User Manual UMN:CLI
V5808
441
9.3.1.2 TTL Threshold
You can specify a TTL threshold for multicast packets on an interface. This configuration
is used on a border router which limits a multicast domain, since only the multicast
packets with a TTL value greater than a TTL specified on an interface are forwarded to
outgoing interfaces. If you intend the router to operate as a border router, the TTL
threshold must be a very high value.
To specify a TTL threshold for multicast packets, use the following command.
ip multicast ttl-threshold
<0-255>
Specifies a TTL threshold for multicast packets.
0-255: TTL value (default: 1)
no ip multicast ttl-threshold
Deletes a specified TTL threshold for multicast packets.
By the supported IGMP standards and RFCs, IP packet that carries an IGMP packet has
a value of 1 in its TTL field. However, the switch handles and forwards all IGMP packets
even if the IGMP packet is received with different TTL value. You can block the IGMP
packets with an IP TTL field value that is not equal to 1.
To block IGMP packets based on TTL value, use the following command.
Blocks IGMP packets with an IP TTL field value that is
not equal to 1.
Permits IGMP packets with an IP TTL field value that is
not equal to 1. (default)
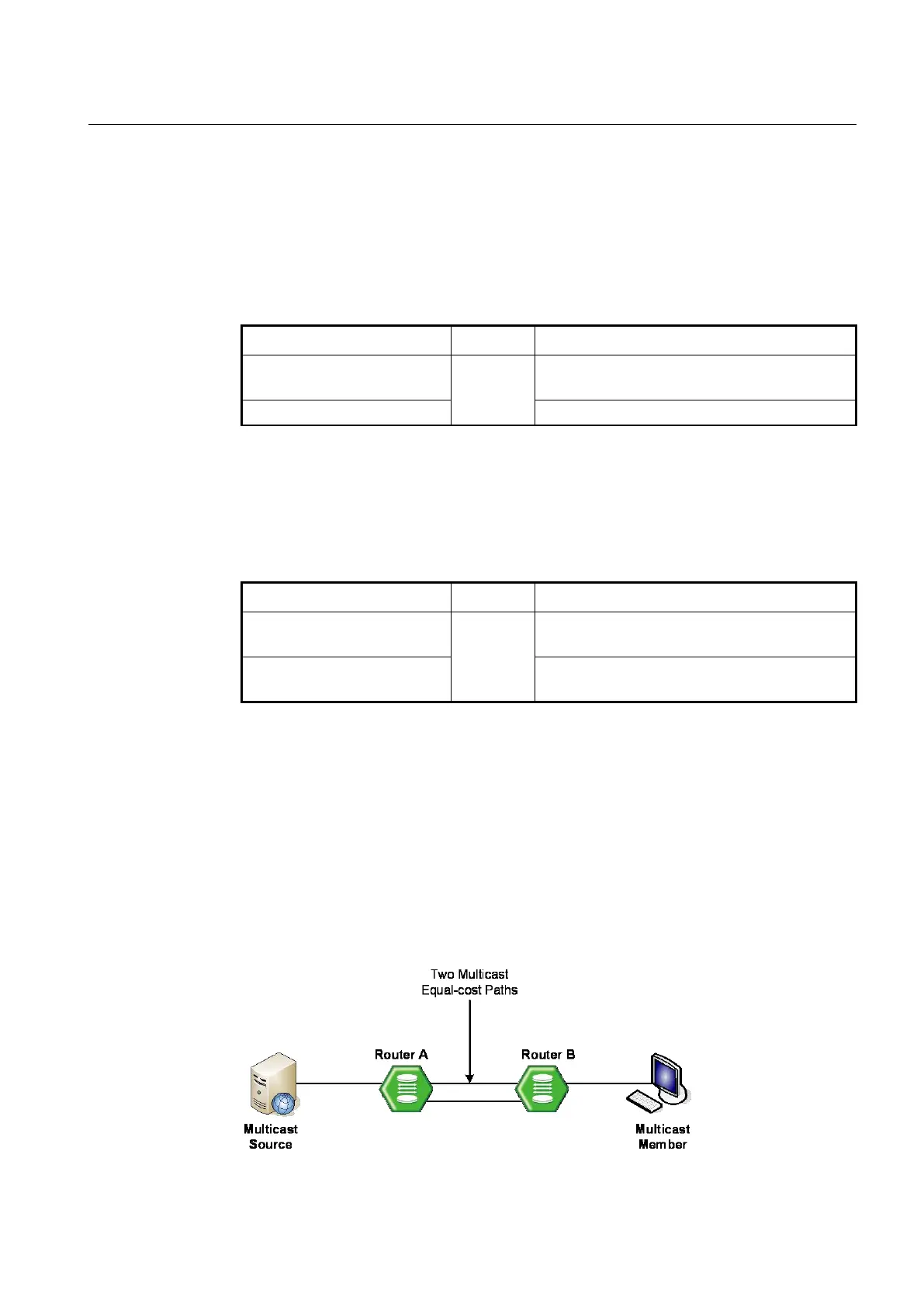
9.3.1.3 ECMP Load Splitting
Multicast routing protocols have different forwarding policies for the equal cost multipath
(ECMP). In case of PIM, the interface with highest IP address is used to forward multicast
traffic over the equal cost multipath.
The purpose of this feature is load splitting for forwarding multicast traffic over ECMP,
allowing more efficient use of network resources and preventing traffic congestion. With
this feature, multicast traffic is split across the equal cost multipath based on either its
source address or its source and group address.
Fig. 9.5 Multicast Equal Cost Multipath (ECMP)

 Loading...
Loading...