Firewall (FW) RM0367
134/1043 RM0367 Rev 7
The Volatile data segment is a bit different from the two others. The segment can be:
• Shared (VDS bit in the register)
It means that the area and the data located into this segment can be shared between
the protected code and the user code executed in a non-protected area. The access is
allowed whether the Firewall is opened or closed or disabled.
The VDS bit gets priority over the VDE bit, this last bit value being ignored in such a
case. It means that the Volatile data segment can execute parts of code located there
without any need to open the Firewall before executing the code.
• Execute
The VDE bit is considered as soon as the VDS bit = 0 in the FW_CR register. If the
VDS bit = 1, refer to the description above on the Volatile data segment sharing. If VDS
= 0 and VDE = 1, the Volatile data segment is executable. To avoid a system reset
generation from the Firewall, the “call gate” sequence should be applied on the Volatile
data segment to open the Firewall as an entry point for the code execution.
Segments properties
Each segment has a specific length register to define the segment size to be protected by
the Firewall: CSL register for the Code segment length register, NVDSL for the Non-volatile
data segment length register, and VDSL register for the Volatile data segment length
register. Granularity and area ranges for each of the segments are presented in Table 29.
5.3.5 Firewall initialization
The initialization phase should take place at the beginning of the user code execution (refer
to the Write protection).
The initialization phase consists of setting up the addresses and the lengths of each
segment which needs to be protected by the Firewall. It must be done before enabling the
Firewall, because the enabling bit can be written once. Thus, when the Firewall is enabled, it
cannot be disabled anymore until the next system reset.
Once the Firewall is enabled, the accesses to the address and length segments are no
longer possible. All write attempts are discarded.
A segment defined with a length equal to 0 is not considered as protected by the Firewall.
As a consequence, there is no reset generation from the Firewall when an access to the
base address of this segment is performed.
After a reset, the Firewall is disabled by default (FWDIS bit in the SYSCFG register is set). It
has to be cleared to enable the Firewall feature.
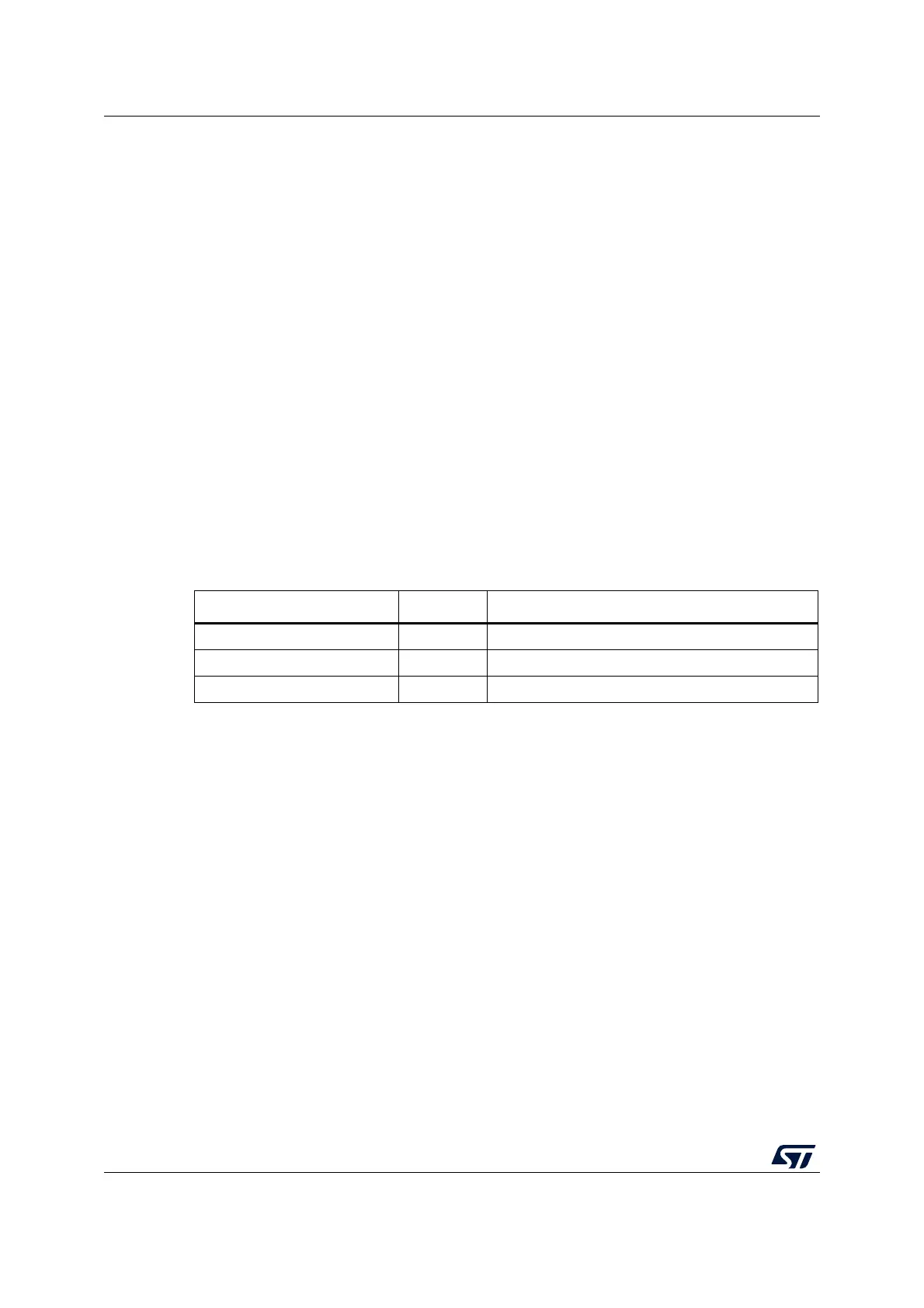
Table 29. Segment granularity and area ranges
Segment Granularity Area range
Code segment 256 byte up to 64 Kbytes - 256 bytes
Non-volatile data segment 256 byte up to 64 Kbytes - 256 bytes
Volatile data segment 64byte 8Kbytes - 64bytes

 Loading...
Loading...