Operation Manual – Routing Protocol
H3C S3600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 4
OSPF Configuration
4-13
4.4.2 Configuring OSPF Area Attributes
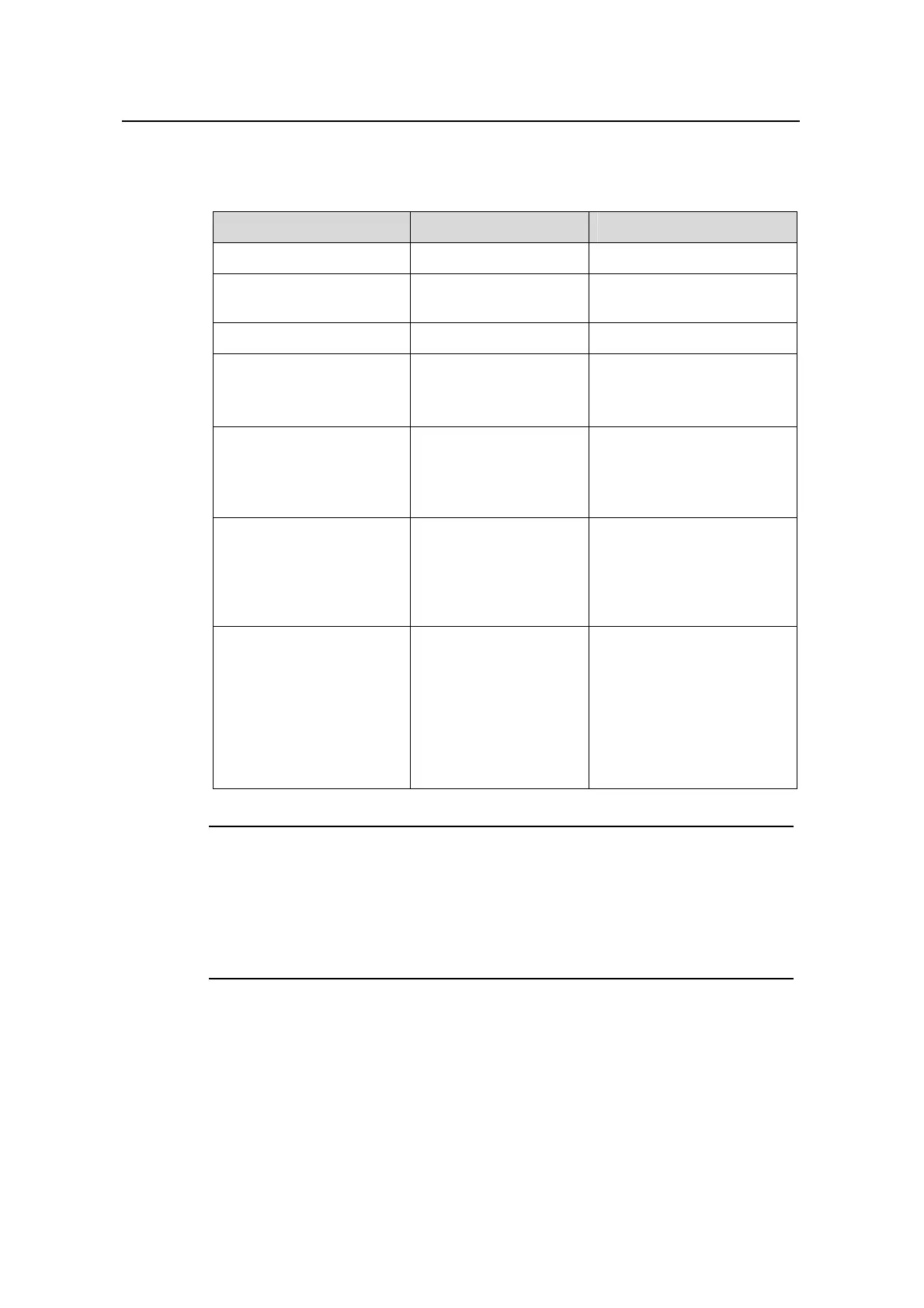
Table 4-3 Configure OSPF area attributes
Operation Command Description
Enter system view
system-view
—
Enter OSPF view
ospf [ process-id
[ router-id router-id ] ]
—
Enter OSPF area view
area area-id
—
Configure the current area
to be a stub area
stub [ no-summary ]
Optional
By default, no area is
configured as a stub area.
Configure the current area
to be an NSSA area
nssa
[ default-route-adverti
se | no-import-route |
no-summary ]*
Optional
By default, no area is
configured as an NSSA
area.
Configure the cost of the
default route transmitted
by OSPF to a stub or
NSSA area
default-cost cost
Optional
This can be configured on
an ABR only. By default, the
cost of the default route to a
stub or NSSA area is 1.
Create and configure a
virtual link
vlink-peer router-id
[ hello seconds |
retransmit seconds |
trans-delay seconds |
dead seconds | simple
password | md5 keyid
key ]*
Optional
For a virtual link to take
effect, you need to use this
command at both ends of
the virtual link and ensure
consistent configurations of
the hello, dead, and other
parameters at both ends.
Note:
z You must use the stub command on all the routers connected to a stub area to
configure the area with the stub attribute.
z You must use the nssa command on all the routers connected to an NSSA area to
configure the area with the NSSA attribute.
4.5 OSPF Network Type Configuration
OSPF divides networks into four types by link layer protocol. See section 4.1.4
"OSPF Network Type". An NBMA network must be fully connected. That is, any two
routers in the network must be directly reachable to each other through a virtual circuit.

 Loading...
Loading...