P.3.154
SEL-411L Relay Protection Manual Date Code 20151029
Protection Functions
Directionality
Directionality
Zone 1 and Zone 2 distance element directions are fixed in the forward
direction. You can select the other distance protection zones (Zone 3, Zone 4,
and Zone 5) independently as forward-looking (F), or reverse-looking (R)
with settings DIR3, DIR4, and DIR5.
Level 1 and Level 2 directional overcurrent element directions are fixed in the
forward direction for residual ground and negative-sequence directional
overcurrent elements. Level 3 and Level 4 residual and negative-sequence
directional overcurrent elements (67Q3, 67Q4, 67G3, and 67G4) share the
same direction as the corresponding zones of distance protection, also using
settings DIR3 and DIR4.
This directional control option is performed in addition to the regular torque
control settings for each element (the torque control setting acts as a
supervisory input).
The phase directional overcurrent elements (67P1–67P4) and the selectable
operating quantity time-overcurrent elements (51001–51010) do not have any
built-in directional control. The torque control settings (67P1TC, 67P2TC,
67P3TC, 67P4TC, 51TC01, 51TC02, 51TC03) can be used to achieve
directional control.
.
CVT Transient Detection
The relay detects CVT (capacitor voltage transformer) transients that can
cause Zone 1 distance elements to overreach during external faults. If CVT
transient blocking is enabled and the relay detects a high SIR (source-to-
impedance ratio) when a Zone 1 distance element is picked up, the relay
delays tripping for as long as 1.5 cycles to allow the CVT transients to
stabilize.
You do not need to enter settings. The relay adapts automatically to different
system SIR conditions by monitoring the measured voltage and current.
If the distance calculation does not change significantly (i.e., is smooth), the
relay unblocks CVT transient blocking resulting from low voltage and low
current during close-in faults driven by a source with a high SIR. Therefore,
Zone 1 distance elements operate without significant delay for close-in faults.
Consider using CVT transient detection logic when you have either of the
following two conditions:
➤ SIR greater than or equal to five
➤ CVTs with AFSC (active ferroresonance-suppression circuits)
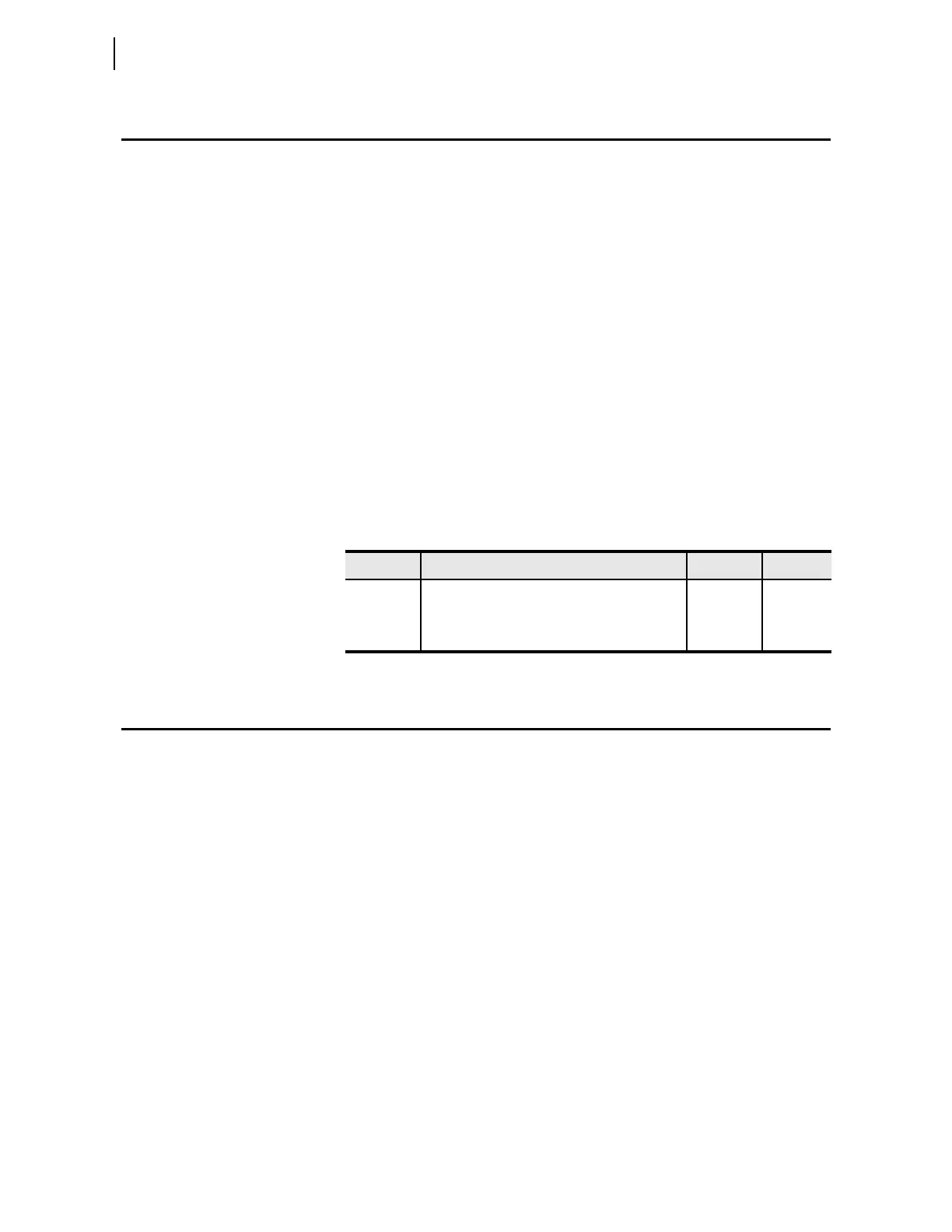
Table 3.81 Zone Directional Settings
Setting Description Range Default
DIR3 Zone/Level 3 directional control F, R R
DIR4 Zone/Level 4 directional control F, R F
DIR5 Zone/Level 5 directional control F, R F

 Loading...
Loading...