• Either a transmit error or an SQE occurs on one of the channels and the corresponding interrupt is
not masked
in
the EMACO_ISER. One of the following scenarios can occur.
-
If the other channel has not yet requested MAL service when the channel for which the error
occurred receives notification from MAL that the transmit operation has
completed,
EMACO_ TMRO[GNPD]
is cleared (EMACO_ TMRO[GNPD] = 0) and the EMACO_ISR[DBDM] is
immediately set (EMAC_ISR[DBDM]=1).
- If the other channel was receiving data from MAL, it initiates early termination. If a second
packet was being transmitted on the media, it is stopped.
In
these cases, EMACO_ TMRO[GNPD]
is cleared (EMACO_ TMRO[GNPD] = 0) and the EMACO_ISR[DBDM] = 1 only after notification
from MAL that the transmit operation has
completed has been received for the second channel.
At this point, neither channel activates a request to MAL until EMACO_ TMRO[GNPD] = 1 and
EMACO_ISR[DBDM] =
o.
The channel specified by EMACO_ TMRO[FC] is the first to request service
from MAL. Subsequent requests continue in an
alternating, sequential manner.
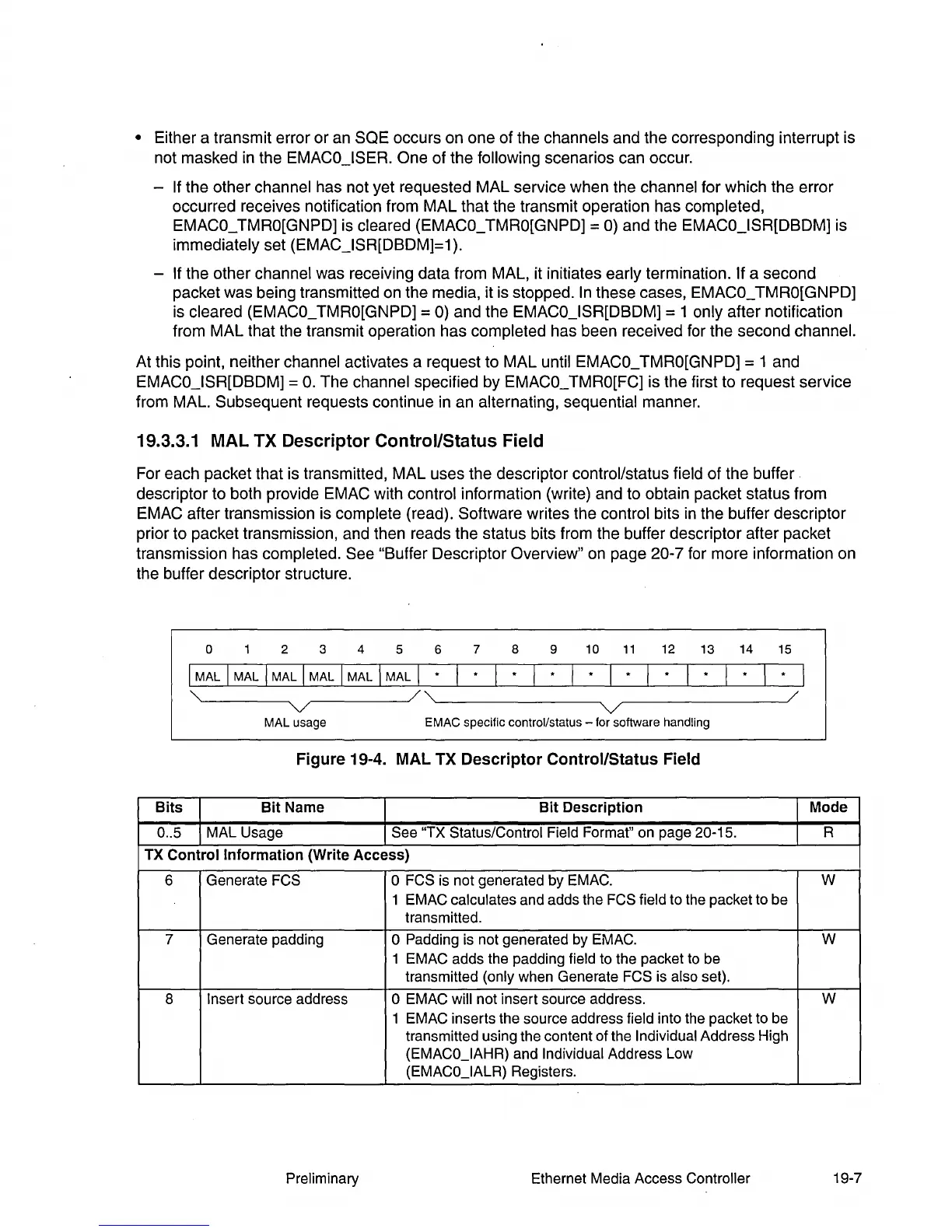
19.3.3.1 MAL TX Descriptor Control/Status Field
For each packet that is transmitted, MAL uses the descriptor control/status field of the buffer.
descriptor to both provide EMAC with
control information (write) and to obtain packet status from
EMAC after transmission is
complete (read). Software writes the control bits
in
the buffer descriptor
prior to packet transmission, and then reads the status bits from the buffer descriptor after packet
transmission has
completed. See "Buffer Descriptor Overview"
on
page 20-7 for more information on
the buffer descriptor structure.
0 2 3 4
5
6
7 8
9
10
11
12
13 14
15
I MAL I MAL I MAL I MAL I MAL I MAL I
.
I
.
I
.
I
I
.
I
.
I
.
I
.
I I
.
"
/"
/
V
V
MAL usage
EMAC specific control/status - for software
handling
Figure
19-4.
MAL
TX
Descriptor
Control/Status
Field
Bits
Bit
Name
Bit
Description
Mode
0
..
5
MAL
Usage
See "TX Status/Control Field Format" on page 20-15. R
TX
Control
Information
(Write
Access)
6 Generate FCS
° FCS is
not
generated
by
EMAC.
W
1 EMAC calculates and adds the FCS field to the packet to
be
transmitted.
7 Generate padding
° Padding is not generated by EMAC.
W
1 EMAC adds the padding field to the packet to be
transmitted (only when Generate FCS is also set).
8 Insert source address
° EMAC will
not
insert source address.
W
1 EMAC inserts the source address field into the packet to be
transmitted using the content of the Individual
Address
High
(EMACO_IAHR) and Individual Address Low
(EMACO_IALR) Registers.
Preliminary Ethernet Media
Access
Controller
19-7

 Loading...
Loading...











