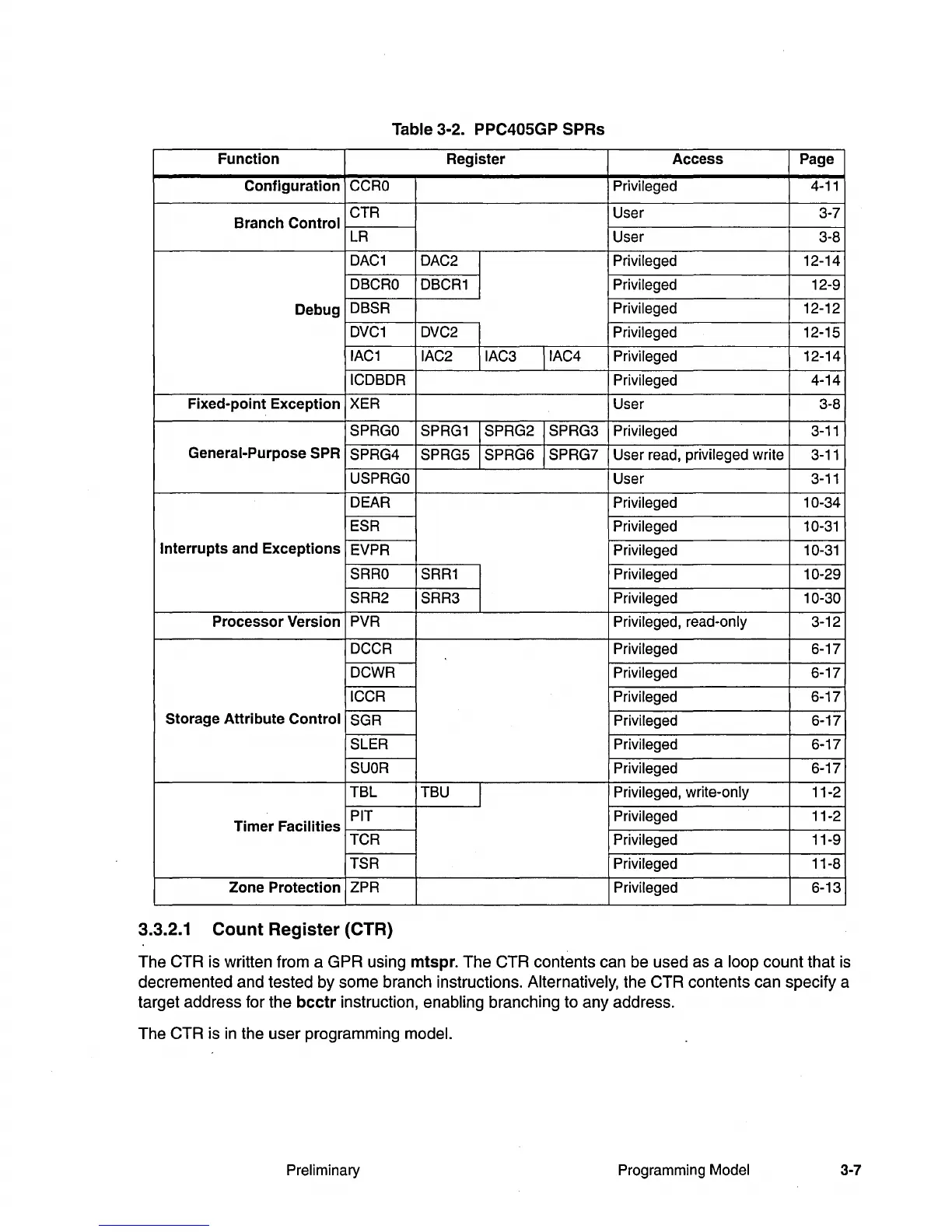
Table 3-2. PPC40SGP SPRs
Function
Register
Access
Page
Configuration
CCRO
Privileged
4-11
Branch
Control
CTR User 3-7
LR
User 3-8
DAC1
DAC2
I
Privileged
12-14
DBCRO
DBCR1
I
Privileged
12-9
Debug
DBSR
Privileged
12-12
DVC1
DVC2
I
Privileged
12-15
IAC1
IAC2
IIAC3 IIAC4
Privileged
12-14
ICDBDR
Privileged
4-14
Fixed-point
Exception
XER
User 3-8
SPRGO
SPRG1 ISPRG2 ISPRG3
Privileged
3-11
General-Purpose SPR
SPRG4
SPRG5 ISPRG6 ISPRG7
User read, privileged write
3-11
USPRGO
User
3-11
DEAR Privileged 10-34
ESR Privileged 10-31
Interrupts
and
Exceptions
EVPR
Privileged 10-31
SRRO
SRR1
I
Privileged 10-29
SRR2 SRR3
I
Privileged 10-30
Processor
Version
PVR
Privileged,
read-only 3-12
DCCR
Privileged
6-17
DCWR
Privileged 6-17
ICCR
Privileged
6-17
Storage
Attribute
Control
SGR
Privileged
6-17
SLER
Privileged 6-17
SUOR
Privileged
6-17
TBL TBU
j
Privileged, write-only 11-2
Timer
Facilities
PIT Privileged 11-2
TCR
Privileged
11-9
TSR Privileged 11-8
Zone
Protection
ZPR
Privileged
6-13
3.3.2.1
Count
Register (CTR)
The
eTR
is written from a GPR using mtspr. The
eTR
contents can be used as a loop count that is
decremented and tested by some branch instructions.
Alternatively, the
eTR
contents can specify a
target address for the
bcctr
instruction, enabling branching to any address.
The
eTR
is
in
the user programming model.
Preliminary Programming Model 3-7
 Loading...
Loading...











