40-4
Catalyst 4500 Series Switch, Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide - Cisco IOS XE 3.9.xE and IOS 15.2(5)Ex
Chapter 40 Configuring Bidirection Forwarding Detection
Information About Bidirectional Forwarding Detection
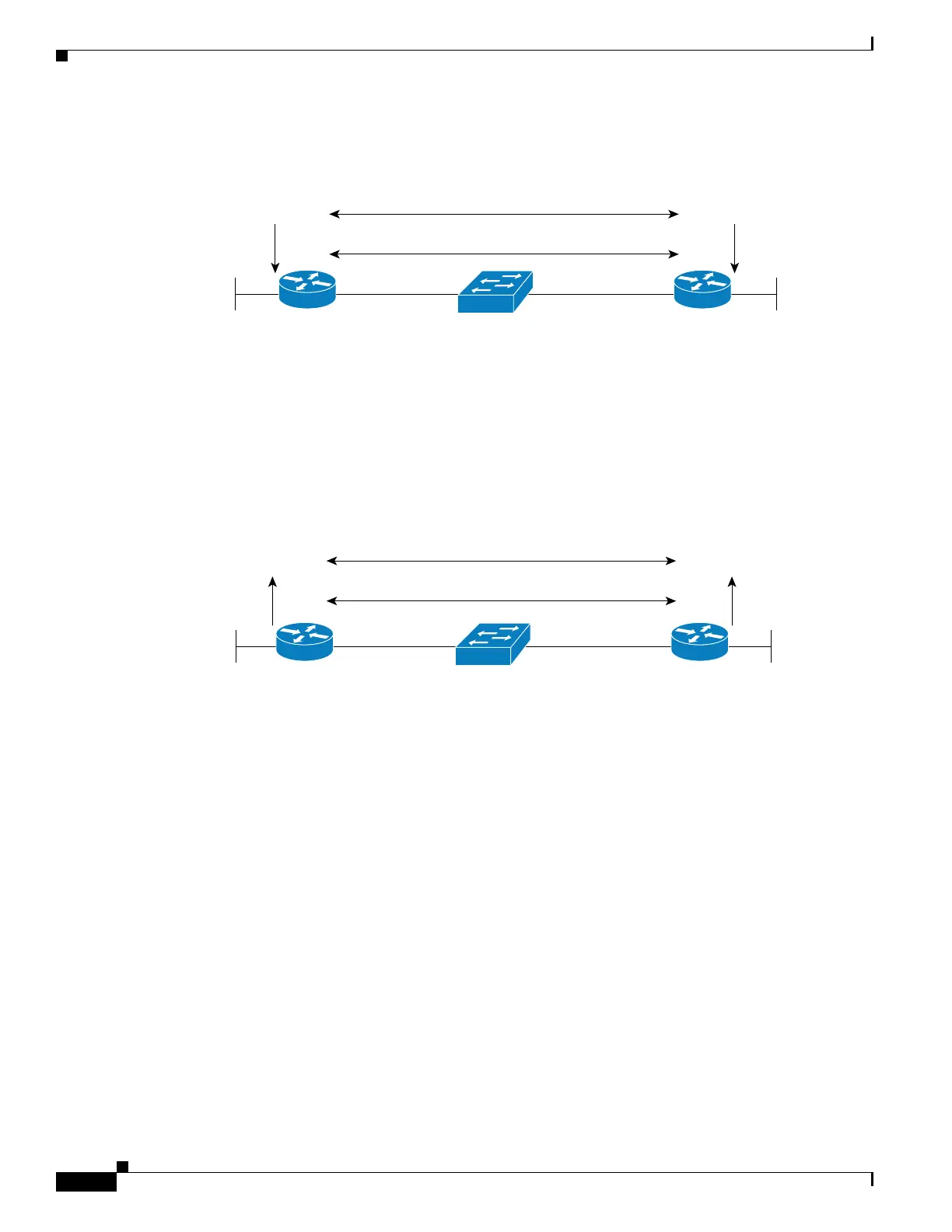
Figure 40-1 Establishing a BFD Neighbor Relationship
Figure 40-2 shows what happens when a failure occurs in the network (1). The BFD neighbor session
with the OSPF neighbor router is torn down (2). BFD notifies the local OSPF process that the BFD
neighbor is no longer reachable (3). The local OSPF process tears down the OSPF neighbor relationship
(4). If an alternative path is available, the routers will immediately start converging on it.
Figure 40-2 Tearing Down an OSPF Neighbor Relationship
A routing protocol needs to register with BFD for every neighbor it acquires. Once a neighbor is
registered, BFD initiates a session with the neighbor if a session does not already exist.
OSPF registers with BFD when:
• A neighbor finite state machine (FSM) transitions to full state.
• Both OSPF BFD and BFD are enabled.
On broadcast interfaces, OSPF establishes a BFD session only with the designated router (DR) and
backup designated router (BDR), but not between any two switches (routers) in DROTHER state.
BFD Detection of Failures
Once a BFD session has been established and timer negations are complete, BFD peers send BFD control
packets that act in the same manner as an IGP hello protocol to detect liveliness, except at a more
accelerated rate. The following information should be noted:
• BFD is a forwarding path failure detection protocol. BFD detects a failure, but the routing protocol
must take action to bypass a failed peer.
• Typically, BFD can be used at any protocol layer. However, the Cisco implementation of BFD
supports only Layer 3 clients, in particular, the BGP, EIGRP, and OSPF routing protocols, and static
routing.
172.16.10.2 172.16.10.1
172.17.0.1172.18.0.1
BFD
BFD neighbors
3
OSPF
2
BFD
OSPF
2
127844
OSPF neighbors
1
Router A Router B
172.16.10.2 172.16.10.1
172.17.0.1172.18.0.1
BFD
BFD neighbors
2
1
X
X
X
OSPF
3
BFD
Router A Router B
OSPF
3
127845
OSPF neighbors
4

 Loading...
Loading...




















