Operation Manual – Routing Protocol
H3C S3600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 1
IP Routing Protocol Overview
1-4
10.0.0.0
11.0.0.0
12.0.0.0
13.0.0.0
14.0.0.0
15.0.0.0
16.0.0.0
R8
2
10.0.0.1
1
11.0.0.1
3
13.0.0.4
R2
R3
R5
R6
R7
R1
R4
10.0.0.2
16.0.0.316.0.0.1
16.0.0.2
13.0.0.3
15.0.0.1
15.0.0.2
14.0.0.1
14.0.0.2
13.0.0.2
13.0.0.1
12.0.0.1
12.0.0.2
12.0.0.3
Routing t
able of router R8
Destination
network
10.0.0.0
Next hop Interface
10.0.0.1 2
11.0.0.0 11.0.0.1 1
12.0.0.0 11.0.0.2 1
11.0.0.2
13.0.0.0 13.0.0.4 3
14.0.0.0 13.0.0.2 3
15.0.0.0 13.0.0.2 3
16.0.0.0 10.0.0.2 2
10.0.0.0
11.0.0.0
12.0.0.0
13.0.0.0
14.0.0.0
15.0.0.0
16.0.0.0
R8
2
10.0.0.1
1
11.0.0.1
3
13.0.0.4
R2
R3
R5
R6
R7
R1
R4
10.0.0.2
16.0.0.316.0.0.1
16.0.0.2
13.0.0.3
15.0.0.1
15.0.0.2
14.0.0.1
14.0.0.2
13.0.0.2
13.0.0.1
12.0.0.1
12.0.0.2
12.0.0.3
Routing t
able of router R8
Destination
network
10.0.0.0
Next hop Interface
10.0.0.1 2
11.0.0.0 11.0.0.1 1
12.0.0.0 11.0.0.2 1
11.0.0.2
13.0.0.0 13.0.0.4 3
14.0.0.0 13.0.0.2 3
15.0.0.0 13.0.0.2 3
16.0.0.0 10.0.0.2 2
10.0.0.0
11.0.0.0
12.0.0.0
13.0.0.0
14.0.0.0
15.0.0.0
16.0.0.0
R8
2
10.0.0.1
1
11.0.0.1
3
13.0.0.4
R2
R3
R5
R6
R7
R1
R4
10.0.0.2
16.0.0.316.0.0.1
16.0.0.2
13.0.0.3
15.0.0.1
15.0.0.2
14.0.0.1
14.0.0.2
13.0.0.2
13.0.0.1
12.0.0.1
12.0.0.2
12.0.0.3
Routing t
able of router R8
Destination
network
10.0.0.0
Next hop Interface
10.0.0.1 2
11.0.0.0 11.0.0.1 1
12.0.0.0 11.0.0.2 1
11.0.0.2
13.0.0.0 13.0.0.4 3
14.0.0.0 13.0.0.2 3
15.0.0.0 13.0.0.2 3
16.0.0.0 10.0.0.2 2
10.0.0.0
11.0.0.0
12.0.0.0
13.0.0.0
14.0.0.0
15.0.0.0
16.0.0.0
R8
2
10.0.0.1
1
11.0.0.1
3
13.0.0.4
R2
R3
R5
R6
R7
R1
R4
10.0.0.2
16.0.0.316.0.0.1
16.0.0.2
13.0.0.3
15.0.0.1
15.0.0.2
14.0.0.1
14.0.0.2
13.0.0.2
13.0.0.1
12.0.0.1
