Operation Manual – Routing Protocol
H3C S3600 Series Ethernet Switches-Release 1510 Chapter 4
OSPF Configuration
4-4
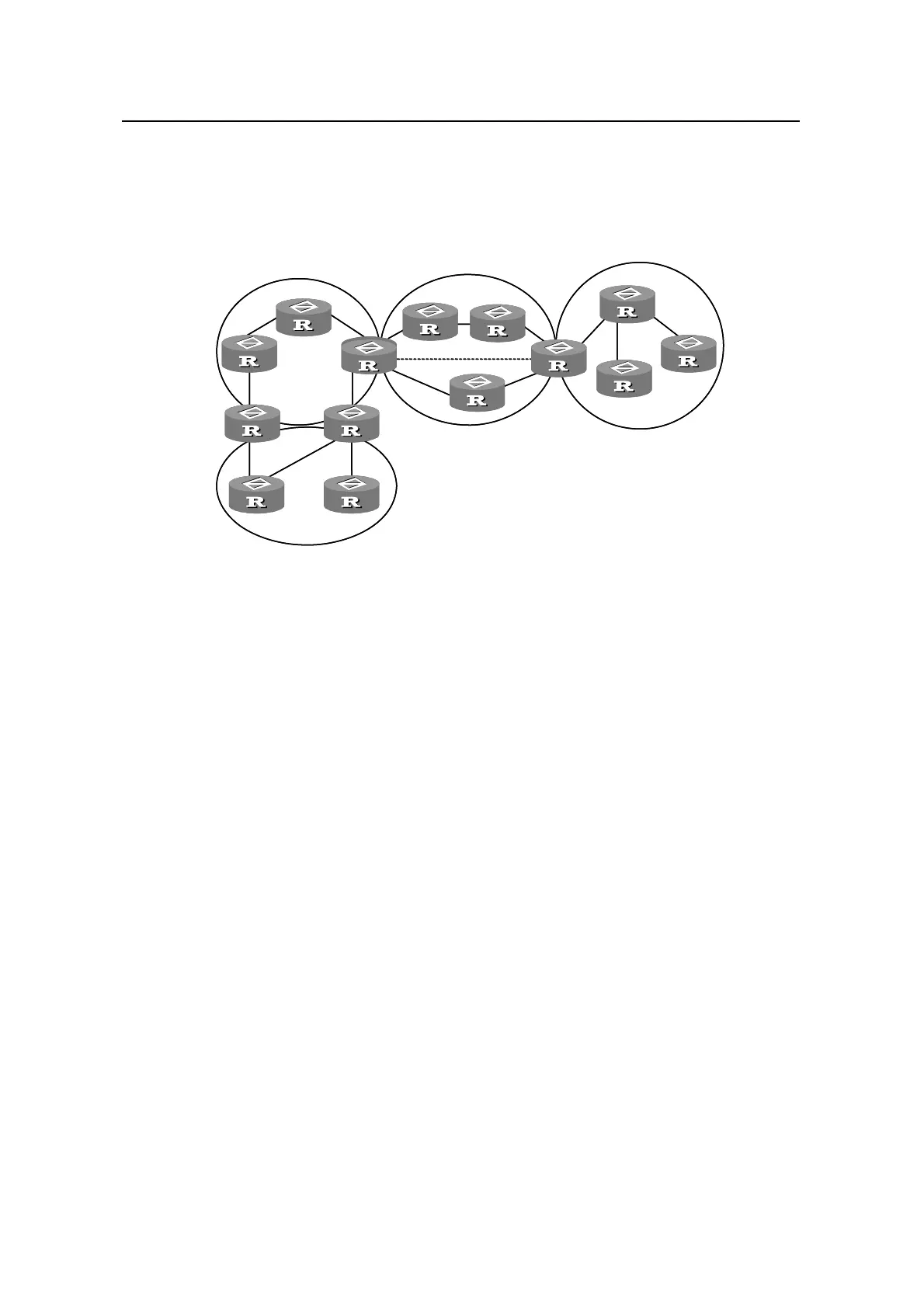
For example, in Figure 4-1, there are three intra-area routes in Area 19: 19.1.1.0/24,
19.1.2.0/24, and 19.1.3.0/24. If route summary is configured, the three routes are
aggregated into one route 19.1.0.0/16, and only one corresponding LSA, which
describes the route after summary, is generated on RTA.
Area 12
Area 8
Area 19
Area 0
Virtual link
19.1.1.0/24
19.1.2.0/24
19.1.3.0/24
RTA
Area 12
Area 8
Area 19
Area 0
Virtual link
19.1.1.0/24
19.1.2.0/24
19.1.3.0/24
RTA
Figure 4-1 Area partition and route aggregation
4.1.4 OSPF Network Type
I. Four OSPF network types
OSPF divides networks into four types by link layer protocols:
z Broadcast: If Ethernet or FDDI is adopted, OSPF defaults the network type to
broadcast. In a broadcast network, protocol packets are sent in multicast
(224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6) by default.
z Non-broadcast multi-access (NBMA): If Frame Relay, ATM, or X.25 is adopted,
OSPF defaults the network type to NBMA. In an NBMA network, protocol packets
are sent in unicast.
z Point-to-multipoint (P2MP): OSPF will not default the network type of any link
layer protocol to P2MP. A P2MP network must be compulsorily changed from
another network type. The common practice is to change an NBMA network into
a P2MP network. In a P2MP network, protocol packets are sent in multicast
(224.0.0.5).
z Point-to-point (P2P): If PPP or HDLC is adopted, OSPF defaults the network type
to P2P. In a P2P network, protocol packets are sent in multicast (224.0.0.5).
II. Principles for configuring an NBMA network
An NBMA network is a non-broadcast and multi-accessible network. ATM and frame
relay networks are typical NBMA networks.

 Loading...
Loading...