P.9.32
SEL-411L Relay Protection Manual Date Code 20151029
Monitoring and Metering
Metering
The factory default setting for SELOGIC control equation FAULT includes
specific time-overcurrent and distance elements pickups: FAULT := 50P1 OR
51S01 OR Z2P OR Z2G OR Z3P OR Z3G.
In addition, the relay also suspends demand metering during the time that
Relay Word Bit DFAULT is asserted.
Demand Metering
Economic operation of the power system involves the proper allocation of the
load demand among the available generating units. By knowing the demand
requirements at different points in the system and at different times of the day
you can optimize your system generation resources or your consumption of
electric power. The relay provides you this demand information and enables
you to operate your power system with an effective economic strategy.
Demand metering and peak demand metering are available only for the LINE
quantities. The relay uses longer-term accumulations of the metering
quantities for reliable demand data. Table 9.18 lists the quantities used for
demand and peak demand metering.
)
Thermal Demand and Rolling Demand
Two methods exist for measuring power system current and power demand.
These methods are thermal demand metering and rolling demand metering.
Figure 9.17 and Figure 9.18 illustrate the step input response of the two
demand measuring methods with setting DMTC (demand meter time
constant) at 15 minutes.
Thermal Demand
Thermal demand is a continuous exponentially increasing or decreasing
accumulation of metered quantities. Thermal demand measurement is similar
to parallel RC network integration. Thermal demand metering response is at
90 percent (0.9 per unit) of the full applied value after a period equal to the
DMTC setting (15 minutes in Figure 9.17).
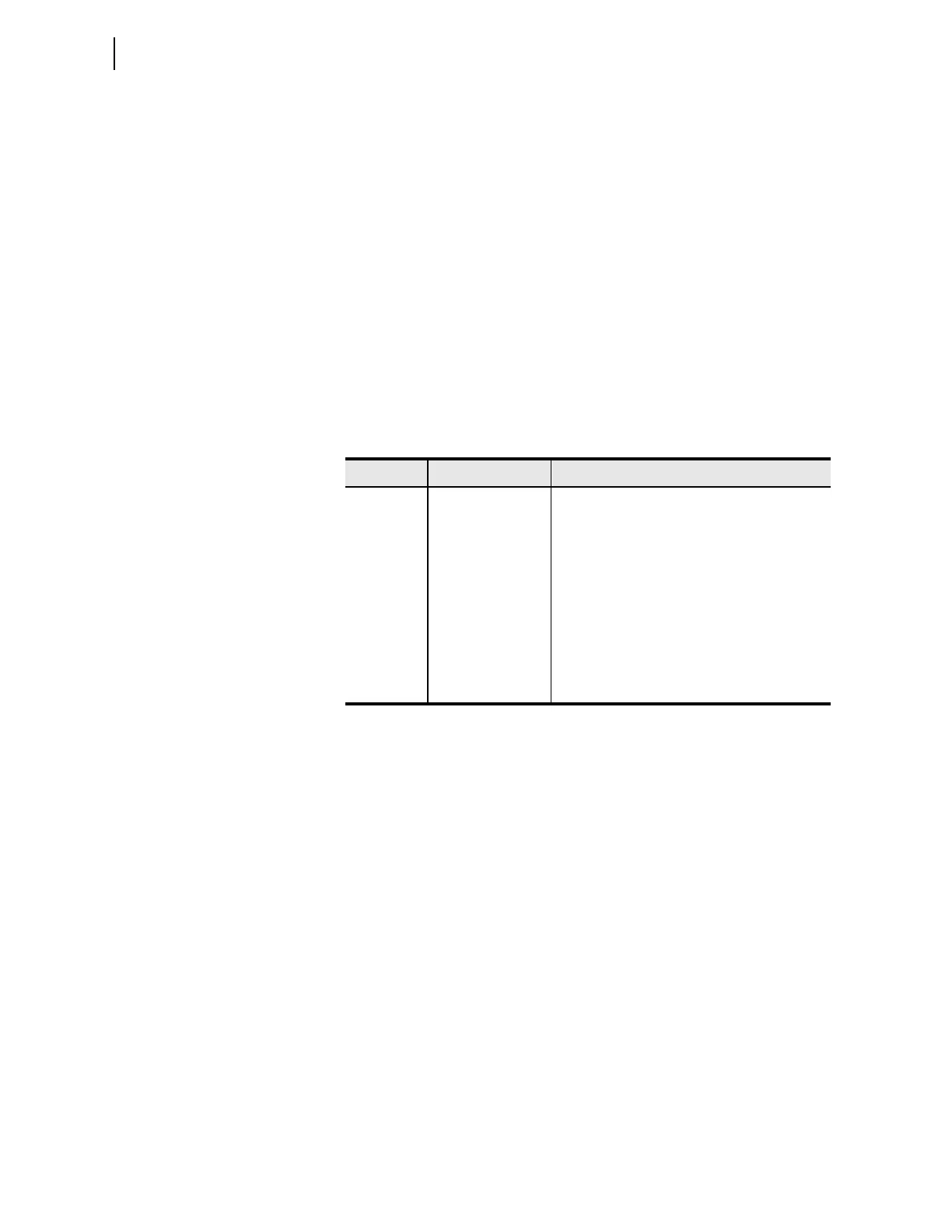
Table 9.18 Demand and Peak Demand Metering Quantities—(LINE)
a
a
(I
G
= 3I
0
= I
A
+ I
B
+ I
C
).
Symbol Units Description
I
rms
A, primary Input rms currents
I
Grms
A, primary Residual ground rms current
3I
2
A, primary Negative-sequence current
P
MW, primary Single-phase real powers (with harmonics)
Q
MVAR, primary Single-phase reactive powers
U
MVA, primary Single-phase total powers (with harmonics)
3P MW, primary Three-phase real power (with harmonics)
3Q MVAR, primary Three-phase reactive power
3U MVA, primary Three-phase total power (with harmonics)
 Loading...
Loading...