78-5
Catalyst 4500 Series Switch, Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide - Cisco IOS XE 3.9.xE and IOS 15.2(5)Ex
Chapter 78 Configuring Cisco IOS IP SLA Operations
Understanding Cisco IOS IP SLAs
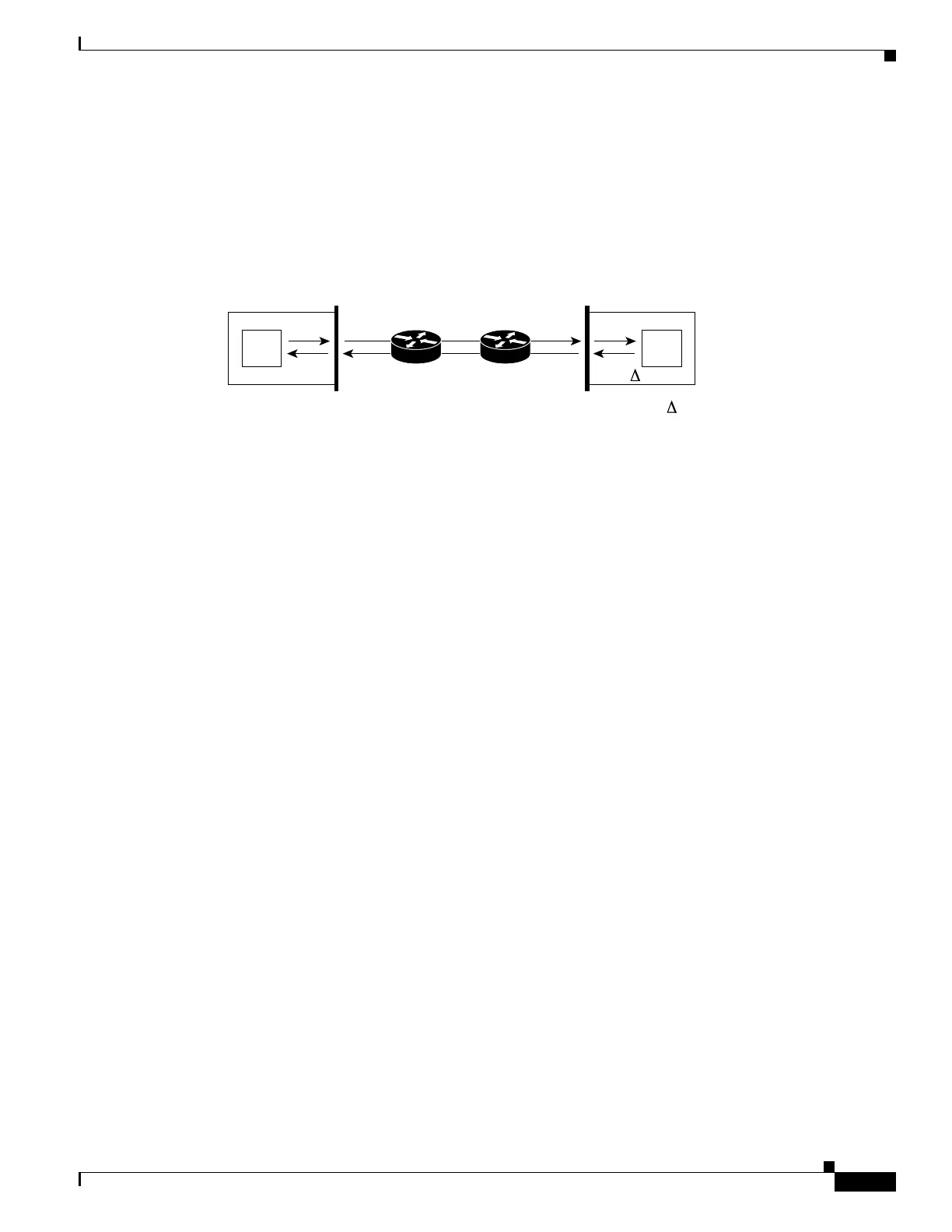
Figure 78-2 demonstrates how the responder works. Four time stamps are taken to make the calculation
for round-trip time. At the target router, with the responder functionality enabled, time stamp 2 (TS2) is
subtracted from time stamp 3 (TS3) to produce the time spent processing the test packet as represented
by delta. This delta value is then subtracted from the overall round-trip time. Notice that the same
principle is applied by IP SLAs on the source router where the incoming time stamp 4 (TS4) is also taken
at the interrupt level to allow for greater accuracy.
Figure 78-2 Cisco IOS IP SLAs Responder Time Stamping
An additional benefit of the two time stamps at the target device is the ability to track one-way delay,
jitter, and directional packet loss. Because much network behavior is asynchronous, it is critical to have
these statistics. However, to capture one-way delay measurements, you must configure both the source
router and target router with Network Time Protocol (NTP) so that the source and target are
synchronized to the same clock source. One-way jitter measurements do not require clock
synchronization.
IP SLAs Operation Scheduling
When you configure an IP SLAs operation, you must schedule the operation to begin capturing statistics
and collecting error information. You can schedule an operation to start immediately or to start at a
certain month, day, and hour. You can use the pending option to set the operation to start at a later time.
The pending option is an internal state of the operation that is visible through SNMP. The pending state
is also used when an operation is a reaction (threshold) operation waiting to be triggered. You can
schedule a single IP SLAs operation or a group of operations at one time.
You can schedule several IP SLAs operations by using a single command through the Cisco IOS CLI or
the CISCO RTTMON-MIB. Scheduling the operations to run at evenly distributed times allows you to
control the amount of IP SLAs monitoring traffic. This distribution of IP SLAs operations helps
minimize the CPU utilization and thus improves network scalability.
For more details about the IP SLAs multioperations scheduling functionality, see the “IP
SLAs—Multiple Operation Scheduling” chapter of the Cisco IOS IP SLAs Configuration Guide:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6441/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.ht
ml
IP SLAs Operation Threshold Monitoring
To support successful service level agreement monitoring, you must have mechanisms that notify you
immediately of any possible violation. IP SLAs can send SNMP traps that are triggered by events such
as these:
• Connection loss
• Timeout
121380
T1
Source router
RTT (Round-trip time) = T4 (Time stamp 4) - T1 (Time stamp 1) -
Target router
Responder
=T3-T2
T4
T2
T3

 Loading...
Loading...




















