User Manual UMN:CLI
V5808
205
number of packets, and is easy to drop high priority of packets. Unlike RED, WRED is not
as random when dropping packets. WRED combines the capabilities of the RED
algorithm with the IP precedence feature to provide for preferential traffic handling of
high-priority packets.
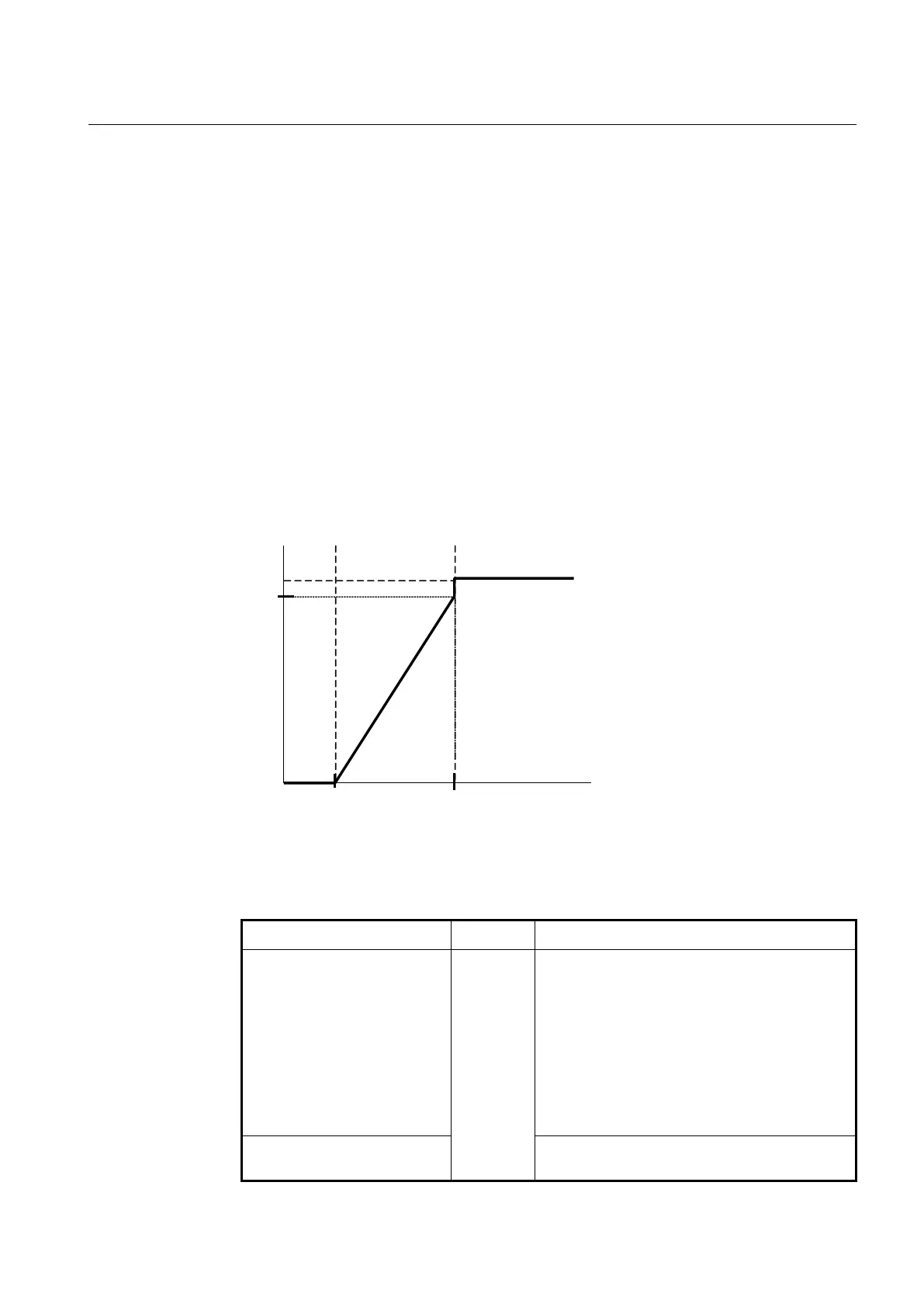
To utilize WRED function, a start queue length value, end queue length value and drop
probability are necessary.
– WRED min-threshold (start queue length value) is the starting point of random
packet dropping.
– WRED max-threshold (end queue length value) is the point of complete drop-
ping.
– drop probability indicates the percentage of packet dropping from the starting
point of random packet dropping to the point of complete dropping. .
If probability is a large value, the amount of packets would be dropped. Therefore
complete dropping point is slowly reached. On the other hand, if probability is small, a
small amount of packets would be dropped. Therefore complete dropping point is quickly
reached. If the probability value is 1, dropping packet would be none and the value is 100,
all packets would be discarded from the point of start queue length value is reached.
Fig. 7.13 WRED Packet Drop Probability
To configure WRED parameters, use the following command.
qos random-detect {green |
yellow | red } <0-7> min <0-
1000> max <0-10000>
probability <0-100>
Configures a WRED parameter values.
0-7: queue number
min: WRED min-threshold
max: WRED max-threshold
0-1000: minimum threshold to begin dropping (default:
32 cells)
0-10000: maximum threshold to drop all packets
(default: 192 cells)
1-100: drop probability (default: 5%)
qos random-detect <0-7> weight
<0-15>
Configures a WRED queue number and weight.
0-7: queue number
Start End
Queue Length
Drop
100%
Probability
 Loading...
Loading...