12 Interface Naming Convention
Interface Naming Convention
FASTPATH software references physical entities such as cards and ports by using
a slot/port naming convention. The FASTPATH software also uses this
convention to identify certain logical entities, such as link aggregation groups
(LAGs), which are also known as port-channels.
When a command indicates that the variable is
slot/port
, an example of a valid
entry is 0/1. This represents slot 0, port 1 on the switch. To configure port 12, the
slot/port to enter would be 0/12.
To configure a LAG, which is a group of ports acting as a single interface, you
enter the keyword
lag
followed by the LAG number, for example
lag 2
.
For many commands, you can also specify a range of physical or LAG interfaces
to configure at the same time with the same settings. To specify a range of
interfaces, the slot/port is separated by a dash, for example 0/1-0/4 indicates that
the same settings will apply to ports 1, 2, 3, and 4.
The slot number has two uses. In the case of physical ports, it identifies the card
containing the ports. In the case of logical and CPU ports it also identifies the
type of interface or port.
The port identifies the specific physical port being managed on a given slot.
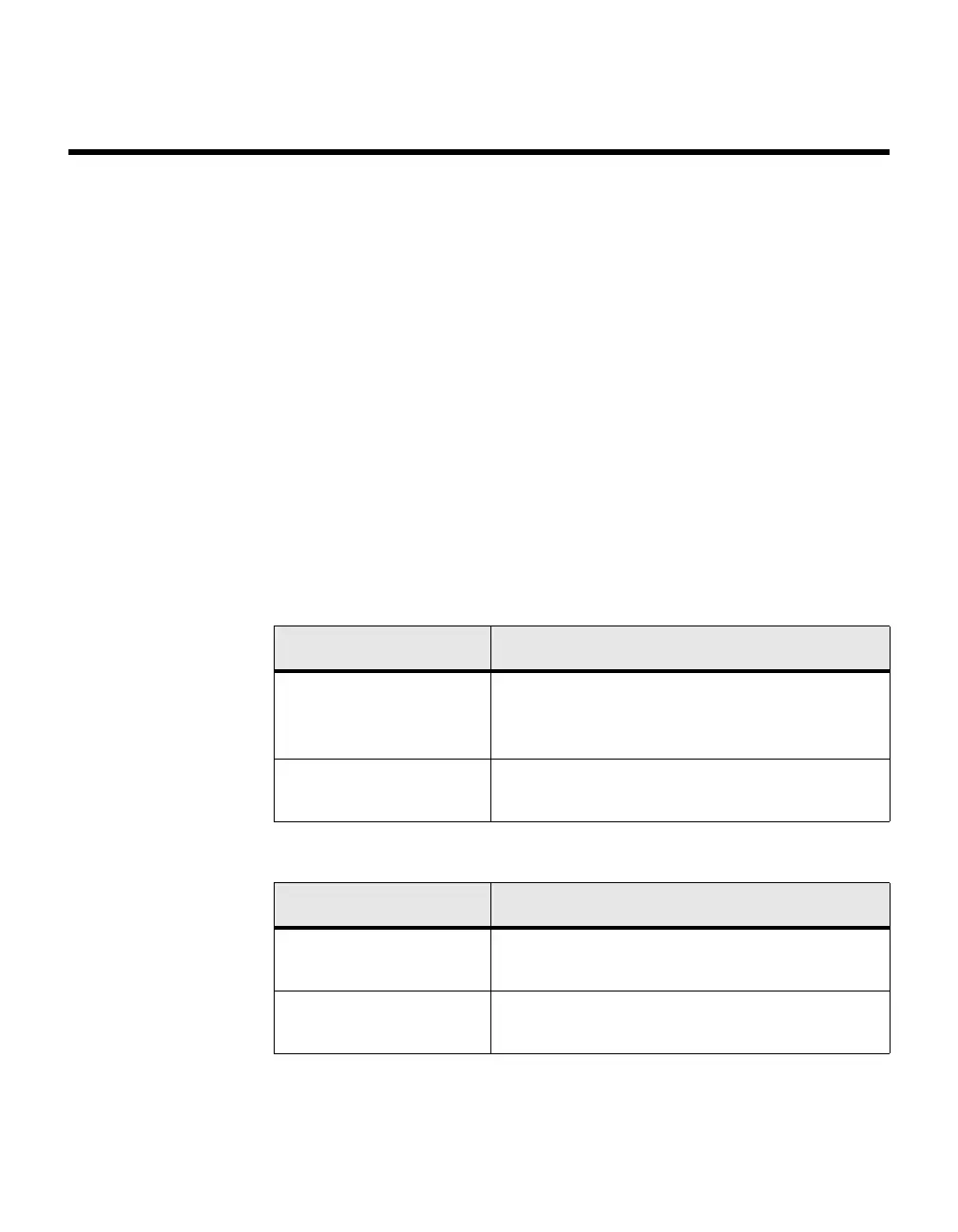
Slot Type Description
Physical slot numbers Physical slot numbers begin with zero, and are
allocated up to the maximum number of physical
slots.
CPU slot numbers The CPU slots immediately follow the logical
slots.
Port Type Description
Physical ports The physical ports for each slot are numbered
sequentially starting from zero.
CPU ports CPU ports are handled by the driver as one or
more physical entities located on physical slots.
 Loading...
Loading...