Managing Physical Interfaces Configuration Examples
User Guide
103
Gi1/0/2 N/A Gi1/0/1-28,Po1-14
Gi1/0/3 N/A Gi1/0/1-28,Po1-14
Gi1/0/4 N/A Gi1/0/1
...
5.2 Example for Loopback Detection
5.2.1 Network Requirements
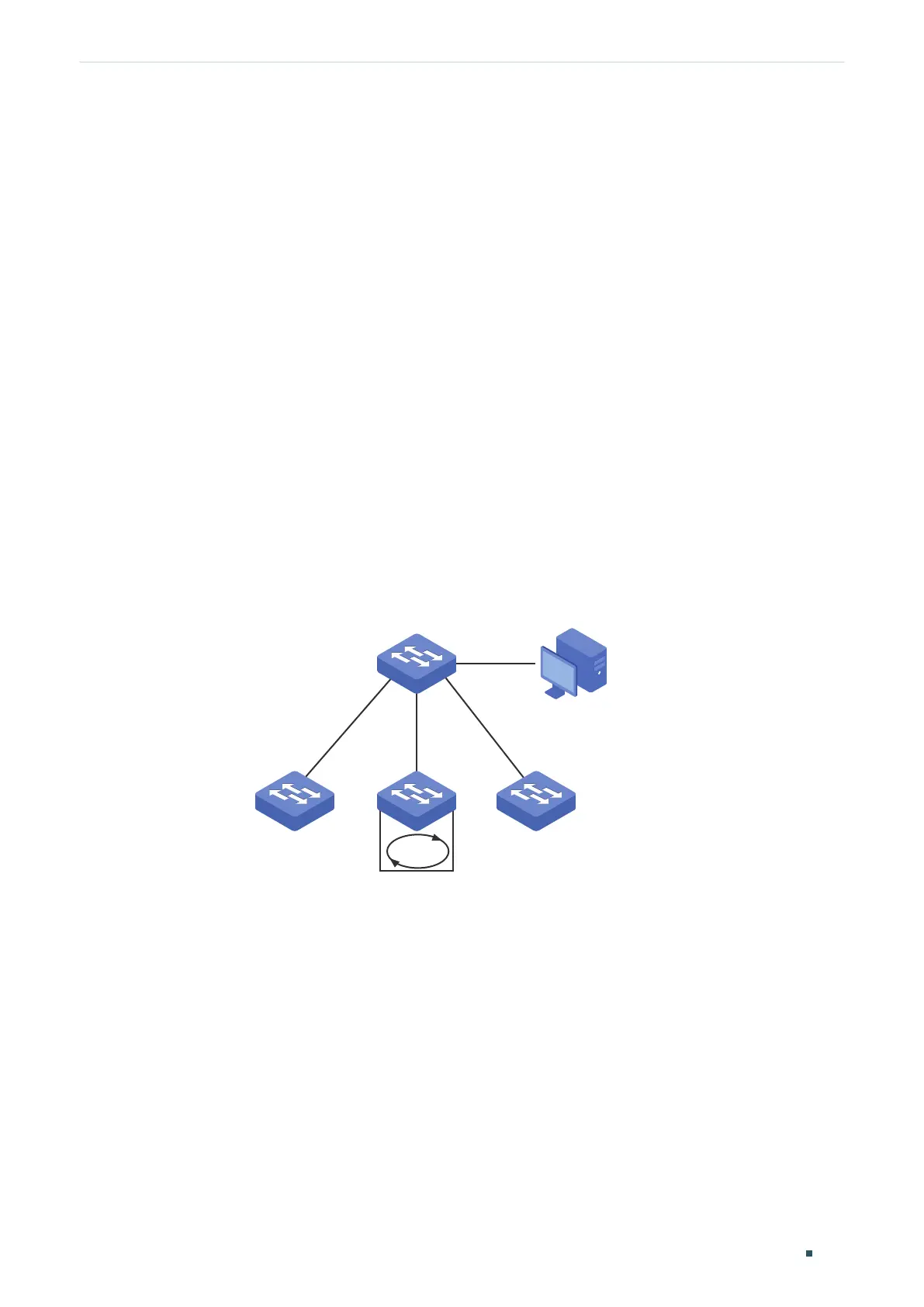
As shown below, Switch A is a convergence-layer switch connecting to several access-
layer switches. Loops can be easily caused in case of misoperation on the access-
layer switches. If there is a loop on an access-layer switch, broadcast storms will occur
on Switch A or even in the entire network, creating excessive traffic and degrading the
network performance.
To reduce the impacts of broadcast storms, users need to detect loops in the network via
Switch A and timely block the port on which a loop is detected.
Figure 5-5 Network Topology
Switch A
Management Host
Access-layer Switches
Gi1/0/1
Gi1/0/2
Loop
Gi1/0/3
5.2.2 Configuration Scheme
Enable loopback detection on ports 1/0/1-3 and configure SNMP to receive the trap
notifications. For detailed instructions about SNMP, refer to Configuring SNMP & RMON.
Here we introduce how to configure loopback detection and monitor the detection result
on the management interface of the switch.
Demonstrated with T2600G-28TS, the following sections provide configuration procedure
in two ways: using the GUI and using the CLI.

 Loading...
Loading...











