Description
2.6 Interface identifiers and addresses
SCALANCE XM-400/XR-500 Command Line Interface (CLI)
48 Configuration Manual, 11/2015, C79000-G8976-C252-10
Rules / simplifications:
● If one or more fields have the value 0, a shortened notation is possible.
The address fd00:
:ffff:02d1:7d01:0000:8f21 can also be shortened and written
as follows:
fd00
ffff:02d1:7d01:0000:8f21
To ensure uniqueness, this shortened form can only be used once within the entire
address.
● Leading zeros within a field can be omitted.
The address fd00:0000:0000:ffff:
:7d01:0000:8f21 can also be shortened and written
as follows:
fd00
ffff:
:7d01:0000:8f21
● Decimal notation with periods
The last 2 fields or 4 bytes can be written in the normal decimal notation with periods.
Example: The IPv6 address fd00::ffff.125.1.0.1 is equivalent to fd00::ffff:7d01:1
Structure of the IPv6 address
The IPv6 protocol distinguishes three types of address: Unicast , anycast and multicast. The
following section describes the structure of the global unicast addresses.
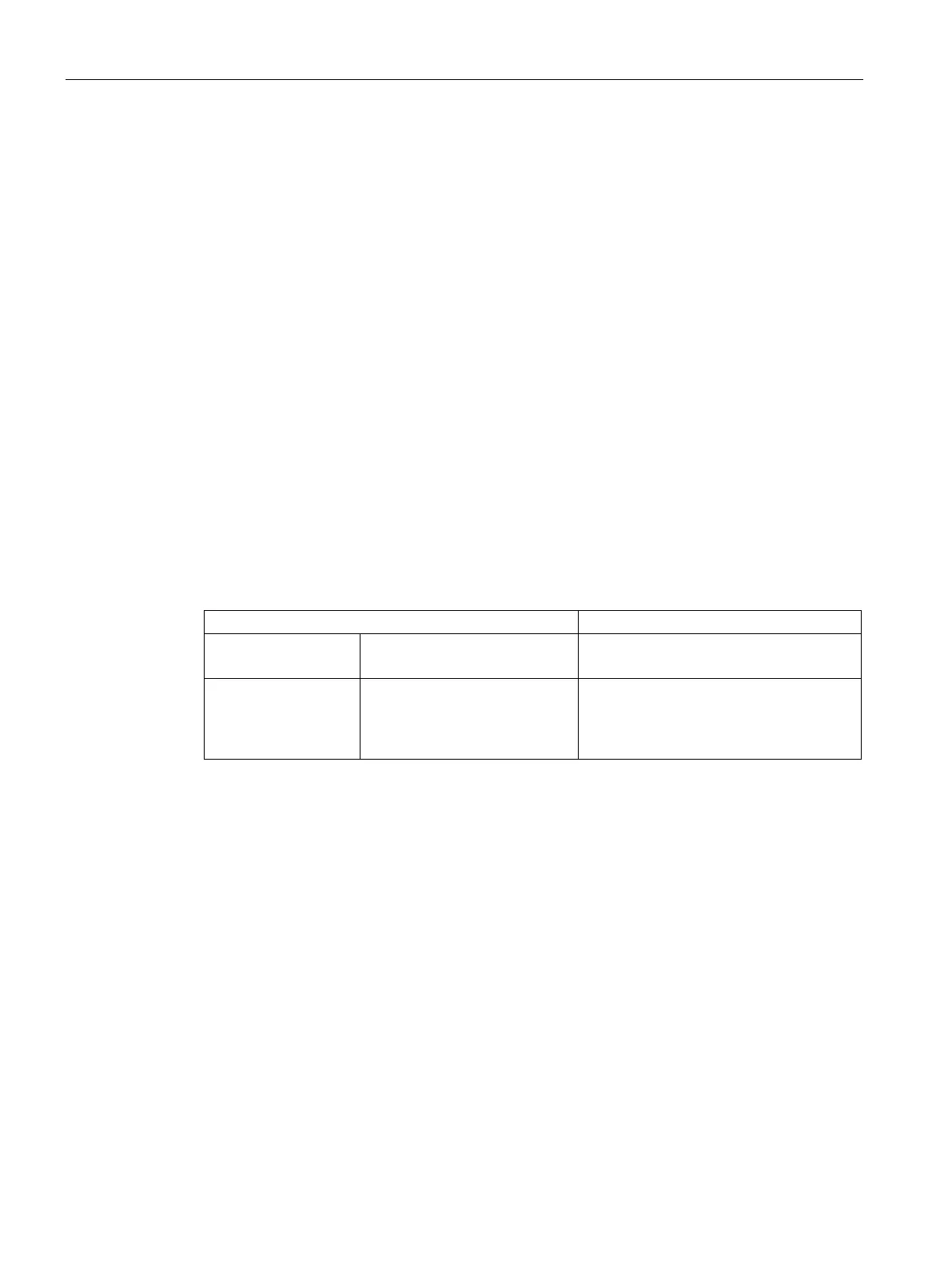
Global prefix:
Subnet ID
Interface ID
Assigned address
range
Description of the location, also
subnet prefix or subnet
Unique assignment of the host in the net-
work.
The ID is generated from the MAC ad-
The prefix for the link local address is always fe80:0000:0000:0000. The prefix is shortened
and noted as follows: fe80::
Specified in: RFC 4291
The IPv6 prefix represents the subnet identifier.
Prefixes and IPv6 addresses are specified in the same way as with the CIDR notation
(Classless Inter-Domain Routing) for IPv4.
IPv6 address / prefix length
IPv6 address: 2001:0db8:1234::1111/48
Prefix: 2001:0db8:1234::/48
Interface ID: ::1111

 Loading...
Loading...











