P.13.2
SEL-411L Relay Protection Manual Date Code 20151029
Time-Synchronized Measurements
Configuring High-Accuracy Timekeeping
NOTE: The SEL-2407 Satellite
Synchronized Clock meets both the
relay accuracy and IEEE C37.118
requirements for a high-accuracy time
source.
The IRIG-B BNC connector can be used for high-accuracy timekeeping
purposes, with up to 1 s accuracy with an appropriate time source. Either
input can be used for general-purpose timekeeping, and the relay will have up
to 500 s accuracy. See Table 13.1 for relay timekeeping mode details.
NOTE: If the time-code signal
connected to the BNC connector
degrades in quality, the relay will not
switch-over to the IRIG-B pins of Serial
Port 1. The relay will only switch to
Serial Port 1 if the signal on the BNC
connector completely fails (e.g. the
cable is unplugged).
Only one IRIG-B time source can be used by the relay, and the signal
connected to the IRIG-B BNC connector (shown in Figure 13.1) takes priority
over the Serial Port 1 IRIG-B pins. If a signal is detected on the IRIG-B BNC
input, the IRIG-B pins of Serial Port 1 will be ignored.
The relay determines the suitability of the IRIG-B signal connected to the
BNC connector for high-accuracy timekeeping by applying two tests:
➤ Measuring whether the jitter between positive-transitions
(rising edges) of the clock signal is less than 500 ns.
➤ Decoding the time-error information contained in the IRIG-B
control field and determining that analog quantity TQUAL is
less than 10
-6
seconds (1 µs).
The relay will assert Relay Word bit TSOK only when these two tests are met,
indicating HIRIG mode. The TQUAL analog quantity can be viewed with the
MET PM command, and is shown beside the label.
Time Quality Maximum time synchronization error:. See Figure 6.8 for a
sample.
The IRIG-B control field is defined in the IEEE C37.118 standard. The relay
places the raw time quality information in Relay Word bits TQUAL1,
TQUAL2, TQUAL4, and TQUAL8; and the decoded maximum clock error in
analog quantity TQUAL, in seconds.
If the clock signal is determined to be of low quality, with more than 500 ns of
jitter, the relay will not assert the TSOK Relay Word bit.
Connecting
High-Accuracy
Timekeeping
The procedure in the following steps assumes that you have a modern high-
accuracy GPS receiver with a BNC connector output for an IRIG-B signal.
Use a communications terminal to send commands and receive data from the
relay (see Making an EIA-232 Serial Port Connection on page P.10.5).
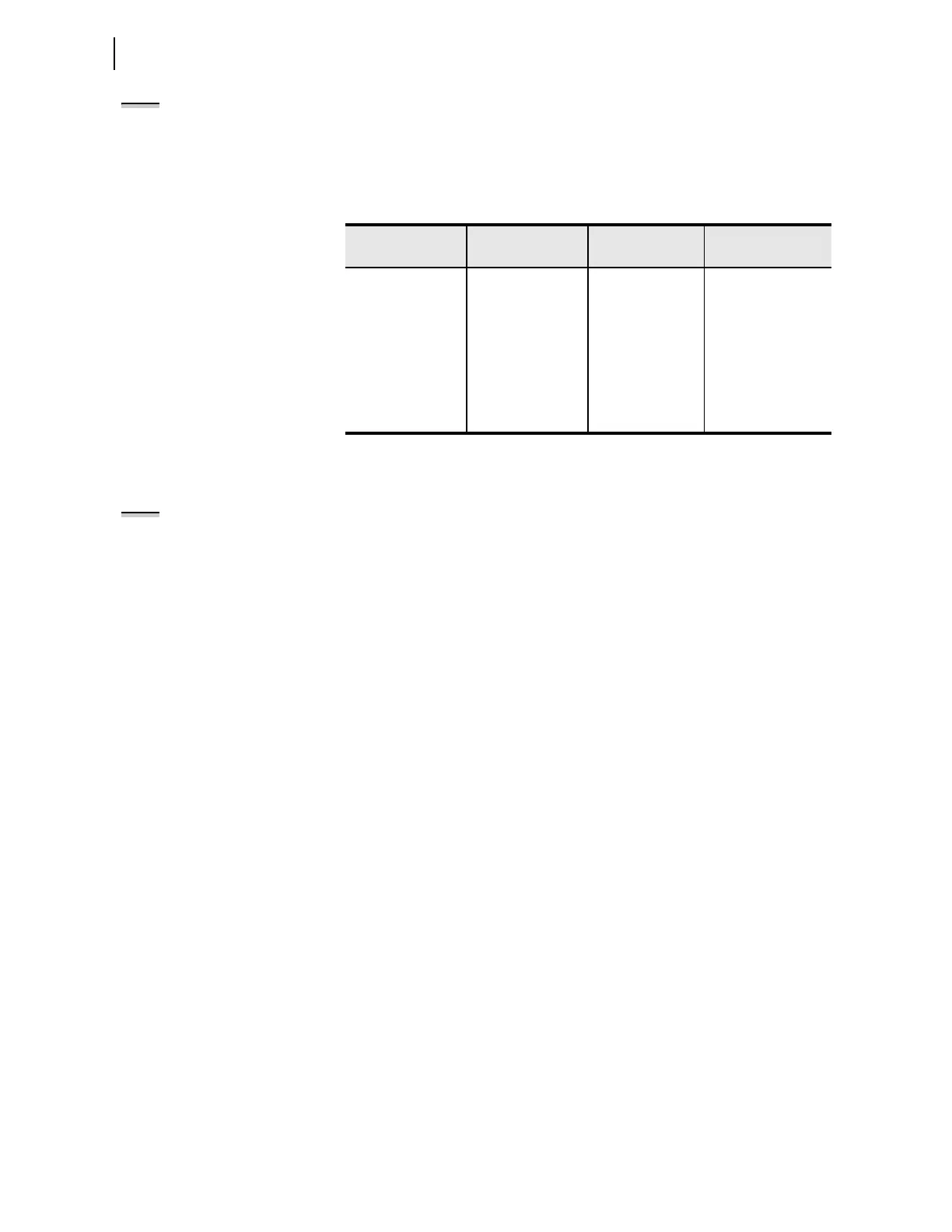
Table 13.1 Relay Timekeeping Modes
Item Internal Clock IRIG
HIRIG (or High-
Accuracy IRIG)
Best accuracy
(condition)
Depends on last
method of setting,
or synchronization
a
a
The internal clock in the relay can be synchronized via SNTP, DNP3, Ethernet card, SEL-2030
Communications Processor, or M
IRRORED BITS communications.
500 µs (when time
source jitter is less
than 3 ms)
1 µs (when time source
jitter is less than 500
ns, and time-error is
less than 1 µs)
b
b
The time source must include the IEEE C37.118 IRIG-B control bit assignments to provide the
Time Error estimate for the clock.
IRIG-B Connection
Required
None BNC connector
(preferred), or
Serial Port 1
BNC connector
(preferred), or
Serial Port 1
Relay Word bits TIRIG = logical 0
TSOK = logical 0
TIRIG = logical 1
TSOK = logical 0
TIRIG = logical 1
TSOK = logical 1
 Loading...
Loading...