P.3.27
Date Code 20151029 Protection Manual SEL-411L Relay
Protection Functions
87L Theory of Operation
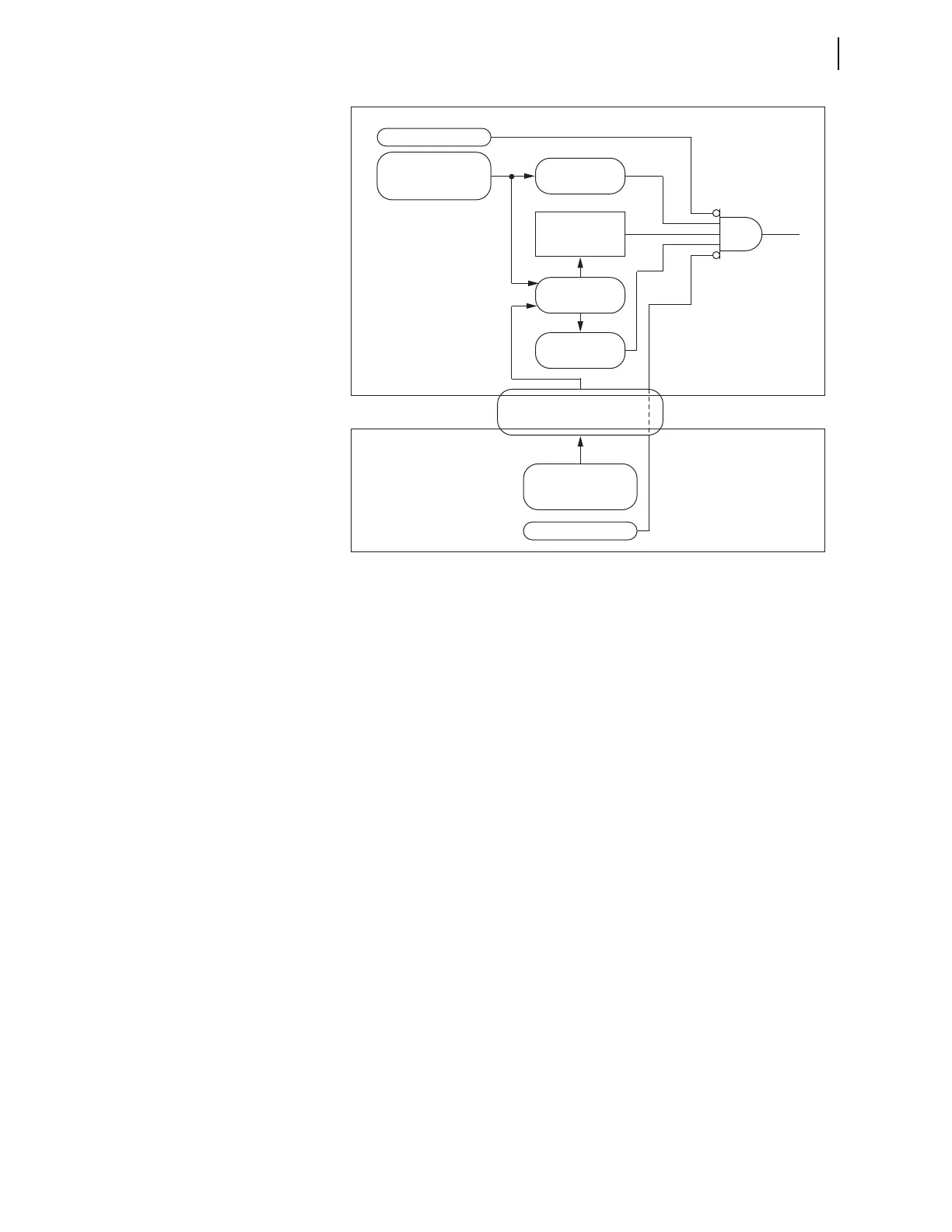
Figure 3.18 Disturbance Detection Guards Against Multiple Problems
Greatly Increasing Security
Consider the following failure modes.
➤ Undetected communications error (defeated BCH check).
Under this scenario, the 87L function and 87DTT may
spuriously pick up as a result of heavily corrupted remote data.
The disturbance detector, which responds to remote currents,
may pick up for the same reason. However, the portion of the
disturbance detection that responds to local currents and
voltages will not assert, preventing misoperation.
➤ A failure in the ac acquisition chain of the local relay (such as
an ADC problem). Under this scenario, the 87L function may
spuriously pick up because of heavily corrupted local data. The
disturbance detector, which responds to local voltages and
currents, may pick up for the same reason. However, the
portion of the disturbance detection that responds to remote
currents will not assert, preventing misoperation in the first few
milliseconds of the event. Subsequently, self-tests will assert in
the local relay and remove it from service. The disturbance
detection logic therefore provides extra time to the self-test
logic and, in combination with this logic, dramatically
improves security of the 87L scheme.
➤ A failure in the ac acquisition chain of the remote relay (such
as an ADC problem). Under this scenario, the 87L function
may spuriously pickup because of heavily corrupted remote
data. The disturbance detector, which responds to remote
currents, may pick up for the same reason. However, the
portion of the disturbance detection that responds to local
currents and voltages will not assert, preventing misoperation
in the first few milliseconds of the event. Subsequently, self-
Local Currents and
Voltages
87L Elements
Channel
Remote Currents
and Voltages
87OP
Self-Tests
Self-Tests
Disturbance
Detection (L)
Data
Alignment
Disturbance
Detection (R)
Local Relay
Remote Relay

 Loading...
Loading...