P.9.27
Date Code 20151029 Protection Manual SEL-411L Relay
Monitoring and Metering
Metering
Power
Table 9.14 shows the power quantities that the relay measures. The
instantaneous power measurements are derived from 10-cycle averages that
the relay reports by using the generator condition of the positive power flow
convention; for example, real and reactive power flowing out (export) is
positive, and real and reactive power flowing in (import) is negative (see
Figure 9.15).
For power factor, LAG and LEAD refer to whether the current lags or leads
the applied voltage. The reactive power Q is positive when the voltage angle is
greater than the current angle (
V
>
I )
, which is the case for inductive loads
where the current lags the applied voltage. Conversely, Q is negative when the
voltage angle is less than the current angle (
V
<
I )
; this is when the current
leads the voltage, as in the case of capacitive loads.
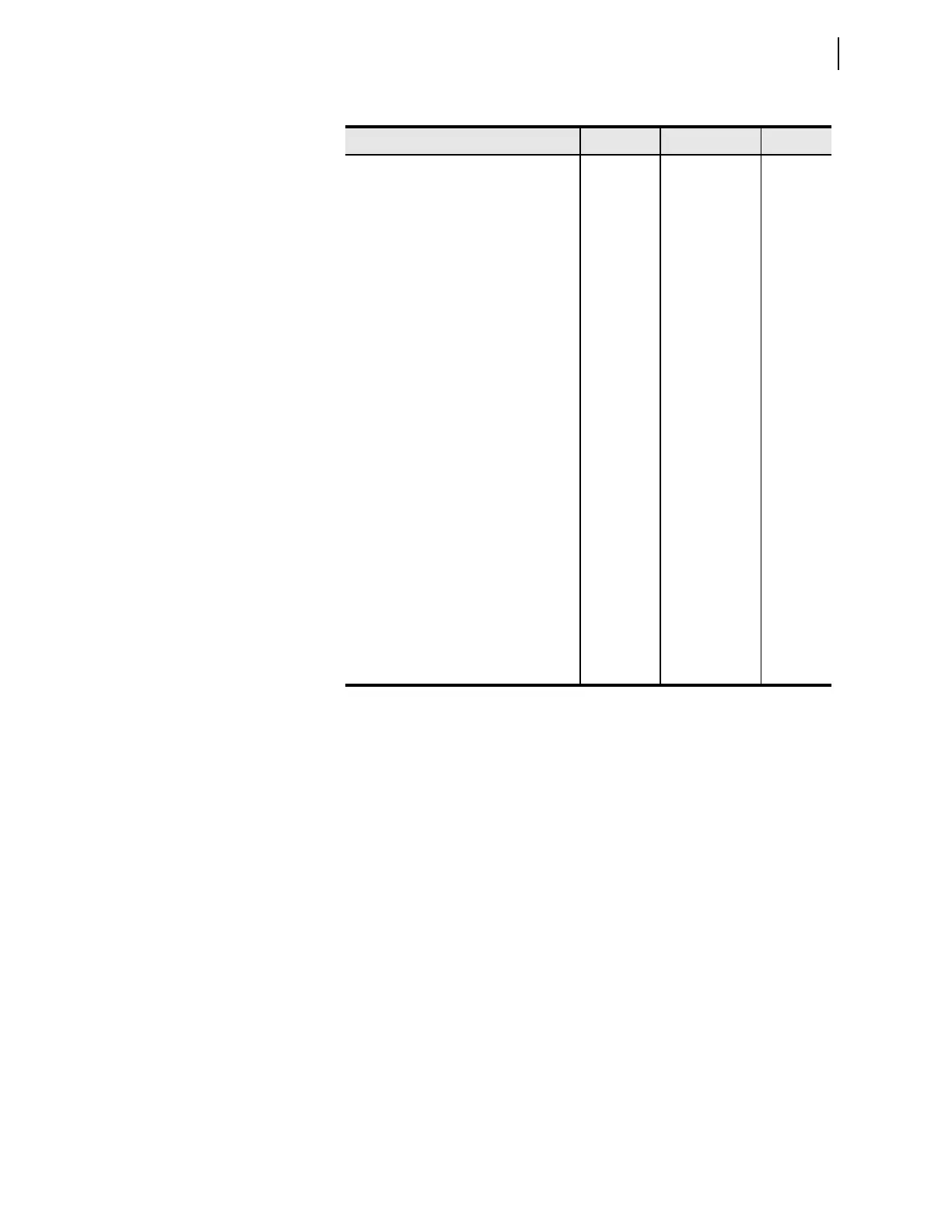
Table 9.13 Instantaneous Metering Quantities—Voltages, Currents, Frequency
Metered Quantity Symbol Fundamental RMS
Phase voltage magnitude
a
a
=A, B, C.
|V
|XX
Phase voltage angle (V
)X
Phase current magnitude |I
|XX
Phase current angle (I
)X
Phase-to-phase voltage magnitude |V
|X X
Phase-to-phase voltage angle (V
)X
Positive-sequence voltage magnitude |V
1
|X
Positive-sequence voltage angle (V
1
)X
Negative-sequence voltage magnitude |3V
2
|X
Negative-sequence voltage angle (3V
2
)X
Zero-sequence voltage magnitude |3V
0
|X
Zero-sequence voltage angle (3V
0
)X
Positive-sequence current magnitude |I
1
|X
Positive-sequence current angle (I
1
)X
Negative-sequence current magnitude |3I
2
|X
Negative-sequence current angle (3I
2
)X
Zero-sequence current magnitude |3I
0
|X
Zero-sequence current angle (3I
0
)X
Battery voltages Vdc X
Frequency f X X
Circuit breaker current magnitudes |I
|XX
Circuit breaker current angles (I
)X

 Loading...
Loading...