P.3.286
SEL-411L Relay Protection Manual Date Code 20151029
Protection Functions
87L Channel Synchronization Logic and Status
Time Quality
Assessment for
Usage in the 87L
Function
The relay monitors internal time quality to supervise 87L data synchronization
in the external time-based mode and other measurements related to 87L
channel monitoring for which there must be absolute time available at both
relays working over a given 87L channel.
The relay provides several time quality status bits related to application of
synchrophasors, time stamping for relay records, and general time-keeping
functionality (see Configuring High-Accuracy Timekeeping on page P.13.1).
The relay provides a separate status bit, 87TOK, to monitor time quality
specifically for the 87L function according to Alpha Plane operating
characteristic tolerance for data synchronization errors.
The 87L function uses internal relay time for data alignment. This internal
time, in turn, is phase locked to the time source connected via the IRIG-B
input. The 87TOK logic monitors the following aspects.
➤ Integrity of the IRIG-B signal in terms of type of connection
(BNC), jitter, etc.
➤ Accuracy of the time source the clock itself reports via the time
quality bits embedded in the IRIG-B signal, per IEEE 1344 and
IEEE C37.118 standards.
➤ Accuracy of the lock between the internal time and the external
time source.
➤ Possible drift of the internal clock after temporary loss of the
time source, as a function of time since loss of or inability to
use the IRIG-B signal.
Based on the previously listed factors, the relay calculates the worst-case time
error at any given time. It then applies factory-selected thresholds and timers
to assert and deassert the 87TOK Relay Word bit in response to the time error
estimate.
The 87TOK Relay Word bit asserts if the total worst-case time error is less
than about 25 microseconds for 250 ms. When asserted, the 87TOK status bit
deasserts if the worst-case error exceeds about 500 microseconds. The later
threshold corresponds to less than 10 electrical degrees at 60 Hz, or 20
degrees, if we assume the worst-case errors in opposite directions in the two
relays working over the 87L channel. We can consider this threshold secure,
given the minimum setting range of the blocking angle setting for the Alpha
Plane.
When asserted, the 87TOK bit may deassert in the following cases.
➤ The IRIG-B connection is lost or heavily impaired. In this
scenario, the relay maintains its internal clock, but it drifts
eventually from the true time if the IRIG-B connection is not
re-established. When the IRIG-B signal is locked, the relay
uses the IRIG signal to calibrate the internal time-keeping
subsystem, so drift after loss of the IRIG-B signal is limited to
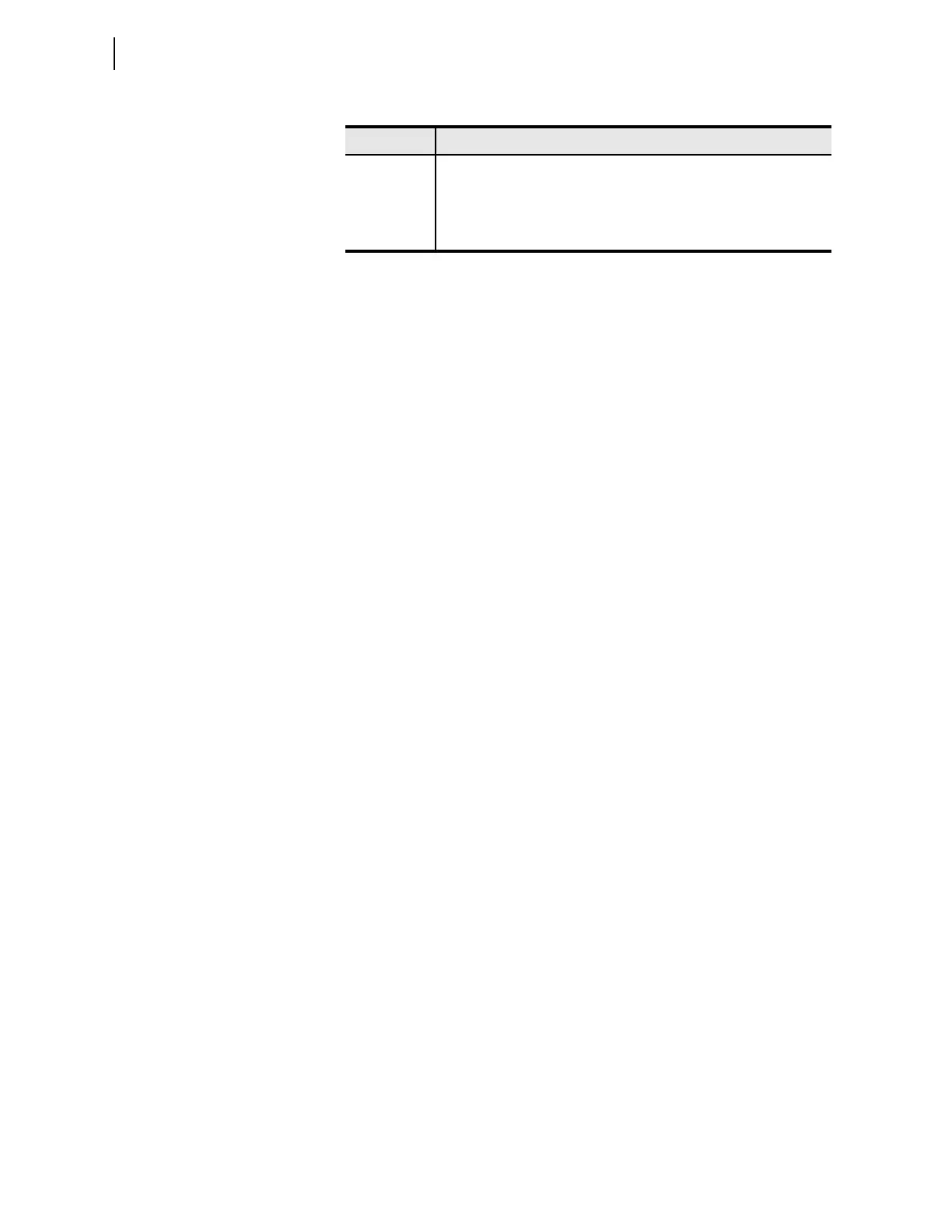
Table 3.150 Clock Offset Calculation Quality Relay Word Bits
Name Description
87CH1CL Coarse quality of clock offset measurement for the 87L serial Channel 1
87CH2CL Coarse quality of clock offset measurement for the 87L serial Channel 2
87CH1CH High precision of clock offset measurement for the 87L serial Channel 1
87CH2CH High precision of clock offset measurement for the 87L serial Channel 2
 Loading...
Loading...