RM0367 Rev 7 419/1043
RM0367 Touch sensing controller (TSC)
432
18.3.5 Spread spectrum feature
The spread spectrum feature allows to generate a variation of the charge transfer
frequency. This is done to improve the robustness of the charge transfer acquisition in noisy
environments and also to reduce the induced emission. The maximum frequency variation
is in the range of 10% to 50% of the nominal charge transfer period. For instance, for a
nominal charge transfer frequency of 250 kHz (4 µs), the typical spread spectrum deviation
is 10% (400 ns) which leads to a minimum charge transfer frequency of ~227 kHz.
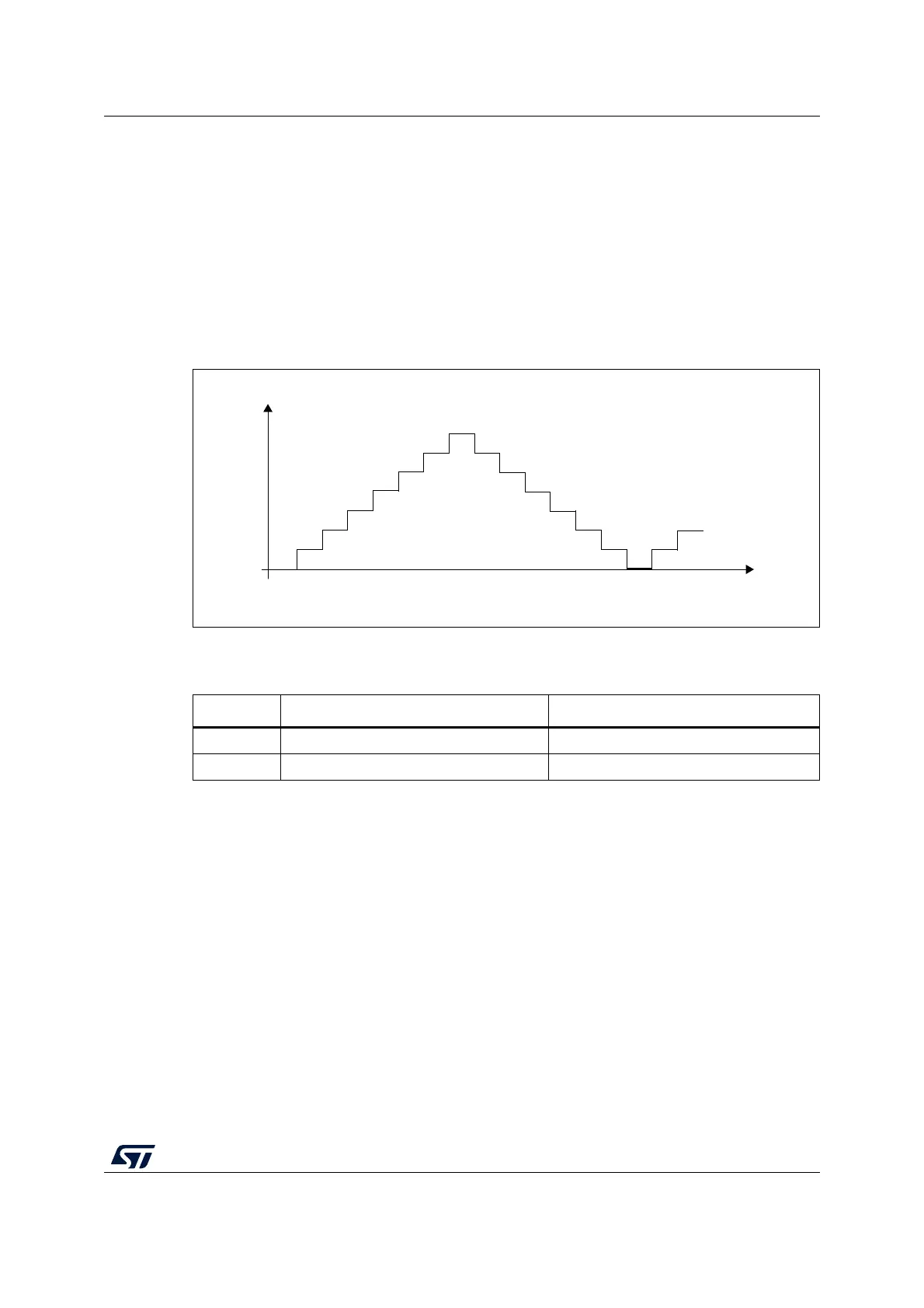
In practice, the spread spectrum consists of adding a variable number of SSCLK periods to
the pulse high state using the principle shown below:
Figure 83. Spread spectrum variation principle
The table below details the maximum frequency deviation with different HCLK
settings:
The spread spectrum feature can be disabled/enabled using the SSE bit in the TSC_CR
register. The frequency deviation is also configurable to accommodate the device HCLK
clock frequency and the selected charge transfer frequency through the SSPSC and
SSD[6:0] bits in the TSC_CR register.
18.3.6 Max count error
The max count error prevents long acquisition times resulting from a faulty capacitive
sensing channel. It consists of specifying a maximum count value for the analog I/O group
counters. This maximum count value is specified using the MCV[2:0] bits in the TSC_CR
register. As soon as an acquisition group counter reaches this maximum value, the ongoing
acquisition is stopped and the end of acquisition (EOAF bit) and max count error (MCEF bit)
flags are both set. An interrupt can also be generated if the corresponding end of acquisition
(EOAIE bit) or/and max count error (MCEIE bit) interrupt enable bits are set.
Table 82. Spread spectrum deviation versus AHB clock frequency
f
HCLK
Spread spectrum step Maximum spread spectrum deviation
24 MHz 41.6 ns 10666.6 ns
32 MHz 27.7 ns 7111.1 ns
Deviation value
0
1
2
3
(SSD +1)
n-1 n+1
n

 Loading...
Loading...