Codes and scanning rules Instruction manual GLM-I
234 38.019.129.001 en
19
19.7.6 EPC-96 Code for RFID labels (UHF only)
If the device is equipped with a write unit or RFID labels (Smart Label, RFID = Radio
Frequency Identification), information can be transmitted by the transponder integrated in
the labels.
RFID label components and functionality
– Transponder with antenna
– analogue circuit for sending and receiving
– a digital circuit for saving information
Transponders in the labels save the transmitted data. Special scanning devices can read
out these data without needing to make contact. The device transmits the information that
needs to be saved at 865-920 Mhz (UHF) to the transponder.
Prespecifications and settings when applying RFID labels
– Activate Smart Label, see page 392
– Create code structure rule, see page 215
– Select code field for smart label, see page 231
Description of the EPC-96 code
The Electronic Product Code EPC-96 is for transmitting 96 bit data to the RFID transpond-
er in the RFID label. The code structure is globally determined by EPC.
The data in the code structure rule are saved as binary data in EPC-96. Data smaller than
one byte have to be entered as binary data. All possible 96 bits of the EPC-96 code must
be defined.
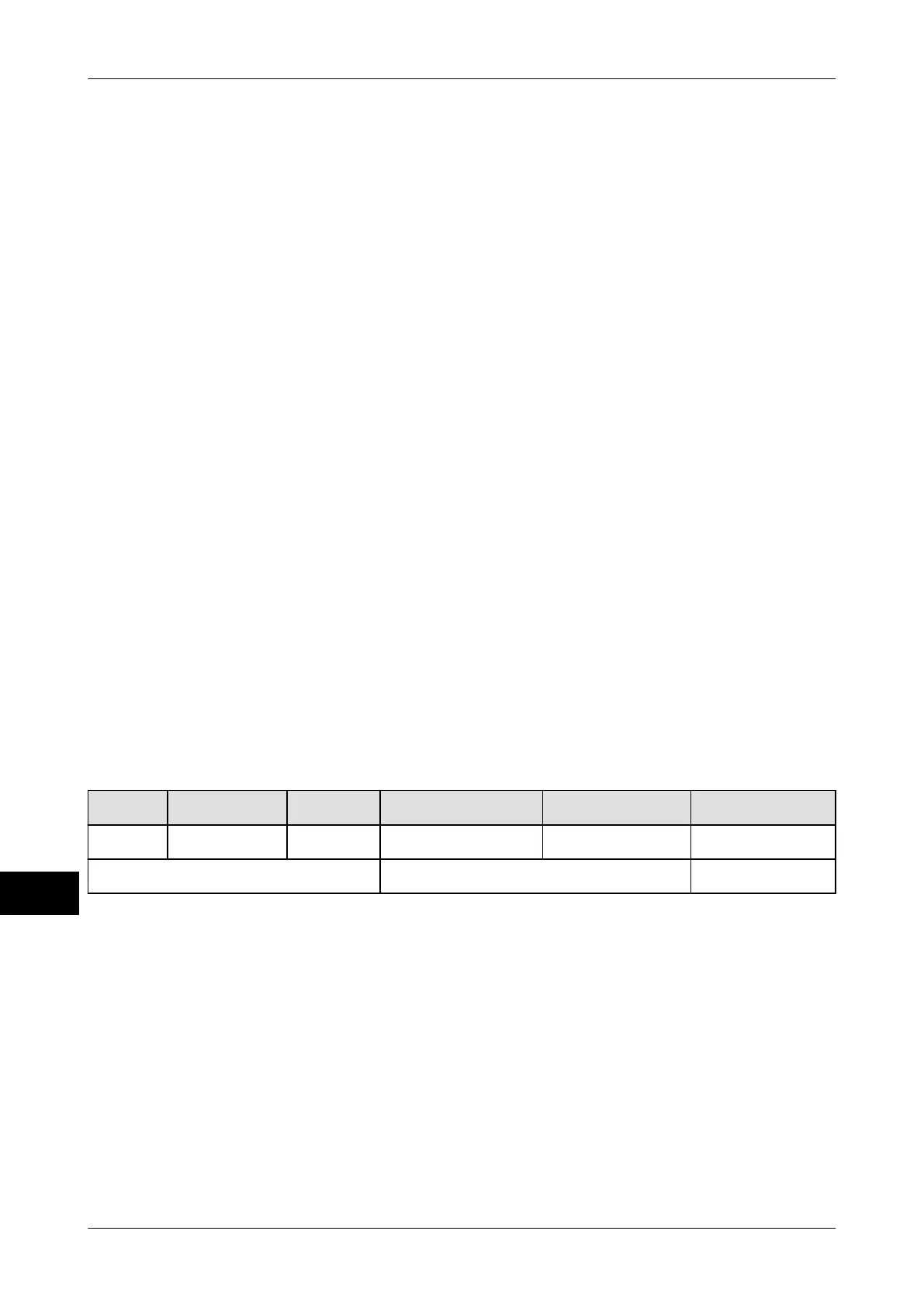
The following examples are based on the code structure rule SGTIN-96. In SGTIN-96, the
96 bits comprise the following:
Header Filter Value Partition Company prefix Item reference Serial number
8 Bits 3 Bits 3 Bits 20-40 Bits 24-4 Bits max. 38 bits
14 Bits together max. 44 Bits 38 Bits
Header: Identifies the following EPC number ID e.g. for SGTIN-96 with a
decimal 96 and binary 01100000
.
Filter value: Type of respective unit in accordance with EPC data standard:
– 1 = Item
– 2 = Inner Pack
– 3 = Case
– 4 = Pallet
– 0 = Other
 Loading...
Loading...