P.11.20
SEL-411L Relay Protection Manual Date Code 20151029
Testing and Troubleshooting
Checking Relay Operation
An ac connection check uses relay metering to verify that the relay current and
voltage inputs are the proper magnitude and phase rotation.
Commissioning tests help you verify that you have properly connected the
relay to the power system and all auxiliary equipment. These tests confirm
proper connection of control inputs and control outputs as well (see Operating
the Relay Inputs and Outputs on page P.10.21).
Brief functional tests and element verification confirm correct internal relay
processing.
Selected Element
Tests
This subsection discusses tests of the following relay elements:
➤ Alpha Plane 87L element: 87LP, 87LQ, 87LG (multi terminal
and single terminal)
➤ Loopback testing
➤ Overcurrent element: negative-sequence instantaneous, 50Q1
➤ Directional element: negative-sequence portion, F32Q/R32Q,
of the phase directional element, F32P/R32P
Alpha Plane 87L
Element
Refer to Test Precautions prior to testing.
Prior to testing the element, execute the COM 87L command to confirm that
the differential element is not disabled or otherwise unavailable. See
Table 3.164 for a list of items that will block the differential element.
Scaling of Currents
The currents feeding the differential elements are represented internally in
per-unit values with reference to the CT with the highest primary value.
See Scaling of 87L Currents and Tap Calculations on page P.3.19. For
example, consider a two terminal system with a breaker-and-a-half system at
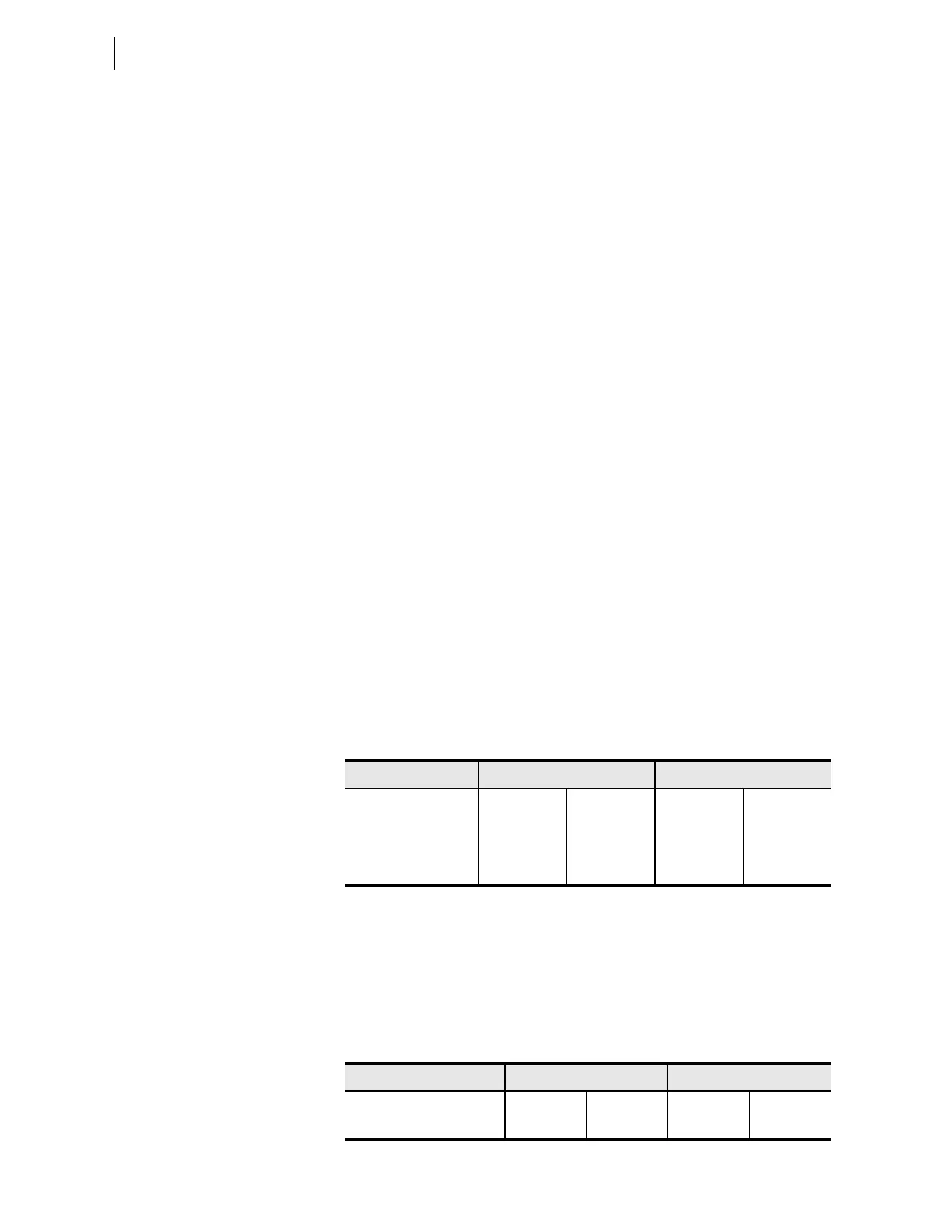
each end, and the CT ratios shown in Table 11.8.
For this example, the highest primary value is the W input of Relay 1.
Therefore, 1200 is the “Maximum CT Primary” to be used in the tap
calculations. For Relay 1, the CT ratio of the X input is 1000/5 = 200 and the
“CT ratio” of the W input is 1200/5 = 240. The tap value (Maximum CT
primary/CT ratio) for the X input is 1200/200 = 6. Therefore, a secondary
current of 6 A injected into the X input results in 1 pu current within the relay.
Table 11.9 shows the tap values of the four terminals in the example.
Table 11.8 CT Ratios for the W and X Current Inputs of Relay 1 and Relay 2
Relay 1 2
Input W X W X
CT Primary 1200 1000 1000 1100
CT Secondary5511
CT Ratio 240 200 1000 1100
Table 11.9 Tap Values of the Four Terminals
Relay 1 2
Input W X W X
Tap 561.21.1
 Loading...
Loading...