30-7
Catalyst 4500 Series Switch, Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide - Cisco IOS XE 3.9.xE and IOS 15.2(5)Ex
Chapter 30 Configuring 802.1Q Tunneling, VLAN Mapping, and Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling
About VLAN Mapping
One way to establish translated VLAN IDs (S-VLANs) is to map customer VLANs to service-provider
VLANs (called VLAN ID translation) on trunk ports connected to a customer network. Packets entering
the port are mapped to a service provider VLAN (S-VLAN) based on the port number and the packet’s
original customer VLAN-ID (C-VLAN).
Service providers’s internal assignments might conflict with a customer’s VLAN. To isolate customer
traffic, a service provider could decide to map a specific VLAN into another one while the traffic is in
its cloud.
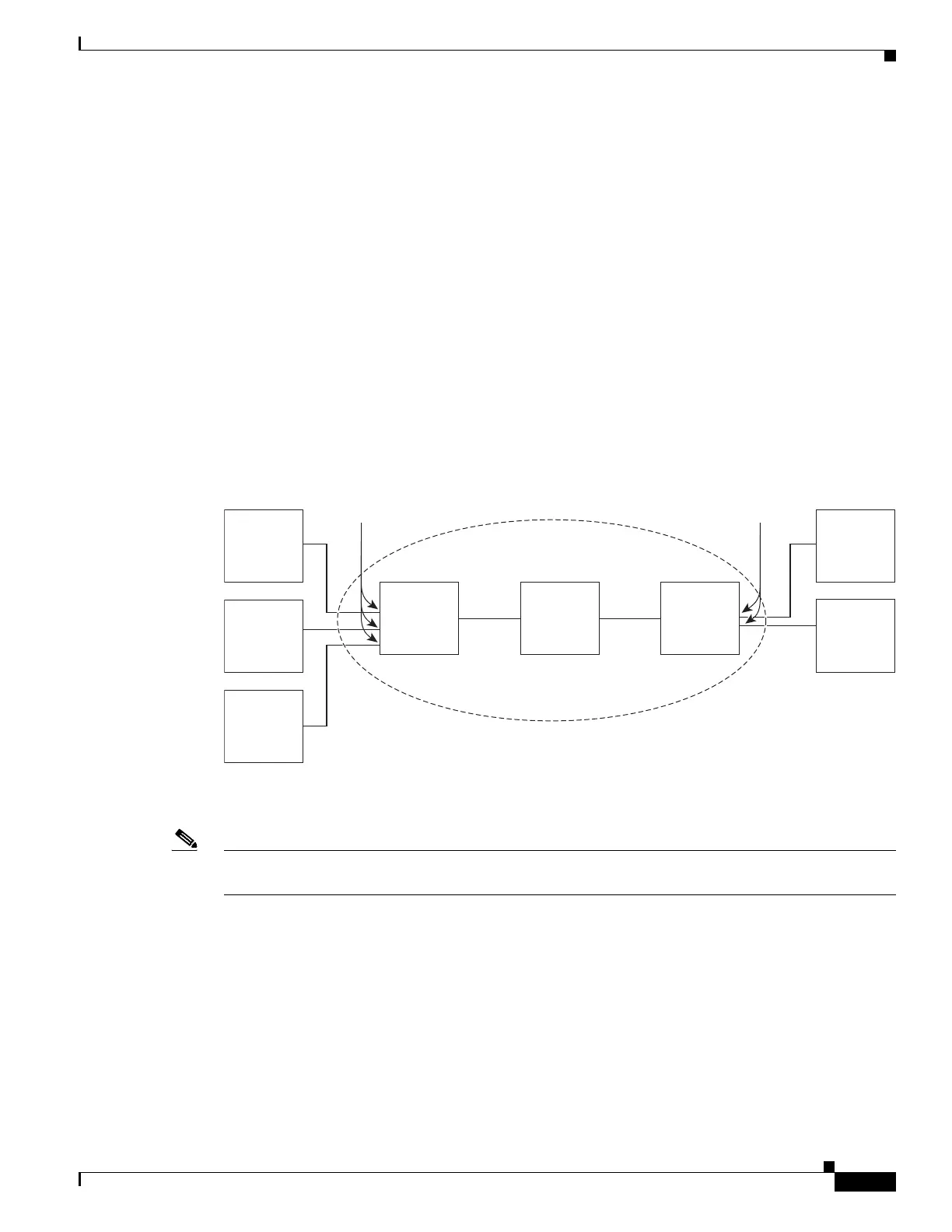
Deployment Example
In Figure 30-4, the service provider provides Layer 2 VPN service to two different customers, A and B.
The service provider separates the data and control traffic between the two customers and from the
providers’ own control traffic. The service provider network must also be transparent to the customer
edge devices.
Figure 30-4 Layer 2 VPN Deployment
All forwarding operations on the Catalyst 4500 series switch are performed using S-VLAN and not
C-VLAN information because the VLAN ID is mapped to the S-VLAN on ingress.
Note When you configure features on a port configured for VLAN mapping, you always use the S-VLAN
rather than the customer VLAN-ID (C-VLAN).
On an interface configured for VLAN mapping, the specified C-VLAN packets are mapped to the
specified S-VLAN when they enter the port. Symmetrical mapping to the customer C-VLAN occurs
when packets exit the port.
The switch supports these types of VLAN mapping on UNI trunk ports:
• One-to-one VLAN mapping occurs at the ingress and egress of the port and maps the customer
C-VLAN ID in the 802.1Q tag to the service-provider S-VLAN ID. You can also specify that packets
with all other Vlan Ids are dropped. See the “One-to-One Mapping” section on page 30-10.
Cat4K
Customer A
edge switch
Cat4K
Customer B
edge switch
Cat4K
Customer B
edge switch
Cat4K
Customer A
edge switch
Cat4K
Customer B
edge switch
SP
Cat4K
SP
Cat4K
SP
Cat4K
SP Network
VLAN translation
configured TRUNK
PORTS
VLAN translation
configured TRUNK
PORTS
278009

 Loading...
Loading...




















