Inter-integrated circuit (I2C) interface RM0367
696/1043 RM0367 Rev 7
The following additional features are also available depending on the product
implementation (see Section 28.3: I2C implementation):
• SMBus specification rev 3.0 compatibility:
– Hardware PEC (packet error checking) generation and verification with ACK
control
– Command and data acknowledge control
– Address resolution protocol (ARP) support
– Host and Device support
– SMBus alert
– Timeouts and idle condition detection
• PMBus rev 1.3 standard compatibility
• Independent clock: a choice of independent clock sources allowing the I2C
communication speed to be independent from the PCLK reprogramming
• Wakeup from Stop mode on address match.
28.3 I2C implementation
This manual describes the full set of features implemented in I2C1, I2C3. I2C2 supports a
smaller set of features, but is otherwise identical to I2C1/I2C3. The differences are listed
below.
28.4 I2C functional description
In addition to receiving and transmitting data, this interface converts it from serial to parallel
format and vice versa. The interrupts are enabled or disabled by software. The interface is
connected to the I
2
C bus by a data pin (SDA) and by a clock pin (SCL). It can be connected
with a standard (up to 100 kHz), Fast-mode (up to 400 kHz) or Fast-mode Plus (up to
1MHz) I
2
C bus.
This interface can also be connected to a SMBus with the data pin (SDA) and clock pin
(SCL).
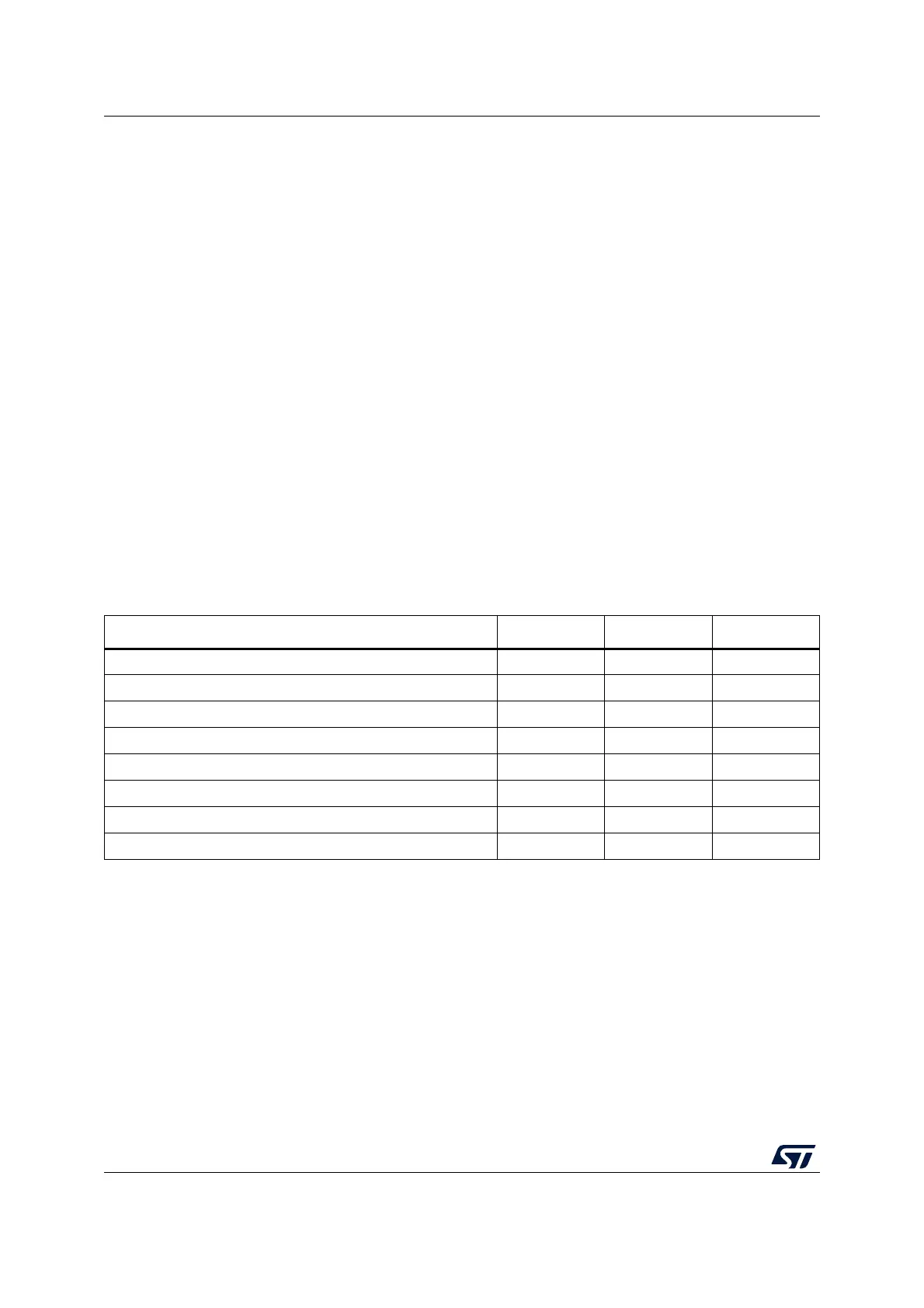
Table 122. STM32L0x3 I2C features
I2C features
(1)
I2C1 I2C2 I2C3
7-bit addressing mode X X X
10-bit addressing mode X X X
Standard-mode (up to 100 kbit/s) X X X
Fast-mode (up to 400 kbit/s) X X X
Fast-mode Plus with 20mA output drive I/Os (up to 1 Mbit/s)
(2)
XXX
Independent clock X - X
Wakeup from Stop mode X - X
SMBus/PMBus X - X
1. X = supported.
2. Refer to the datasheet for the list of I/Os that support this feature.

 Loading...
Loading...