66-2
Catalyst 4500 Series Switch, Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide - Cisco IOS XE 3.9.xE and IOS 15.2(5)Ex
Chapter 66 Configuring SPAN and RSPAN
About SPAN and RSPAN
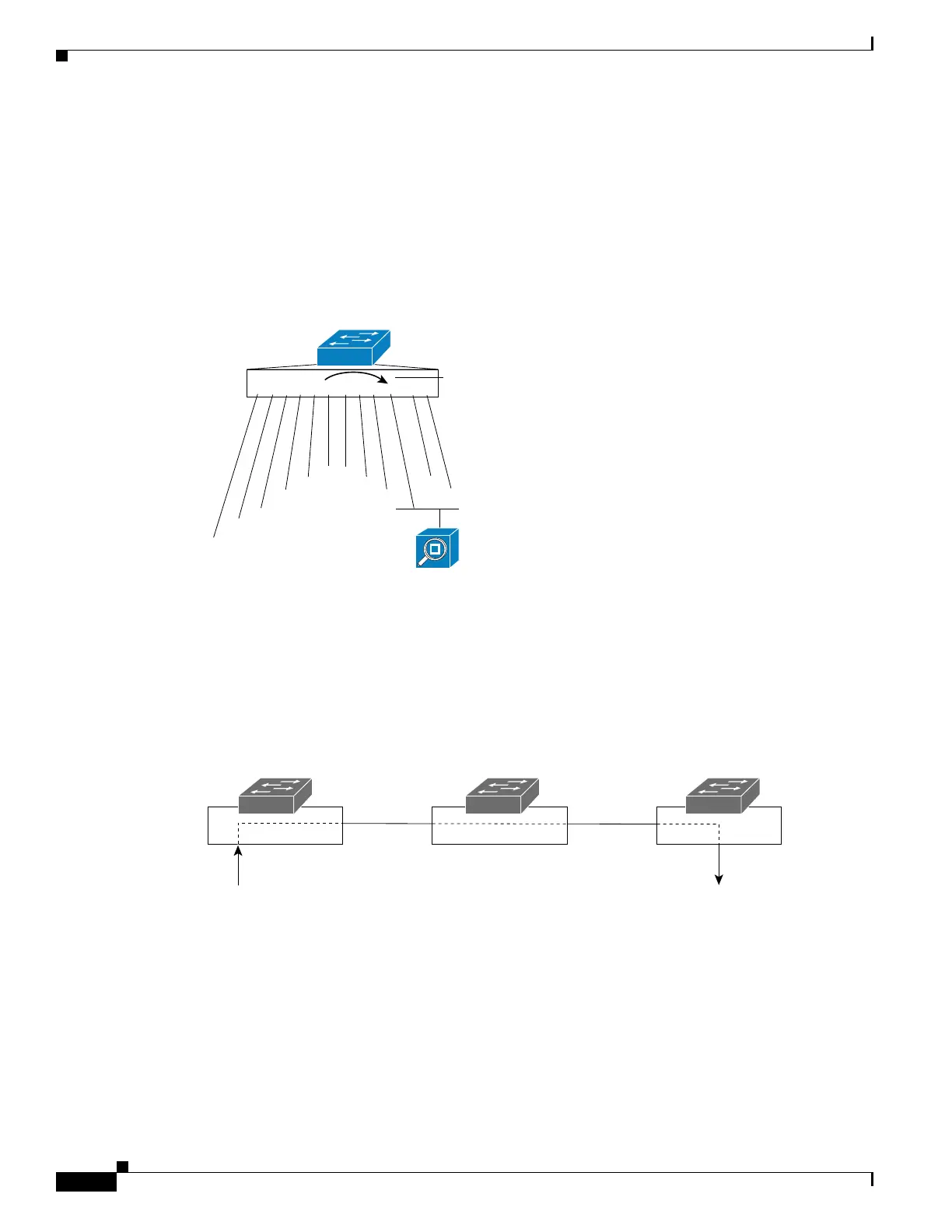
SPAN mirrors traffic from one or more source interfaces on any VLAN or from one or more VLANs to
a destination interface for analysis. In Figure 66-1, all traffic on Ethernet interface 5 (the source
interface) is mirrored to Ethernet interface 10. A network analyzer on Ethernet interface 10 receives all
network traffic from Ethernet interface 5 without being physically attached to it.
For SPAN configuration, the source interfaces and the destination interface must be on the same switch.
SPAN does not affect the switching of network traffic on source interfaces; copies of the packets received
or transmitted by the source interfaces are sent to the destination interface.
Figure 66-1 Example SPAN Configuration
RSPAN extends SPAN by enabling remote monitoring of multiple switches across your network. The
traffic for each RSPAN session is carried over a user-specified RSPAN VLAN that is dedicated for that
RSPAN session in all participating switches. The SPAN traffic from the sources is copied onto the
RSPAN VLAN and then forwarded over trunk ports that are carrying the RSPAN VLAN to any RSPAN
destination sessions monitoring the RSPAN VLAN, as shown in Figure 66-2.
Figure 66-2 Example of RSPAN Configuration
SPAN and RSPAN do not affect the switching of network traffic on source ports or source VLANs; a
copy of the packets received or sent by the sources is sent to the destination. Except for traffic that is
required for the SPAN or RSPAN session, by default, destination ports do not receive or forward traffic.
You can use the SPAN or RSPAN destination port to forward transmitted traffic from a network security
device. For example, if you connect a Cisco Intrusion Detection System (IDS) sensor appliance to a
destination port, the IDS device can send TCP reset packets to close down the TCP session of a suspected
attacker.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Port 5 traffic mirrored
on port 10
E3
E2
E1
E4
E5
E6 E7
E8
E9
E11
E12
E10
Network analyzer
S6884
Source switch Intermediate switch Destination switch
105028
RSPAN
source port
RSPAN
destination port
RSPAN
VLAN
RSPAN
VLAN

 Loading...
Loading...




















