RM0367 Rev 7 103/1043
RM0367 Flash program memory and data EEPROM (FLASH)
122
3.5.1 Hard fault
A hard fault is generated on:
• The memory bus if a read access is attempted when RDP is set.
• The memory bus if a read as data is received; then, the memory interface is waiting for
a data/address during a half-page write (after the 1
st
address and before the 16
th
address).
• The register bus if an incorrect value is written in PEKEYR, PRGKEYR, or OPTKEYR.
3.6 Memory interface management
The purpose of this section is to clarify what happens when one operation is requested
while another is ongoing: the way the different operations work together and are managed
by the memory interface.
3.6.1 Operation priority and evolution
There are three types of operations and each of them has different flows:
Read
• If no operation is ongoing and the read address is not protected, the read is executed
without delays and with the actual configurations.
• If the read address is protected, the operation is filtered (the read requested is never
sent to the memory) and an error is raised.
• If the read address is not protected but the memory interface is busy and cannot
perform the operation, the read is put on hold to be executed as soon as possible.
Write/erase
• If no operation is ongoing and the write address is not protected, the write/erase will
start immediately; after some clock pulses (see Table 17) during which the bus and the
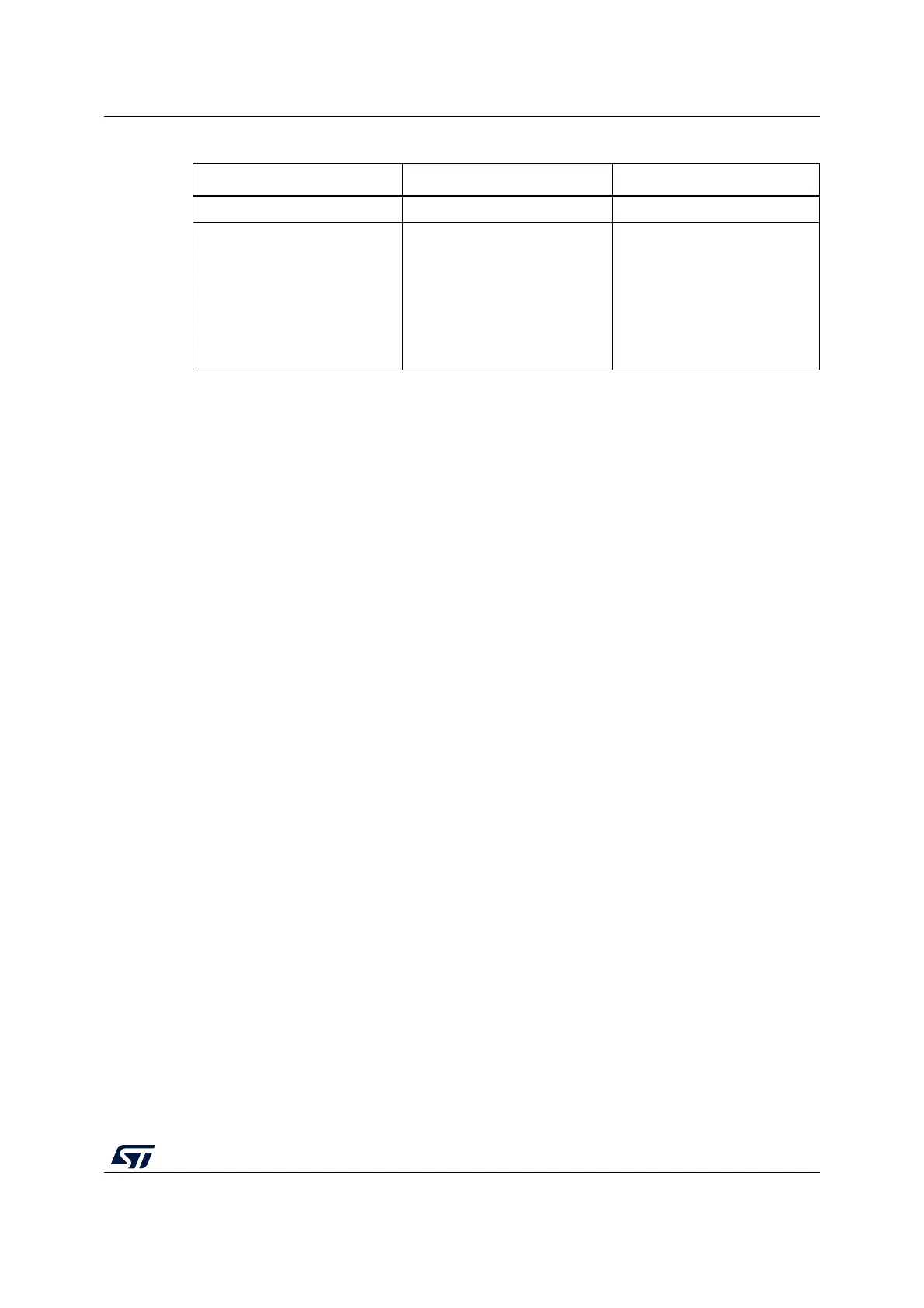
Table 22. Flash interrupt request
Interrupt event Event flag Enable control bit
End of operation EOP EOPIE
Error
RDERR
WRPERR
PGAERR
OPTVERR
SIZERR
FWWERR
NOTZEROERR
ERRIE

 Loading...
Loading...