23-40
Catalyst 4500 Series Switch, Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide - Cisco IOS XE 3.9.xE and IOS 15.2(5)Ex
Chapter 23 Configuring STP and MST
About Detecting Unidirectional Link Failure
Link type is point-to-point by default
PVST Simulation is enabled
BPDU: sent 132, received 1
This example shows the interface details when the PVST+ simulation feature is disabled and a PVST
Peer inconsistency has been detected on the port:
Switch# show spanning-tree interface gi3/13 detail
Port 269 (GigabitEthernet3/13) of VLAN0002 is broken (PVST Peer Inconsistent)
Port path cost 4, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.297.
Designated root has priority 32769, address 0013.5f20.01c0
Designated bridge has priority 32769, address 0013.5f20.01c0
Designated port id is 128.297, designated path cost 0
Timers: message age 0, forward delay 0, hold 0
Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1
Link type is point-to-point by default
PVST Simulation is disabled
BPDU: sent 132, received 1
About Detecting Unidirectional Link Failure
The dispute mechanism that detects unidirectional link failures is included in the IEEE 802.1D-2004
RSTP and IEEE 802.1Q-2005 MSTP standard, and requires no user configuration.
The switch checks the consistency of the port role and state in the BPDUs it receives, to detect
unidirectional link failures that could cause bridging loops. When a designated port detects a conflict, it
keeps its role, but reverts to a discarding (blocking) state because disrupting connectivity in case of
inconsistency is preferable to opening a bridging loop.
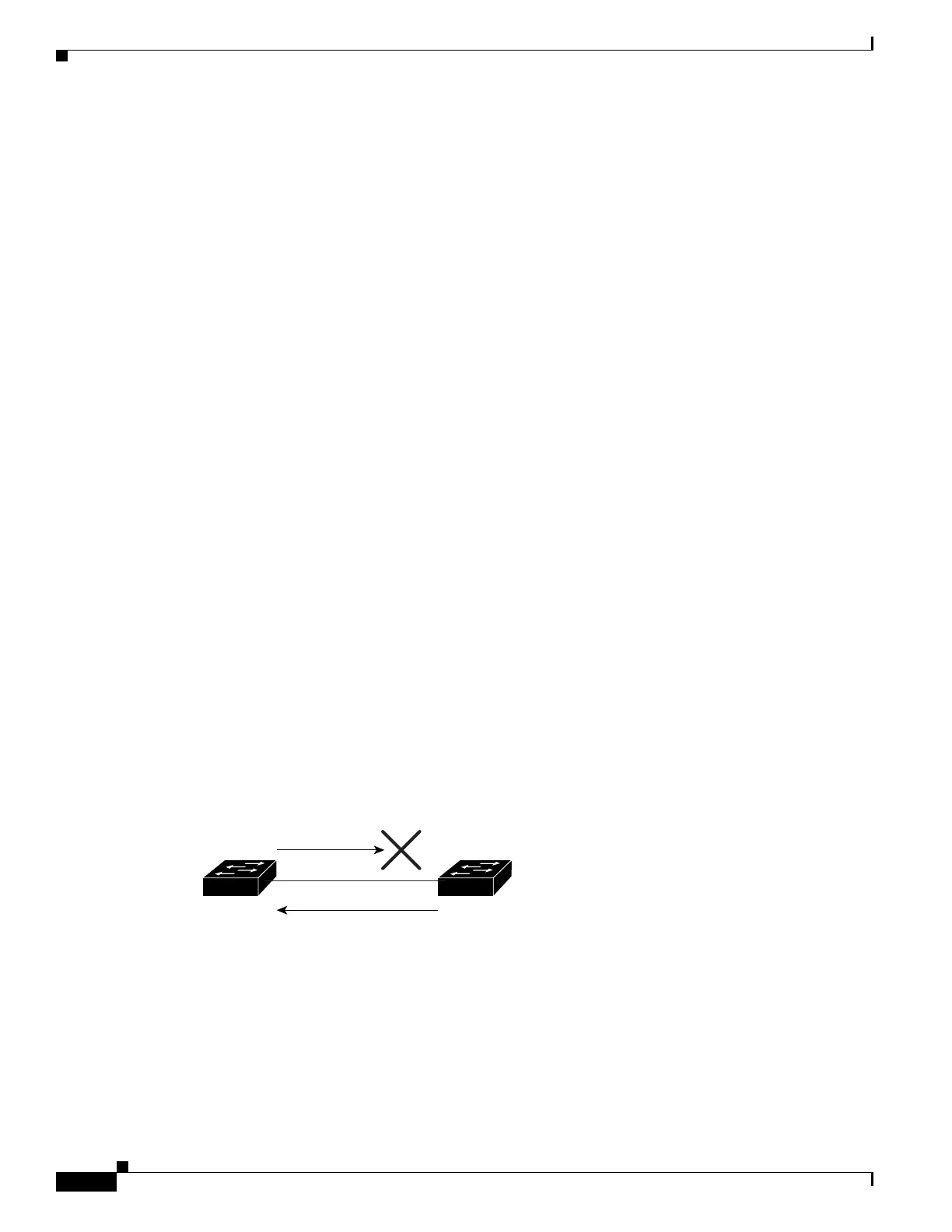
For example, in Figure 23-3, Switch A is the root bridge and Switch B is the designated port. BPDUs
from Switch A are lost on the link leading to switch B.
Since Rapid PVST+ (802.1w) and MST BPDUs include the role and state of the sending port, Switch A
detects (from the inferior BPDU), that switch B does not react to the superior BPDUs it sends, because
switch B has the role of a designated port and not the root bridge.
As a result, switch A blocks (or keeps blocking) its port, thus preventing the bridging loop.
Figure 23-3 Detecting Unidirectional Link Failure
Note these guidelines and limitations relating to the dispute mechanism:
• It works only on switches running RSTP or MST, because the dispute mechanism requires reading
the role and state of the port initiating the BPDUs.
Inferior BPDU,
Designated + Learning bit set
Superior
BPDU
Switch
A
Switch
B
92722

 Loading...
Loading...




















