User Guide 594
Configuring DHCP Service Configuration Examples
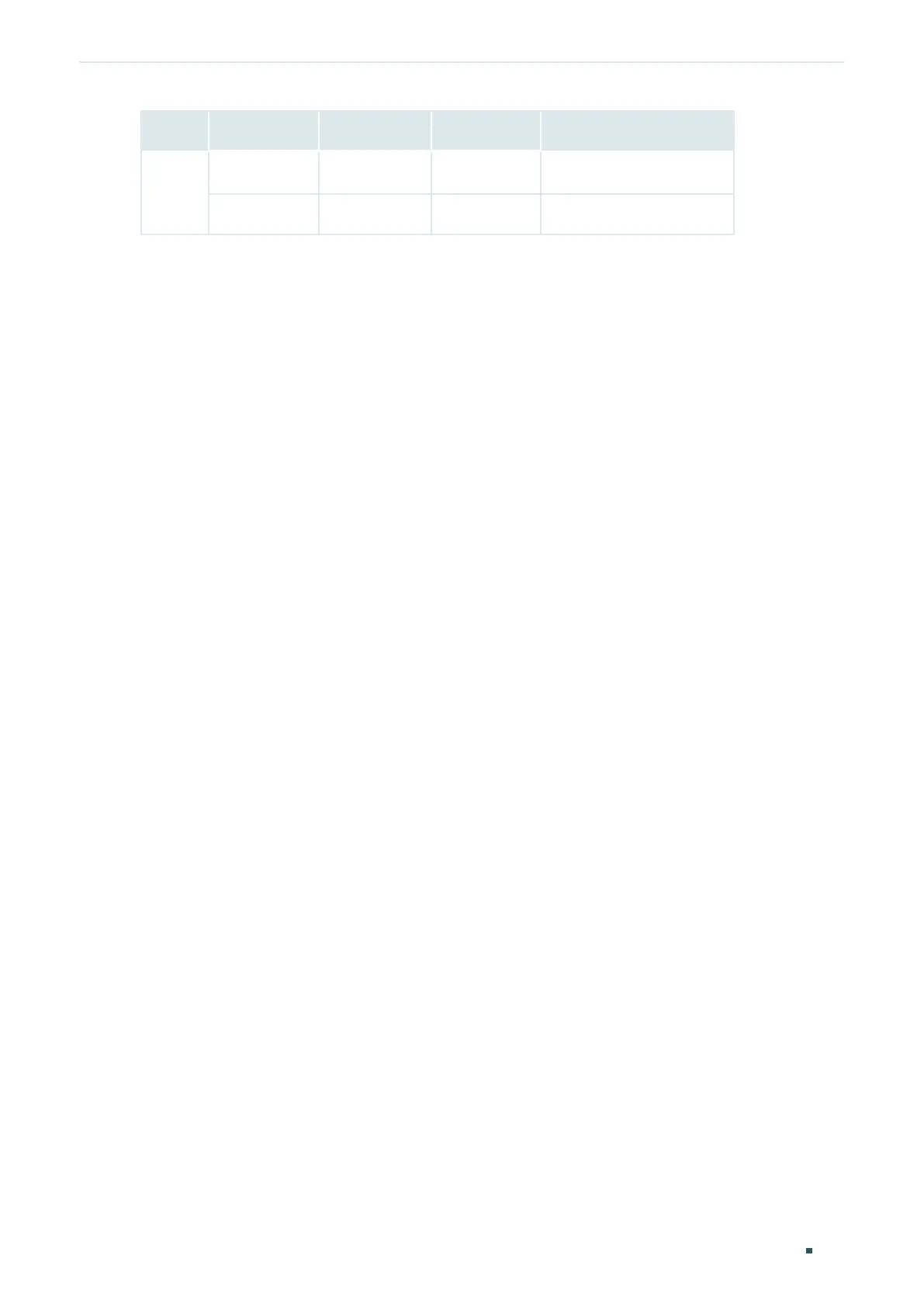
Group Sub-option Type (Hex) Length (Hex) Value (Hex)
2
Circuit ID 00 04 00:02:00:02
Remote ID 00 06 00:00:FF:FF:27:12
The configuration file /etc/dhcpd.conf of the Linux ISC DHCP Server is:
ddns-update-style interim;
ignore client-updates;
# Create two classes to match the pattern of Option82 in DHCP request packets from
# Group1 and Group 2, respectively.
# The agent circuit ID inserted by the DHCP relay switch is 6 bytes long in TLV format, one
# byte for Type, one byte for Length, and 4 bytes for Value. Therefore, the offset is 2 and the
length is 4.
# Similarly, the offset of the agent remote ID is 2 and the length is 6.
class “VLAN2Port1“ {
match if substring (option agent.circuit-id, 2, 4) = 00:02:00:01
and substring (option agent.remote-id, 2, 6) = 00:00:ff:ff:27:12;
}
class “VLAN2Port2“ {
match if substring (option agent.circuit-id, 2, 4) = 00:02:00:02
and substring (option agent.remote-id, 2, 6) = 00:00:ff:ff:27:12;
}
# Create two IP Address pools in the same subnet.
# Assign different IP addresses to the DHCP clients in different groups.
subnet 192.168.2.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
option routers 192.168.2.1;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option domain-name-servers 192.168.0.59;
option domain-name “example.com“;
default-lease-time 600;
max-lease-time 7200;
authoritative;
pool {
range 192.168.2.50 192.168.2.100;
allow members of “VLAN2Port1“;
}
pool {
range 192.168.2.150 192.168.2.200;
allow members of “VLAN2Port2“;
}

 Loading...
Loading...











