Operation Manual – NTP
H3C S3600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 1
NTP Configuration
1-4
1.1.3 NTP Implementation Modes
According to the network structure and the position of the local Ethernet switch in the
network, the local Ethernet switch can work in multiple NTP modes to synchronize the
clock.
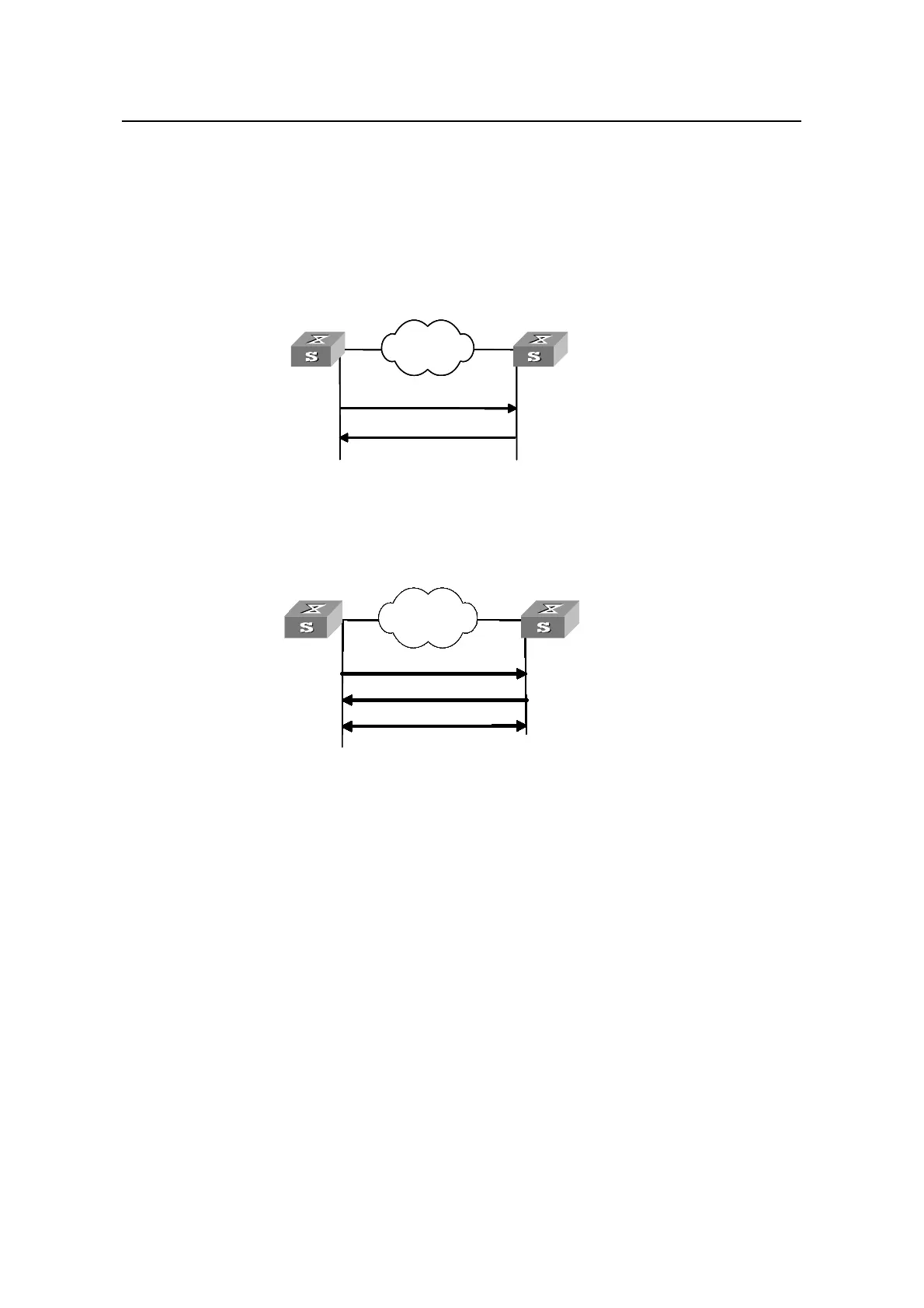
I. Client/server mode
Network
Client Se
rver
Clock synchronization
request packet
Response packet
Filters and selects
a clocks and
synchronize the
local clock to that of
the preferred server
Works in server mode
automatically and send
a response packet
NetworkNetworkNetwork
Figure 1-2 Client/sever mode
II. Peer mode
NetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetwork
Clock synchronization
request packet
NetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetworkNetwork
Active peer
NetworkNetwork
Works in passive pee
mode automatically
sive peer
e
Pas
Response packet
Synchronize
In peer mode, both
sides can be
synchronized to each
other
Figure 1-3 Peer mod
In the peer mode, the local S3600 Ethernet switch serves as the active peer and sends
clock synchronization request packets first, while the remote server serves as the
passive peer automatically.
If both of the peers have reference clocks, the one with a smaller stratum number is
adopted.

 Loading...
Loading...