Concepts and features
R&S
®
ZNB/ZNBT
123User Manual 1173.9163.02 ─ 62
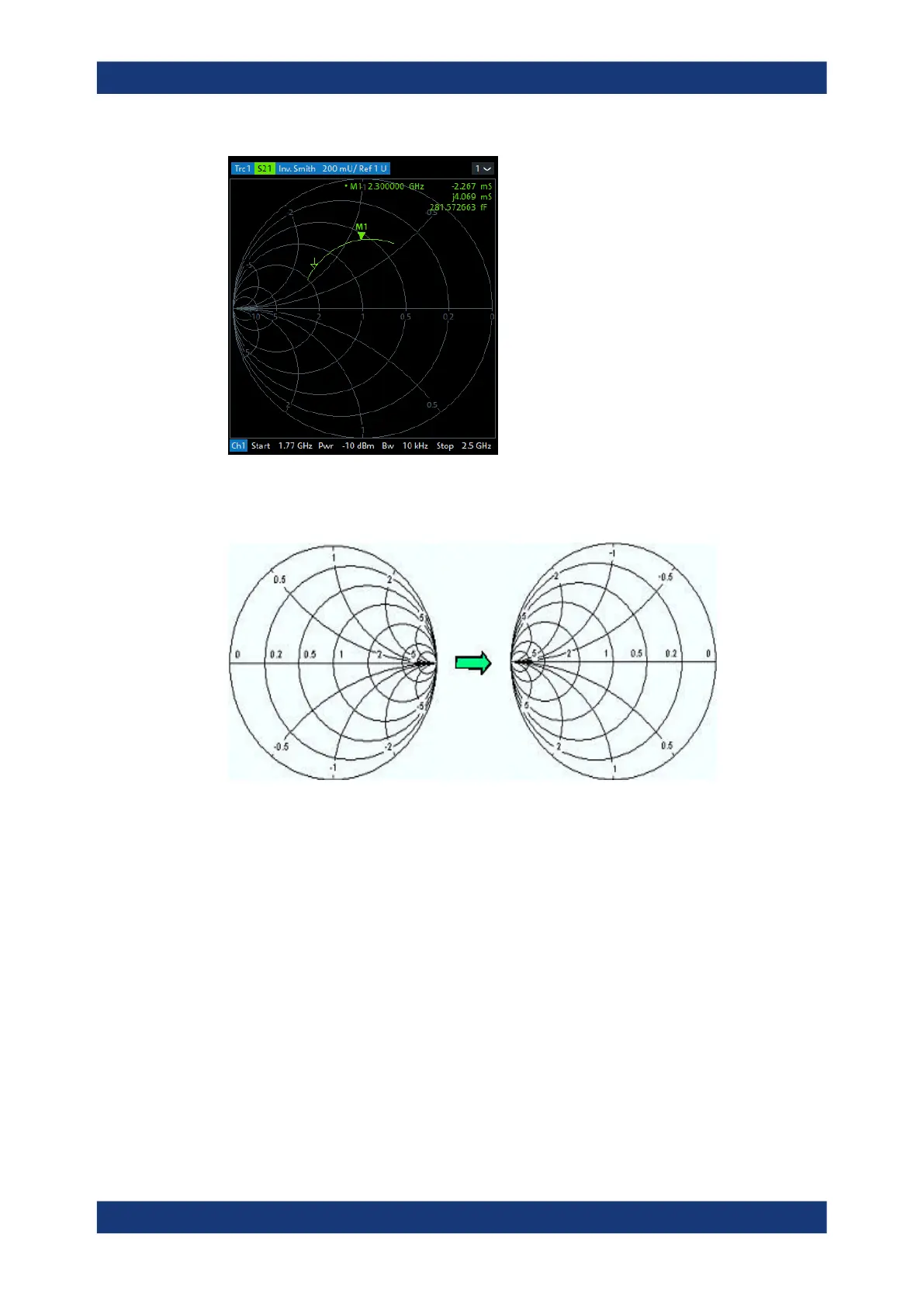
Inverted Smith chart construction
The inverted Smith chart is point-symmetric to the Smith chart:
The basic properties of the inverted Smith chart follow from this construction:
●
The central horizontal axis corresponds to zero susceptance (real admittance). The
center of the diagram represents Y/Y
0
= 1, where Y
0
is the reference admittance of
the system (zero reflection). At the left and right intersection points between the
horizontal axis and the outer circle, the admittance is infinity (short) and zero
(open).
●
The outer circle corresponds to zero conductance (purely imaginary admittance).
Points outside the outer circle indicate an active component.
●
The upper and lower half of the diagram correspond to negative (inductive) and
positive (capacitive) susceptive components of the admittance, respectively.
Example: Reflection coefficients in the inverted Smith chart
If the measured quantity is a complex reflection coefficient Γ (e.g. S
11
, S
22
), then the
inverted Smith chart can be used to read the normalized admittance of the DUT. The
coordinates in the normalized admittance plane and in the reflection coefficient plane
are related as follows (see also: definition of matched-circuit (converted) admittances):
Screen elements

 Loading...
Loading...