P.9.21
Date Code 20151029 Protection Manual SEL-411L Relay
Monitoring and Metering
Station DC Battery System Monitor
Station DC Battery
System Monitor
Application
Not only does the station dc monitor provide a view of how much the station
dc battery voltage dips when tripping, closing, and when other dc control
functions occur, the dc monitor also alarms for undervoltage or overvoltage dc
battery conditions in five sensing regions. The following describes how to
apply the dc battery monitor to a typical 125-Vdc protection battery system
with a 48-Vdc communication equipment battery system. Adjust the values
used here to meet the specifications of your company.
Battery Voltage
When setting the station dc battery monitor, you must determine the minimum
and maximum dc levels in the battery system. In addition, you must also
establish the threshold levels for different battery system states or conditions.
The following voltage levels describe these battery system conditions:
➤ Trip/Close—the lowest dc voltage point at which circuit
breaker trip and close operations occur
➤ Open-circuit—the dc battery voltage when all cells are fully
charged and not connected to the battery charger
➤ Float low—the lowest charging voltage supplied by the battery
charger
➤ Float high—the highest charging voltage supplied by the
battery charger
➤ Equalize mode—a procedure during which the batteries are
overcharged intentionally for a pre-selected time in order to
bring all cells to a uniform output
Set the low end of the allowable dc battery system voltage according to the
recommendations of C37.90–1989 (R1994) IEEE Standard for Relays and
Relay Systems Associated with Electric Power. Section 6.4 in this standard is
titled Allowable Variation from Rated Voltage for Voltage Operated Auxiliary
Relays. This section calls for an 80 percent low-end voltage and 28, 56, 140,
or 280-Vdc high-end voltages for the popular nominal station battery voltages.
Table 9.8 lists expected battery voltages under various conditions using
commonly accepted per-cell voltages.
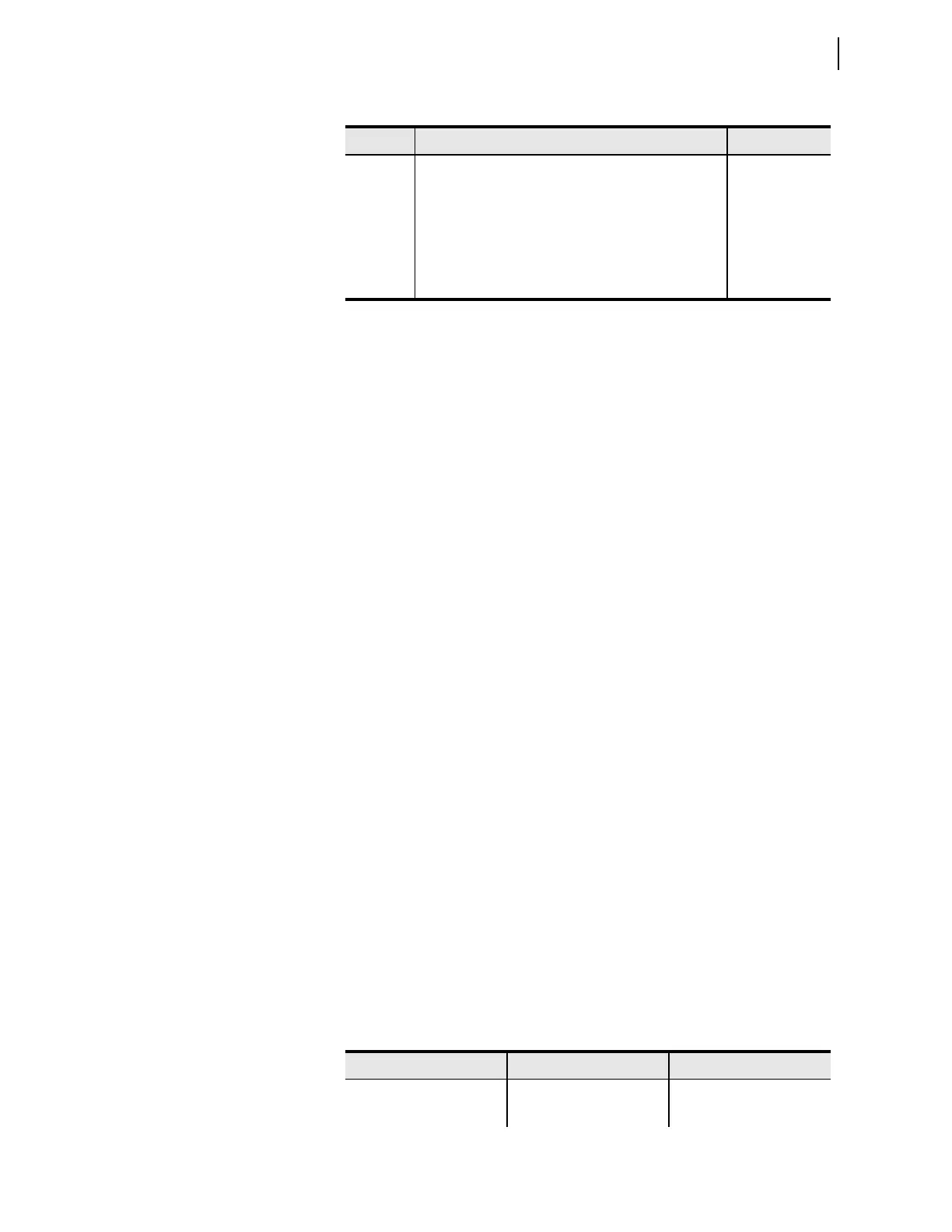
Table 9.7 DC Monitor Settings and Relay Word Bit Alarms
Setting
a
a
For DC2 Monitor Settings and Relay Word bit Alarms, substitute 2 for 1 in the setting names
and Relay Word bit names.
Definition Relay Word Bit
DC1LFP Low Level Fail Pickup (OFF, 15–300 Vdc)
b
b
Minimum setting step size is 1 V for voltage settings.
DC1F
DC1LWP Low Level Warn Pickup (OFF, 15–300 Vdc)
a
DC1W
DC1HWP High Level Warn Pickup (OFF, 15–300 Vdc)
a
DC1W
DC1HFP High Level Fail Pickup (OFF, 15–300 Vdc)
a
DC1F
DC1RP Peak to Peak AC Ripple Pickup (1–300 Vac)
a
DC1R
DC1GF Ground Detection Factor (1.00–2.00) (advanced setting) DC1G
Table 9.8 Example DC Battery Voltage Conditions (Sheet 1 of 2)
Condition Calculation Battery Voltage (Vdc)
Trip/Close 80% • 125 Vdc 100.0
Open-Circuit 60 (cells) • 2.06 (volts/cell) 123.6

 Loading...
Loading...