16.5 External Bus Master Interface
The ESC includes an External Sus Master (ESM) interface supporting a shared bus protocol which
allows an ESM to gain control of the peripheral bus. Once an external master has been granted
access to the
peripheral interface it can read and write all PLS- and OPS-addressable memory, with
the exception of devices
controlled by the ESC. Typical destinations for ESM transactions are PCI
address space and SDRAM memory. For ESC-attached peripherals and memory, the external master
is required to directly
control the target.
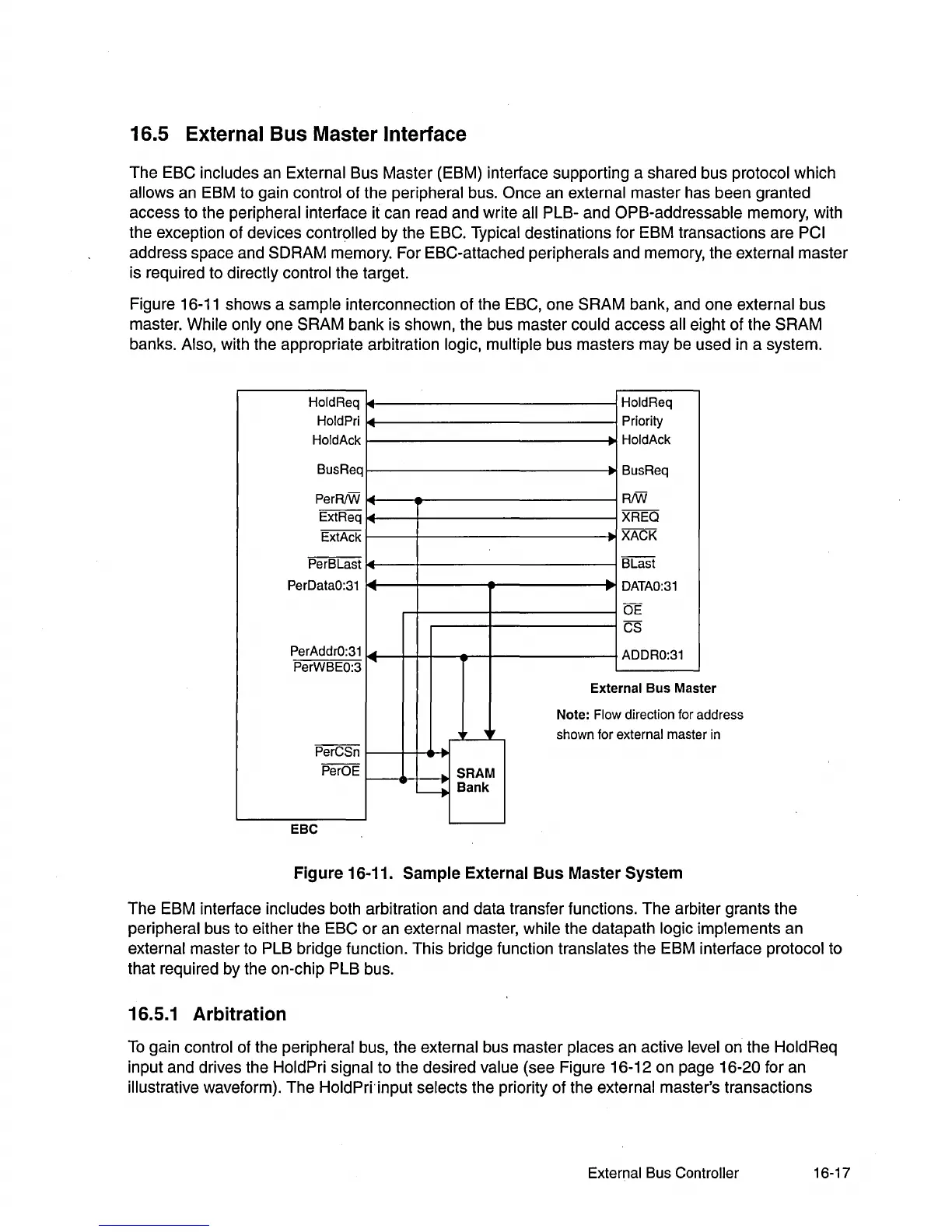
Figure 16-11 shows a
sample interconnection of the ESC, one SRAM bank, and one external bus
master. While
only one SRAM bank is shown, the bus master could access all eight of the SRAM
banks.
Also, with the appropriate arbitration logic, multiple bus masters may be used
in
a system.
HoldReq
HoldPri ,
HoldAck
BusReq
PerRiW ,
ExtReq
~
ExtAck
PerBLast
PerDataO:31
~
PerAddrO:31
~
PerWBEO:3
....
~
~,
PerCSn
PerDE
SRAM
~
Bank
EBC
HoldReq
Priority
..
HoldAck
..
BusReq
R!W
XREQ
.~
XACK
BLast
..
DATAO:31
..
DE
CS
ADDRO:31
External
Bus
Mast
er
Note: Flow direction for a
ddress
r
in
shown for external maste
Fig ure 16-11. Sample External Bus Master System
The ESM interface includes both arbitration and data transfer functions. The arbiter grants the
peripheral bus to either the ESC or an external master, while the datapath logic implements an
external master to PLS bridge function. This bridge function translates the ESM interface protocol to
that required by the on-Chip
PLS bus.
16.5.1 Arbitration
To
gain control of the peripheral bus, the external bus master places an active level on the HoldReq
input and drives the HoldPri signal to the desired value (see Figure 16-12 on page 16-20 for an
illustrative waveform). The HoldPri' input selects the priority of the external master's transactions
External
Bus
Controller 16-17
 Loading...
Loading...











