MAX32665-MAX32668 User Guide
Maxim Integrated Page 119 of 457
6. General-Purpose I/O and Alternate Function Pins (GPIO)
General-purpose I/O (GPIO) pins can be individually configured to operate in a digital I/O mode or in an alternate function
(AF) mode which maps a signal associated with an enabled peripheral to that GPIO . The number of GPIO pins and the
assignment of alternate functions are shown in the GPIO and Alternate Function Matrices. The GPIO support dynamic
switching between I/O mode and its alternate function modes. Configuring a pin for an alternate function supersedes its
use as a digital I/O, however the state of the GPIO can still be read via the GPIO input register.
The electrical characteristics of a GPIO pin are identical whether the pin is configured as an I/O or alternate function,
except where explicitly noted in the data sheet electrical characteristics tables.
GPIO are logically divided into ports of 32 pins. Some devices and package variants may not implement all pins of a specific
32-bit GPIO port.
Each pin of a port has an interrupt function that can be independently enabled, and configured as a level- or edge-sensitive
interrupt. All GPIOs of a given port share the same interrupt vector as detailed in the section GPIO Interrupt Handling.
The features for each GPIO pin include:
• Full CMOS outputs with configurable drive strength settings.
• Input modes options:
High-impedance
Weak pullup/pulldown
Strong pullup/pulldown
• Output data can be from GPIOn_OUT register or an enabled AF peripheral
• Input data can be read from GPIOn_IN input register or the enabled peripheral
• Bit set and clear registers for efficient bit-wise write access to the pins and configuration registers
• Wake from low-power modes using edge triggered inputs
• Selectable GPIO voltage supply
V
DDIO
V
DDIOH
• Selectable interrupt events:
Level triggered low
Level triggered high
Edge triggered rising edge
Edge triggered falling edge
Edge triggered rising or falling edge
• All GPIO pins default to input mode with weak-pullup during power-on-reset events.
6.1 Instances
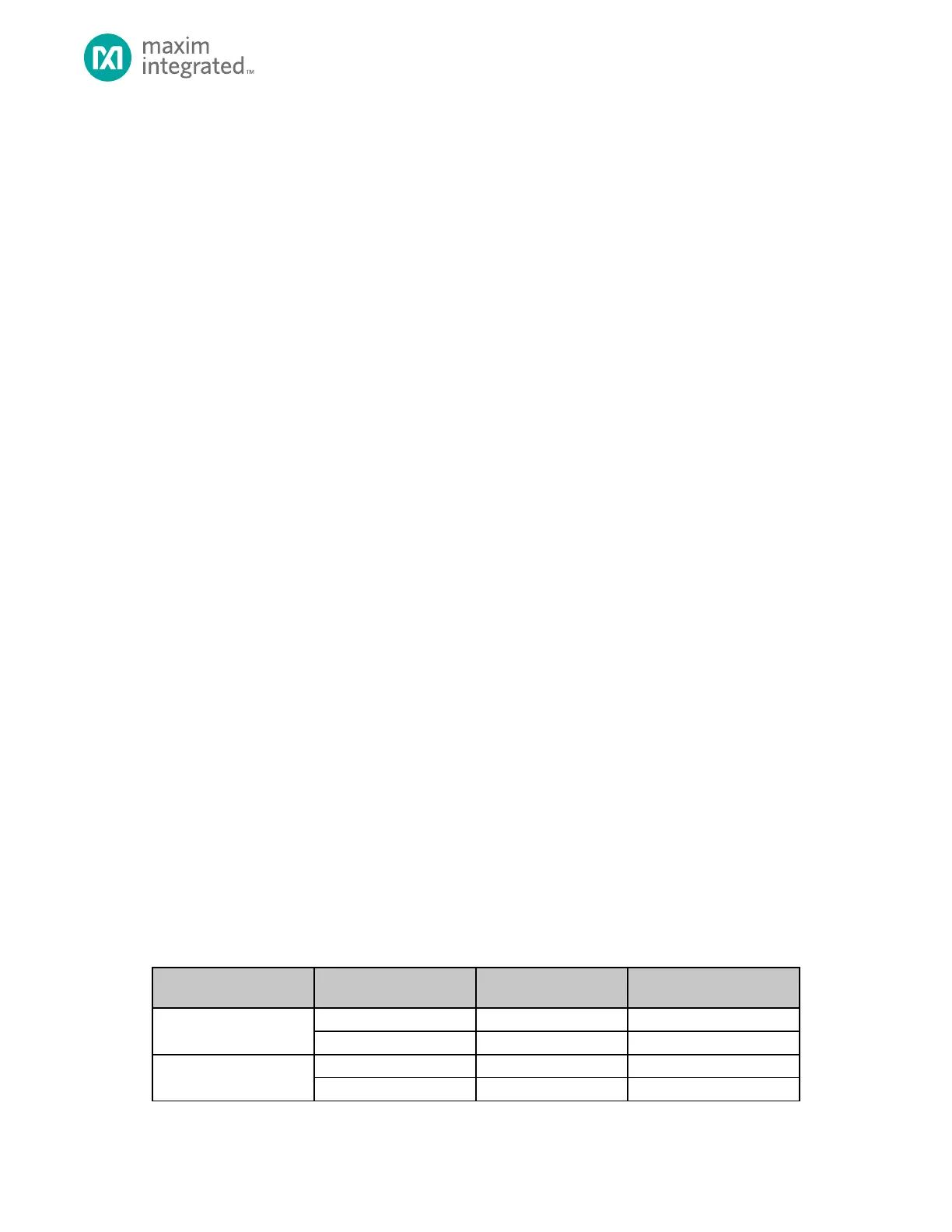
Table 6-1 shows the number of GPIO available on each IC package. Some packages and part numbers do not implement all
bits of a 32-bit GPIO port. Register fields corresponding to unimplemented GPIO contain indeterminate values and should
not be modified.
Table 6-1: MAX32665—MAX32668 GPIO Pin Count
 Loading...
Loading...