12.0.0.2
12.0.0.3
Routing t
able of router R8
Destination
network
10.0.0.0
Next hop Interface
10.0.0.1 2
11.0.0.0 11.0.0.1 1
12.0.0.0 11.0.0.2 1
11.0.0.2
13.0.0.0 13.0.0.4 3
14.0.0.0 13.0.0.2 3
15.0.0.0 13.0.0.2 3
16.0.0.0 10.0.0.2 2
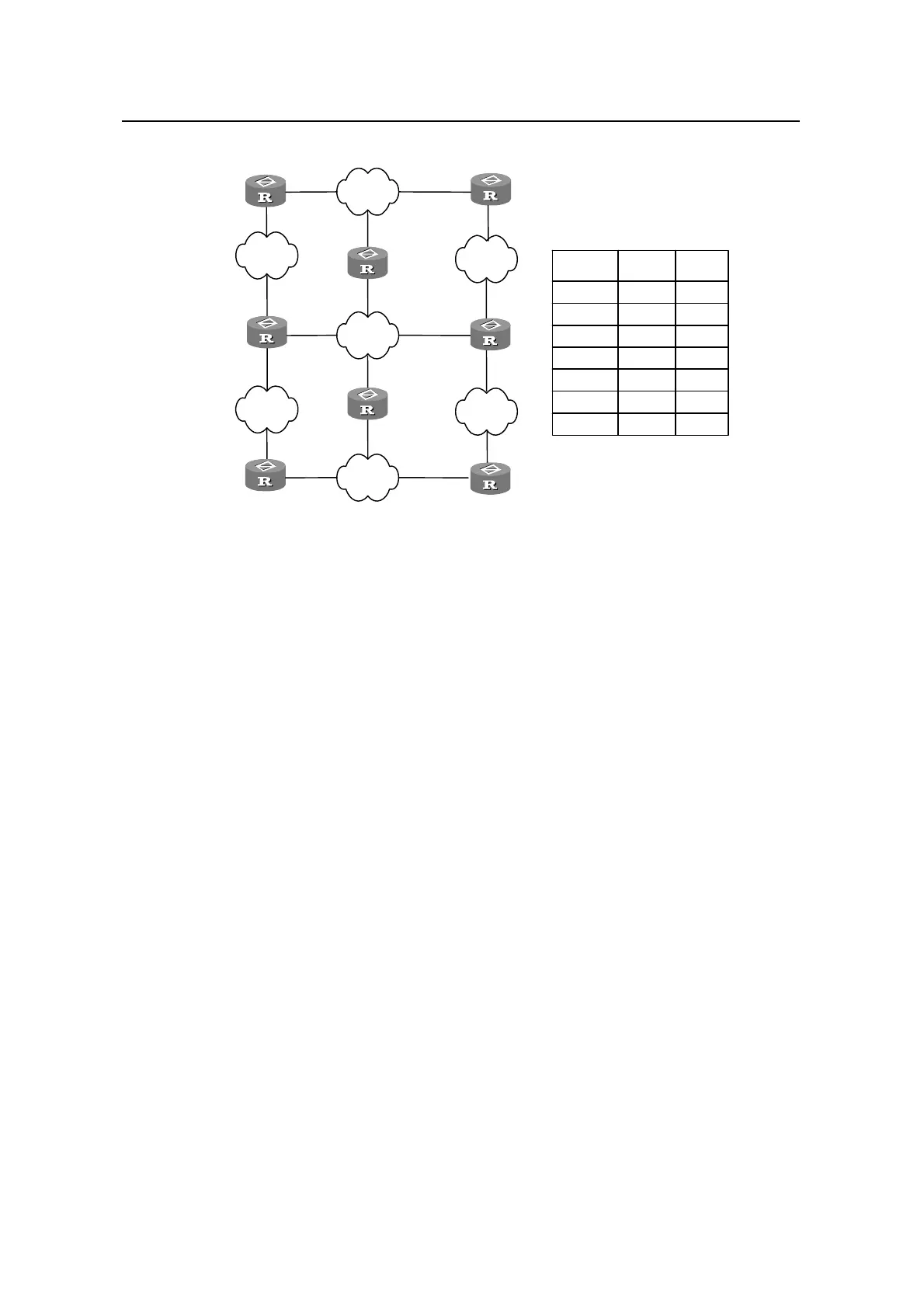
Figure 1-2 Routing table
The H3C S3600 Series Ethernet Switches (hereinafter referred to as S3600 series)
support the configuration of static routes as well as a series of dynamic routing
protocols such as RIP and OSPF. Moreover, the switches in operation can
automatically obtain some direct routes according to interface status and user
configuration.
1.2 Routing Management Policy
On an S3600 Ethernet switch, you can manually configure a static route to a certain
destination, or configure a dynamic routing protocol to make the switch interact with
other routers in the internetwork and find routes by routing algorithm. On an S3600
Ethernet switch, the static routes configured by the user and the dynamic routes
discovered by routing protocols are managed uniformly. The static routes and the
routes learned or configured by different routing protocols can also be shared among
routing protocols.
1.2.1 Routing Protocols and Preferences
Different routing protocols may discover different routes to the same destination, but
only one route among these routes and the static routes is optimal. In fact, at any
given moment, only one routing protocol can determine the current route to a specific
destination. Routing protocols (including static routing) are endowed with different
preferences. When there are multiple routing information sources, the route
discovered by the routing protocol with the highest preference will become the current

 Loading...
Loading...