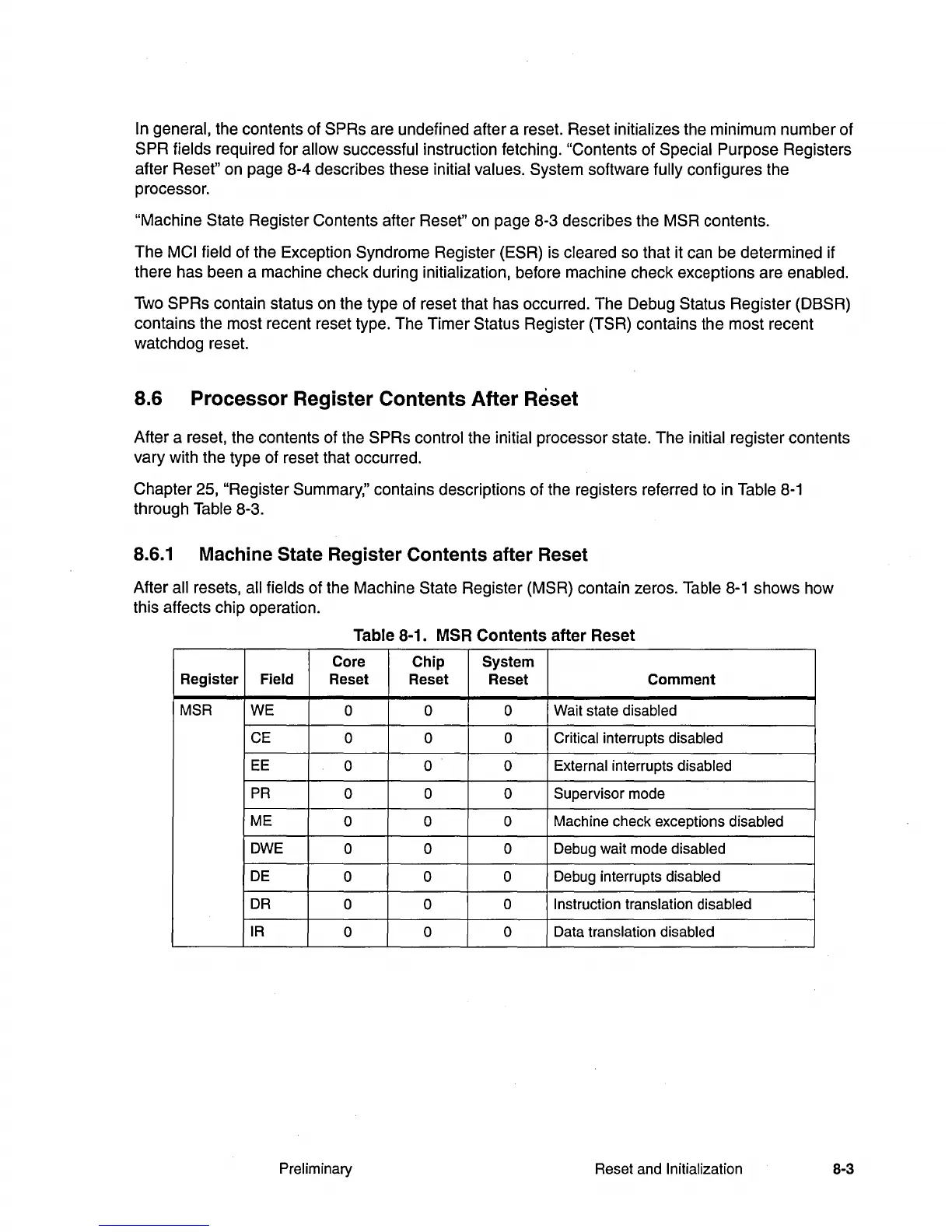
After all resets, all fields of the Machine State Register (MSR) contain zeros. Table
8-1
shows how
this affects chip operation.
Table 8-1.
MSR
Contents after Reset
Core
Chip
System
Register
Field
Reset
Reset Reset
Comment
MSR
WE
0 0 0
Wait state disabled
CE
0 0 0 Critical interrupts disabled
EE
0 0 0
External interrupts disabled
PR
0 0 0 Supervisor mode
ME
0 0 0 Machine check exceptions disabled
DWE
0 0
0
Debug wait mode disabled
DE
0 0 0
Debug interrupts disabled
DR
0 0
0
Instruction translation disabled
IR
0 0
0
Data translation disabled
Preliminary
Reset and Initialization 8-3

 Loading...
Loading...











