P.3.172
SEL-411L Relay Protection Manual Date Code 20151029
Protection Functions
Out-of-Step Logic (Zero Settings)
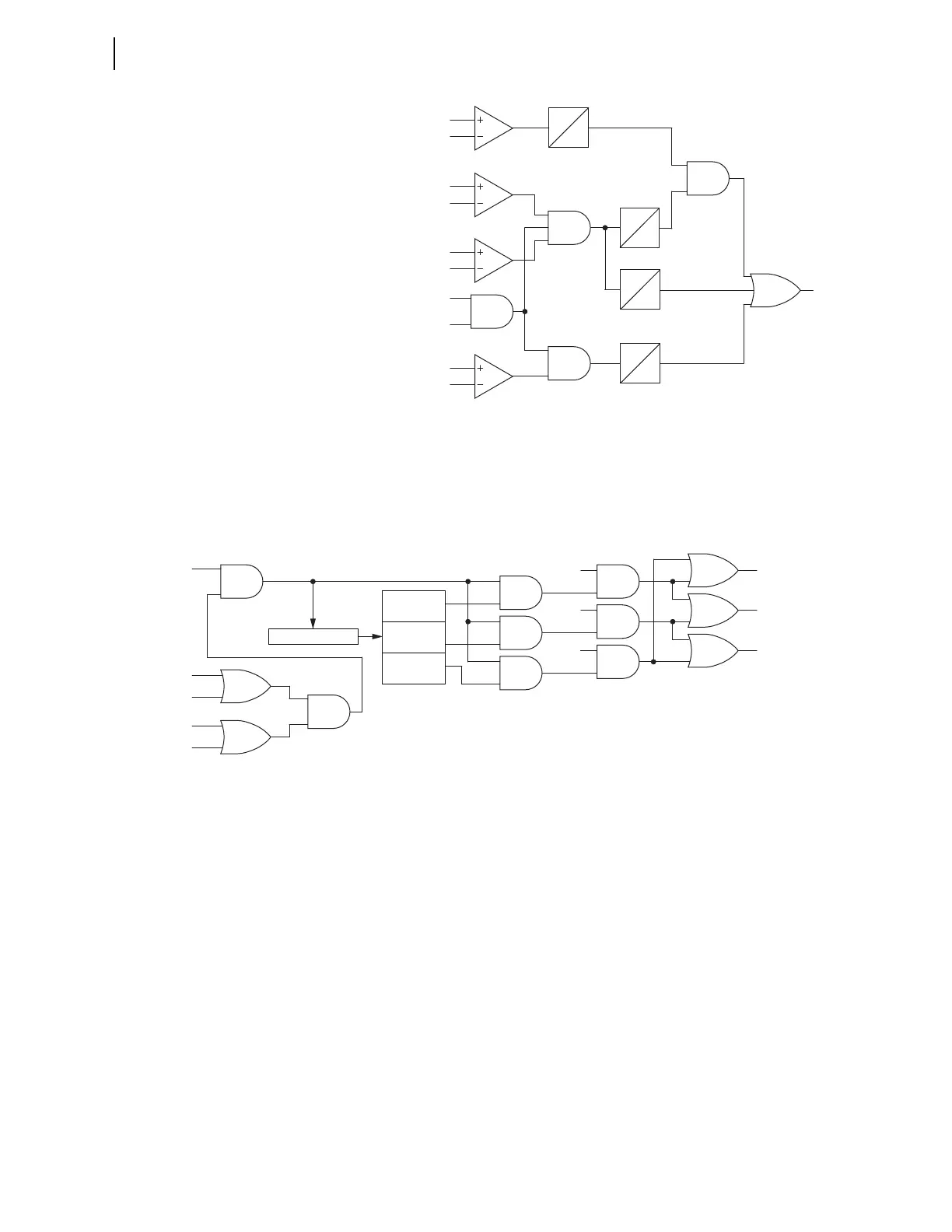
Figure 3.111 Logic Diagram of the Three-Phase Fault Detector
Detection of Ground
Faults During a Pole
Open
Regarding the ground-distance elements supervision, if the pole open OOS
logic (OSBA, OSBB, OSBC, see Figure 3.105) is deasserted, AND 4 turns
off. When AND 4 turns off, the ground-distance elements cannot cause the
swing signature detector to assert. Figure 3.112 shows the pole open logic that
blocks the ground-distance elements during a power swing condition.
Figure 3.112 Pole Open OOS Blocking Logic
If a power swing occurs during an open-pole condition, the power swing as
seen by the relay is no longer balanced. The open-pole OOS blocking logic
determines which phase is open so that the relay can correctly identify faults
that may occur on the closed phases during the power swing. To identify the
open phase, the relay calculates the angle of the ratio of the zero-sequence
current and the negative-sequence currents. If the angular relationship
indicates a fault, the logic in Figure 3.105 turns off AND 4, thus preventing
the swing signature detection (SSD) from asserting. When SSD is deasserted,
the distance elements can clear the fault.
For example, if the A-phase is open, the angle of the ratio normally lies
between –60 and +60 degrees. If a fault now occurs on B-phase or C-phase (or
both), this angular relationship is no longer true. In Figure 3.112, OSBA
asserts if either B-phase or C-phase is open, and no fault is present. If a fault
occurs on B-phase or C-phase (or both), OSBA deasserts because the angular
relationship indicates a fault.
| d2SCV1_UF |
0.23
max{0.1, cos(Z1ANG)}
| SCV1 |
| dSCV1_S |
0.01
OSB_I
R1T
| dSCV1_S |
max{0.1, cos(Z1ANG)}
0
CYC
6
CYC
2
CYC
0
CYC
20
CYC
0
CYC
5
CYC
0
CYC
DTF
SPO
SPOA
AND 3
AND 1
AND 2
OR 1
OR 2
AND 4
AND 5
AND 6
AND 7
AND 8
SPOB
SPOC
3IOLFA — 3IA2LFA
50QR
50QF
OSBB
OSBC
OSBA
ENABLE
50GR
50GF
OR 3
OR 4
OR 5
—60 to 60
60 to 180
—60 to —180

 Loading...
Loading...